Title 08
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Subtitle 18 BOATING—SPEED LIMITS AND
OPERATION OF VESSELS
08.18.01 General
Authority: Natural Resources Article, §8-704, Annotated Code of
Maryland
Notice of Proposed Action
[25-060-P]
The Secretary of Natural Resources proposes to amend Regulation .08
under COMAR 08.18.01 Boating—Speed Limits and Operation of Vessels.
Statement of Purpose
The purpose of this action is to update the section of the Patapsco
River designated as Class III white water. The current section described in
regulation is from Woodstock (Md. Rte. 125) to Glen Artney (Patapsco State
Park—Old Dam). The reference to an “old dam” in Glen Artney is not completely
clear; additionally, all of the Patapsco River dams have been removed, except
for Daniels Dam, which is much further upstream than Glen Artney. After review
of the area, a physical landmark was chosen as the endpoint to make it easy for
users to understand. The proposed action designates Gun Road as the new
endpoint. Gun Road crosses the river and is an easy landmark. Updating the
endpoint of the Class III section of the Patapsco River will properly apprise
paddlers of potential dangers.
Estimate of Economic Impact
The proposed action has no economic impact.
Economic Impact on Small Businesses
The proposed action has minimal or no economic impact on small
businesses.
Impact on Individuals with Disabilities
The proposed action has no impact on individuals with disabilities.
Opportunity for Public Comment
Comments may be sent to White
Water Regulation, Regulatory Staff, Maryland Department of Natural Resources
Fishing and Boating Services, 580 Taylor Avenue
E-4, Annapolis, MD 21401, or call 410-260-8300, or email to [email protected]
or complete the comment form at
dnr.maryland.gov/boating/Pages/regulations/changes_boating.aspx#wwss. Comments
will be accepted through August 11, 2025. A public hearing has not been
scheduled.
.08 Boating on White Water Portions of
Designated Stream Segments.
A.—C. (text unchanged)
D. The Department of
Natural Resources is designating the following stream segments for purposes of
this boating safety regulation only, and intends no determination whether there
is any right of public access to, navigation along, landing along, or egress
from, any of these designated stream segments. This regulation does not apply
to the use of vessels on non-white water portions of designated stream segments
for any purpose other than access to white water. The designated stream
segments are:
(1) Class III—stream
segments:
(a)—(g) (text unchanged)
(h) Patapsco
River—Woodstock (Md. Rte. 125) to [Glen Artney (Patapsco State Park—Old
Dam)] Gun Road;
(i)—(m) (text unchanged)
(2)—(4) (text unchanged)
E.—F. (text unchanged)
JOSH KURTZ
Secretary of Natural
Resources
Title 10
MARYLAND DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH
Subtitle 32 BOARD OF PHYSICIANS
10.32.06 Licensure of
Polysomnographic Technologists
Authority: Health Occupations Article, §§1-213, 1-221,
1-606, 14-205, and 14-5C-01—14-5C-23, Annotated Code of Maryland
Notice of Proposed Action
[25-123-P]
The Secretary of Health proposes to amend Regulations .02, .04,
.06, .07, and .09—13 under COMAR 10.32.06 Licensure of
Polysomnographic Technologists. This
action was considered at public meetings on December 4, 2019 and January 29,
2020, notice of which was given by
publication on the Board’s Website at https://www.mbp.state.md.us from November
15, 2019 through December 4, 2019 and January 13, 2020 through January 29, 2020
respectively pursuant to General Provisions Article, §3-302(c), Annotated Code
of Maryland.
Statement of Purpose
The purpose of this proposed action is to update existing
regulations for clarity, consistency with other Board regulations, and to
reflect statutory changes pursuant to 2017 sunset legislation: Chapter
218: “State Board of Physicians and
Allied Health Advisory Committees—Sunset Extension and Program Evaluation.”
Specifically, the proposal includes but is not limited to:
(1) Restructuring of COMAR 10.32.06.04 to clarify the pathways to
licensure. A definition of the phrase
“enrolled in a sleep technologist program” has been added to support the
proposed revisions to Regulation .04;
(2) Adding a statement to Regulation .09 about non-refundable fees
for consistency with other Board regulations;
(3) Removing duplicative language from Regulation .11 regarding
reporting requirements;
(4) Changing the “Board” to a “disciplinary panel” in Regulations
.10, .12, and .13 pursuant to 2017 sunset legislation;
(5) Renaming Regulation .12 to reflect all topics covered;
(6) Revising certain section titles under Regulation .12; and
(7) Other revisions or technical corrections as needed.
Estimate of Economic Impact
The proposed action has no economic impact.
Economic Impact on Small Businesses
The proposed action has minimal or no economic impact on small
businesses.
Impact on Individuals with Disabilities
The proposed action has no impact on individuals with disabilities.
Opportunity for Public Comment
Comments may be sent to Jordan Fisher Blotter, Director, Office of
Regulation and Policy Coordination, Maryland Department of Health, 201 West
Preston Street, Room 534 Baltimore, Maryland 21201, or call 410-767-0938, or
email to [email protected]. Comments will be accepted through August 11,
2025. A public hearing has not been scheduled.
.02 Definitions.
A. (text unchanged)
B. Terms Defined.
(1)—(8) (text unchanged)
(9) “Enrolled in a sleep technologist educational program” means
that a student has started the Accredited Sleep Technology Program self-study
online modules developed by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine but has not
completed the final self-study module.
[(9)] (10) "General supervision"
means supervision by a licensed physician who is available to give
immediately available direction, either in person, by telephone, or by
electronic means.
[(10)] (11)—[(15)] (16)
(text unchanged)
[(16)] (17) "Practice
polysomnography" means:
(a) (text unchanged)
(b) Using the data collected under [§B(15)(a)] §B(17)(a)
of this regulation for the purposes of assisting a licensed physician in the
diagnosis and treatment of sleep and wake disorders.
[(17)] (18)—[(19)] (20)
(text unchanged)
.04 Application for Initial Licensure as a Polysomnographic
Technologist.
A. An applicant shall:
(1)—(6) (text unchanged)
[(7) Provide documentation of one of the following:
(a) For those candidates applying for a license on or before
September 30, 2013:
(i) Passing the national certifying examination of the Board of
Registered Polysomnographic Technologists on or before September 30, 2013; and
(ii) Certification by the Board of Registered Polysomnographic
Technologists as a registered polysomnographic technologist at the time of
application;
(b) Graduation from a polysomnographic educational program that is
accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education
Programs;
(c) Both of the following:
(i) Graduation from a respiratory care educational program that is
accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education
Programs; and
(ii) Completion of the Committee on Accreditation for Respiratory
Care’s curriculum for a polysomnography certificate that is accredited by the
Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs;
(d) Both of the following:
(i) Graduation from an electroneurodiagnostic technology
educational program that is accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of
Allied Health Education Programs; and
(ii) Completion of an add-on track in polysomnography for
electroneurodiagnostic technologists that is accredited by the Commission on
Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs; or
(e) Each of the following:
(i) Graduation from a sleep technologist educational program
accredited by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine;
(ii) Proof of meeting core competencies in the 3 years preceding
the application as assessed by a sleep technologist credentialed as a
Registered Polysomnographic Technologist, a sleep technologist with national
certification approved by the Board, or a physician who is either
board-eligible or board-certified in sleep medicine by the American Board of
Sleep Medicine, American Board of Medical Specialties, or American Osteopathic
Association;
(iii) A letter of attestation for completion of clinical hours and
competencies from a physician who is either board-eligible or board-certified
in sleep medicine by the American Board of Sleep Medicine, American Board of
Medical Specialties, or American Osteopathic Association where the applicant
practiced; and
(iv) The requirements listed in §B of this regulation; and
(8) Provide documentation of licensure, certification, or
registration from all states where the applicant has ever held a license,
certificate, or registration in any health profession.
B. If an applicant satisfies the requirements of §A(7) of this
regulation by completing the requirements of §A(7)(e) of this regulation, the
applicant shall provide proof of completion of a minimum of 546 hours of
clinical experience in the 3 years preceding licensure application as either:
(1) A student supervised by a sleep technologist credentialed as a
Registered Polysomnographic Technologist or a sleep technologist with national
certification approved by the Board at an American Academy of Sleep Medicine
accredited sleep laboratory or sleep laboratory accredited by The Joint
Commission; or
(2) A sleep technologist with a current, active, unrestricted
license in another state or is otherwise recognized and has practiced as a
sleep technologist in another state who has:
(a) Full-time practice experience as a sleep technologist in
another state at an American Academy of Sleep Medicine accredited sleep
laboratory or sleep laboratory accredited by The Joint Commission for a minimum
of 6 months in the 3 years preceding the application; and
(b) Maintained an average of 10 continuing education units per year
for the last 2 years.]
(7) Provide documentation of licensure, certification, or
registration from all states where the applicant has ever held a license,
certificate, or registration in any health profession; and
(8) Meet the requirements of §B of this regulation.
B. An applicant shall meet the requirements of one of the
following pathways to licensure:
(1) Graduation from a polysomnographic educational program that
is accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education
Programs;
(2) In regard to a respiratory care educational program:
(a) Graduation from a respiratory care educational program that
is accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education
Programs; and
(b) Completion of the Committee on Accreditation for Respiratory
Care’s curriculum for a polysomnography certificate that is accredited by the
Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs;
(3) In regard to an electroneurodiagnostic technology
educational program:
(a) Graduation from an electroneurodiagnostic technology
educational program that is accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of
Allied Health Education Programs; and
(b) Completion of an add-on track in polysomnography for
electroneurodiagnostic technologists that is accredited by the Commission on
Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs; or
(4) In regard to a sleep technologist educational program,
completion of the requirements of §C of this regulation.
C. An applicant who has
graduated from a sleep technologist education program accredited by the
American Academy of Sleep Medicine shall:
(1) Provide proof of meeting core competencies in the 3 years
preceding the date of the submission of the licensure application as assessed
by a sleep technologist credentialed as a Registered Polysomnographic
Technologist, a sleep technologist with national certification approved by the
Board, or a physician who is either board-eligible or board-certified in sleep
medicine by the American Board of Sleep Medicine, American Board of Medical
Specialties, or American Osteopathic Association;
(2) Provide a letter of attestation for completion of clinical
hours and competencies from a physician who is either board-eligible or
board-certified in sleep medicine by the American Board of Sleep Medicine,
American Board of Medical Specialties, or American Osteopathic Association
where the applicant practiced; and
(3) Provide proof of completion of a minimum of 546 hours of
clinical experience in the 3 years preceding the date of the submission of the
licensure application as either:
(a) A student enrolled in a sleep technologist educational
program supervised at a sleep laboratory accredited by the American Academy of
Sleep Medicine or The Joint Commission by:
(i) A sleep technologist credentialed as a Registered
Polysomnographic Technologist;
(ii) A sleep technologist with national certification approved
by the Board; or
(iii) A licensed physician who is either board-eligible or
board-certified in sleep medicine by the American Board of Sleep Medicine,
American Board of Medical Specialties, or American Osteopathic Association; or
(b) A sleep technologist with a current, active, unrestricted
license in another state or is otherwise recognized and has practiced as a
sleep technologist in another state who has:
(i) Full-time practice experience as a sleep technologist in
another state at a sleep laboratory accredited by the American Academy of Sleep
Medicine or The Joint Commission for a minimum of 6 months in the 3 years
preceding the date of the submission of the licensure application; and
(ii) Completed at least 30 hours of approved continuing
education in the 3 years preceding the date of the submission of the licensure
application.
.06 Identification as Polysomnographic Technologist; Notice of
Name or Address Change.
A. A licensed polysomnographic technologist shall wear an
identification tag or a badge [which identifies that individual as]
displaying in readily visible type that the individual is a licensed
polysomnographic technologist.
B. An individual may not identify himself or herself as a
polysomnographic technologist unless the individual is licensed by the Board.
[B.] C. (text unchanged)
.07 Renewal and Reinstatement.
A. Renewal.
(1) The Board may not renew a license until the Comptroller of
Maryland has verified that the individual has paid all undisputed taxes and
unemployment insurance contributions, or arranged for [repayment, as
required by COMAR 10.31.02.] repayment.
(2) An individual who has been licensed by the Board as a
polysomnographic technologist may renew the license on or before the date
specified by the Board by:
(a)—(b) (text unchanged)
(c) Attesting to the completion of at least 20 hours of approved
continuing education, earned during the 2-year period preceding the expiration
of the license, as specified in Regulation .08 of this chapter; and
(d) (text unchanged)
B. (text unchanged)
.09 Fees.
A. The following fees are applicable to polysomnographic
technologists:
[A. Initial license fees:
(1) Initial licensure application fee — $200; and
(2) Maryland Health Care Commission (MHCC) fee — As determined by
MHCC under COMAR 10.25.03;
B. License renewal fees:
(1) License renewal fee — $150; and
(2) Maryland Health Care Commission (MHCC) fee — As determined by
MHCC under COMAR 10.25.03;
C. Reinstatement fees:
(1) Reinstatement fee — $200; and
(2) Maryland Health Care Commission (MHCC) fee — As determined by
MHCC under COMAR 10.25.03;
D. Written verification of licensure fee — $25;
E. Replacement of registration card — $25; and
F. Replacement of wall license — $75.]
(1) Initial licensure application fee — $200;
(2) License renewal fees:
(a) License renewal fee — $150; and
(b) Maryland Health Care Commission (MHCC) fee — As determined
by MHCC in accordance with COMAR 10.25.02;
(3) Reinstatement fee — $200; and
(4) Written verification of licensure fee — $25.
B. Fees paid to the Board
are non-refundable.
.10 Prohibited Conduct.
A. Subject to the hearing provisions of Health Occupations Article,
§14-405, Annotated Code of Maryland, and in accordance with COMAR 10.32.02,
[the Board] a disciplinary panel may deny a license to any
applicant, reprimand any licensee, place any licensee on probation, or suspend
or revoke a license if the applicant or licensee:
(1)—(28) (text unchanged)
B. Crimes of Moral Turpitude.
(1) Proceedings for crimes of moral turpitude under Health
Occupations Article, §14-5C-17(c), Annotated Code of Maryland, shall be held in
accordance with COMAR [10.32.02.04] 10.32.02.07.
(2) On the filing of certified docket entries with the Board by the
Office of the Attorney General, [the Board] a disciplinary
panel shall order the suspension of a license if the licensee is convicted
of, or pleads guilty or nolo contendere with respect to, a crime involving
moral turpitude, whether or not any appeal or other proceeding is pending to
have the conviction or plea set aside.
(3) After completion of the appellate process, if the conviction
has not been reversed or the plea has not been set aside with respect to a
crime involving moral turpitude, the [Board] disciplinary
panel shall order the revocation of a license on the certification by the
Office of the Attorney General.
.11 Required Reports.
[A. Except as provided in §B, C, or F of this regulation,
hospitals, related institutions, alternative health systems as defined in
Health Occupations Article, §1-401, Annotated Code of Maryland, and employers
shall file with the Board a report that the hospital, related institution,
alternative health system, or employer limited, reduced, otherwise changed, or
terminated any licensed polysomnographic technologist for any reason that might
be grounds for disciplinary action under Health Occupations Article, §14-5C-17,
Annotated Code of Maryland, or any regulation in this chapter.
B. If the action taken by a hospital, related institution,
alternative health system, or employer under §A of this regulation relates to
alcohol or drug impairment, the hospital, related institution, alternative
health system, or employer is not required to report the polysomnographic
technologist to the Board if:
(1) The hospital, related institution, alternative health system,
or employer knows that the licensed polysomnographic technologist is:
(a) In an alcohol or drug treatment program that is accredited by
the Joint Commission on the Accreditation of Health Care Organizations or is
certified by the Department; or
(b) Under the care of a health care practitioner who is competent
and capable of dealing with alcoholism and drug abuse;
(2) The hospital, related institution, alternative health system,
or employer is able to verify that the licensed polysomnographic technologist
remains in the treatment program until discharge; and
(3) The action or condition of the licensed polysomnographic
technologist has not caused injury to an individual while the technologist is
practicing as a licensed polysomnographic technologist.
C. If a licensed polysomnographic technologist enters, or is
considering entering, an alcohol or drug treatment program that is accredited
by the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Health Care Organizations or that
is certified by the Department, the licensed polysomnographic technologist
shall notify the hospital, related institution, alternative health system, or
employer of the licensed polysomnographic technologist's decision to enter the
treatment program.
D. If the licensed polysomnographic technologist fails to provide
the notice required under §C of this regulation, and the hospital, related
institution, alternative health system, or employer learns that the licensed
polysomnographic technologist has entered a treatment program, the hospital,
related institution, alternative health system, or employer shall report to the
Board that the licensed polysomnographic technologist has entered a treatment
program and has failed to provide the required notice.
E. Noncompliance.
(1) If the licensed polysomnographic technologist is found to be
noncompliant with the treatment program's policies and procedures while in the
treatment program, the treatment program shall notify the hospital, related
institution, alternative health system, or employer of the licensed
polysomnographic technologist's noncompliance.
(2) On receipt of the notification required under §E(1) of this
regulation, the hospital, related institution, alternative health system, or
employer of the licensed polysomnographic technologist shall report the
licensed polysomnographic technologist's noncompliance to the Board.
F. A individual is not required under this regulation to make any
report that would be in violation of any federal or state law, rule, or
regulation concerning the confidentiality of alcohol and drug abuse patient
records.
G. The hospital, related institution, alternative health system, or
employer shall submit a required report within 10 days of any action described
in this regulation.
H. A report made under this regulation is not subject to subpoena
or discovery in a civil action other than a proceeding arising out of a hearing
and decision of the Board under Health Occupations Article, Title 14, Annotated
Code of Maryland.]
A reporting entity, as defined in COMAR 10.32.22.02, shall file
all required reports in accordance with Health Occupations Article, §14-5C-18,
Annotated Code of Maryland, and COMAR 10.32.22.
.12 [Penalties.] Penalties,
Fines, and Sanctions.
A. (text unchanged)
B. An individual who violates any provision of Health Occupations
Article, Title 14, Subtitle 5C, Annotated Code of Maryland, or any regulation
in this chapter, is subject to a civil fine of not more than $5,000 to be
levied by the Board or a disciplinary panel.
C. (text unchanged)
D. Employment of an Unlicensed Polysomnography Practitioner.
(1) A person who violates Health Occupations Article, §14-5C-22.1,
Annotated Code of Maryland, is subject to a civil fine of not more than $5,000 to
be levied by the Board.
(2) (text unchanged)
E. [Failure to Make a Required Report.
(1) The Board may impose a fine up to $1,000 for a hospital,
related institution, alternative health system, or employer who fails to make a
report to the Board required by Regulation .11 of this chapter.
(2) The Board shall deposit any funds collected under §E(1) of this
regulation into the State’s General Fund.] The Board may impose a
fine up to $1,000 for a reporting entity, as defined in COMAR 10.32.22.02, that
fails to make a report to the Board required by COMAR 10.32.22.
F. General Application of Sanctioning Guidelines.
(1) Sections F and G of this regulation and Regulation [.16A
and B] .13 of this chapter do not apply to offenses for which a
mandatory sanction is set by statute or regulation.
(2) Except as provided in §G of this regulation, for violations of
the sections of the Maryland Polysomnography Act listed in the sanctioning
guidelines, [the Board] a disciplinary panel shall impose
a sanction not less severe than the minimum listed in the sanctioning
guidelines nor more severe than the maximum listed in the sanctioning
guidelines for each offense.
(3) (text unchanged)
(4) The [Board] disciplinary panel may impose
more than one sanction, provided that the most severe sanction neither exceeds
the maximum nor is less than the minimum sanction permitted in the chart.
(5) (text unchanged)
(6) If a licensee has violated more than one ground for discipline
as set out in the sanctioning guidelines:
(a) (text unchanged)
(b) The [Board] disciplinary panel may impose
concurrent sanctions based on other grounds violated.
(7) Notwithstanding the sanctioning guidelines set forth in
Regulation .13 of this chapter, in order to resolve a pending disciplinary
action, the [Board] disciplinary panel and the licensee
may agree to a surrender of license or a consent order with terms and sanction
agreed to by the [Board] disciplinary panel, the
administrative prosecutor, and the licensee.
(8) Depending on the facts and circumstances of each case, and to
the extent that the facts and circumstances apply, the [Board] disciplinary
panel may consider the aggravating and mitigating factors set out in §G(4)
and (5) of this regulation and may in its discretion determine, based on those
factors, that an exception should be made and that the sanction in a particular
case should fall outside the range of sanctions listed in the sanctioning
guidelines.
(9) If the [Board] disciplinary panel imposes
a sanction that departs from the sanctioning guidelines as set forth in
Regulation .13 of this chapter, the [Board] disciplinary panel
shall state its reasons for doing so in its final decision and order.
G. Aggravating and Mitigating Factors.
(1) Depending on the facts and circumstances of each case, and to
the extent that the facts and circumstances apply, the [Board] disciplinary
panel may consider the aggravating and mitigating factors set out in [§H(4)
and (5)] §G(4)—(5) of this regulation and may in its discretion
determine, based on those factors, that an exception should be made and that
the sanction in a particular case should fall outside the range of sanctions
listed in the sanctioning guidelines.
(2) Nothing in this regulation requires the [Board] disciplinary
panel or an Administrative Law Judge to make findings of fact with respect
to any of these factors.
(3) The existence of one or more of these factors does not impose
on the [Board] disciplinary panel or an Administrative Law
Judge any requirement to articulate its reasoning for not exercising its
discretion to impose a sanction outside of the range of sanctions set out in
the sanctioning guidelines.
(4)—(5) (text unchanged)
(6) A departure from the sanctioning guidelines set forth in
Regulation .13 of this chapter is not a ground for any hearing or appeal of a [Board]
disciplinary panel action.
H. Offenses Related to [Continuing Medical Education
Credits.] Continuing Education Requirements.
(1) If a licensee has submitted an application claiming the
completion of continuing [medical] education credits and the
licensee fails to document the completion of such continuing [medical]
education credits when audited by the Board, the licensee may be charged under
one or more of the following, as appropriate:
(a)—(c) (text unchanged)
(2) Upon a finding of a violation, the [Board] disciplinary
panel may impose any discipline authorized under Health Occupations
Article, §14-5C-17, Annotated Code of Maryland, and the sanctioning guidelines.
I. Payment of Fines Imposed by the Board or a Disciplinary Panel.
(1) An individual shall pay to the Board any fine imposed [under]
pursuant to this regulation within 15 calendar days of the date of the
order, unless the order specifies otherwise.
(2) Filing an appeal under State Government Article, §10-222,
Annotated Code of Maryland, does not stay payment of a fine imposed [by
the Board] pursuant to this regulation.
(3) If an individual fails to pay, in whole or in part, a fine
imposed [by the Board] pursuant to this regulation, the Board may
not restore, reinstate, or renew a license until the fine has been paid in
full.
(4) In its discretion, the Board may refer all cases of delinquent
payment to the Central Collection Unit of the State Department of Budget
and Management to institute and maintain proceedings to ensure an
individual’s prompt payment.
.13 Sanctioning Guidelines for Polysomnographic Technologists.
A. Subject to provisions of Regulation .12F and G of this chapter, [the
Board] a disciplinary panel may impose sanctions as outlined in
§B of this regulation on polysomnographic technologists for violations of
Health Occupations Article, §14-5C-17(a), Annotated Code of Maryland.
B. (text unchanged)
LAURA HERRERA SCOTT
Secretary of Health
Subtitle 34 BOARD OF PHARMACY
10.34.04 Transfer and
Outsourcing of Prescriptions and Prescription Orders
Authority: Health Occupations Article, §12-205 (a)(3)(ii),
Annotated Code of Maryland
Notice of Proposed Action
[25-117-P]
The Acting Secretary of Health proposes to amend Regulations .01
and .03, adopt new Regulation .06, and recodify existing
Regulations .06—.09 to be Regulations .07—.10 under COMAR
10.34.04 Transfer and Outsourcing of Prescriptions and Prescription Orders. This action was considered by the Board of
Pharmacy at a public meeting held on January 15, 2025, notice of which was
given by publication on the Board’s website at
https://health.maryland.gov/pharmacy/Pages/index.aspx pursuant to General Provisions Article,
§3–302(c), Annotated Code of Maryland.
Statement of Purpose
The purpose of this action is to:
(1) Clarify and update policies and procedures;
(2) Clarify and update standards for quality assurance; and
(3) Update required reference materials.
Estimate of Economic Impact
The proposed action has no economic impact.
Economic Impact on Small Businesses
The proposed action has minimal or no economic impact on small
businesses.
Impact on Individuals with Disabilities
The proposed action has no impact on individuals with disabilities.
Opportunity for Public Comment
Comments may be sent to Jordan Fisher Blotter, Director, Office of
Regulation and Policy Coordination, Maryland Department of Health, 201 West
Preston Street, Room 534 Baltimore, Maryland 21201, or call 410-767-0938, or
email to [email protected]. Comments will be accepted through August 11,
2025. A public hearing has not been scheduled.
.01 Scope.
This
chapter governs the:
A.
Transfer of prescriptions for non-controlled
dangerous substances between pharmacies;
B.—C.
(text unchanged)
.03 Permanent Transfer of a Prescription Between Pharmacies.
A
pharmacist from a primary pharmacy may permanently transfer a prescription
order to a secondary pharmacy to be dispensed to a specific patient if [:
A.
The prescription is lawfully refillable;
B.
The prescription is not for a Schedule II controlled dangerous substance noted
in Criminal Law Article, Title 5, Subtitle 4, Annotated Code of Maryland;
C.
The] the pharmacist
transferring the prescription from the primary pharmacy indicates on the
prescription, within the prescription computer database and within any
appropriate other records used for dispensing:
[(1)]A.—[(5)]E. (text unchanged)
.06 Transfers of Prescription for
Controlled Dangerous Substances.
A pharmacist may transfer a
prescription for a controlled dangerous substance in accordance with federal
law.
RYAN B. MORAN, DRPH, MHSA
Acting Secretary of
Health
10.34.07 Pharmacy Equipment
Authority: Health Occupations Article, §§12-205 and 12-403,
Annotated Code of Maryland
Notice of Proposed Action
[25-126-P]
The Acting Secretary of Health proposes to amend Regulation .01-1
under COMAR 10.34.07 Pharmacy Equipment.
This action was considered by the Board of Pharmacy at a public meeting
held on January 15, 2025, notice of which was given by publication on the
Board’s website at https://health.maryland.gov/pharmacy/Pages/index.aspx
pursuant to General Provisions Article, §3–302(c), Annotated Code of Maryland.
Statement of Purpose
The purpose of this action is to:
(1) Clarify and update policies and procedures;
(2) Clarify and update standards for quality assurance; and
(3) Update required reference materials.
Estimate of Economic Impact
The proposed action has no economic impact.
Economic Impact on Small Businesses
The proposed action has minimal or no economic impact on small
businesses.
Impact on Individuals with Disabilities
The proposed action has no impact on individuals with disabilities.
Opportunity for Public Comment
Comments may be sent to Jordan Fisher Blotter, Director, Office of
Regulation and Policy Coordination, Maryland Department of Health, 201 West
Preston Street, Room 534 Baltimore, Maryland 21201, or call 410-767-0938, or
email to [email protected]. Comments will be accepted through August 11,
2025. A public hearing has not been scheduled.
.01-1 Equipment.
A
pharmacy shall have the following equipment to carry out the practice of
pharmacy in Maryland:
A. If
applicable, a Class A prescription balance and weights, or a prescription
balance with equivalent or superior sensitivity to a Class A prescription
balance; and
B. A
refrigerator and freezer, if applicable, solely for the storage of drugs
requiring refrigeration, with a thermometer or a temperature monitoring device[; and].
[C. A freezer, if applicable.]
RYAN B. MORAN, DRPH, MHSA
Acting Secretary of
Health
Subtitle
42 BOARD OF SOCIAL WORK EXAMINERS
10.42.02 Social Work Practice
Authority: Health
Occupations Article, §19-205, Annotated Code of Maryland
Notice of Proposed
Action
[25-112-P]
The Acting Secretary of
Health proposes to amend Regulation .02 and adopt new Regulation .06
under COMAR 10.42.02 Social Work Practice. This action was considered by the Board of
Social Work Examiners at a public meeting held on December 13, 2024, notice of
which was given by publication on the Board’s website at
health.maryland.gov/bswe/Pages/default.aspx pursuant to General Provisions
Article, §3–302(c), Annotated Code of Maryland.
Statement of Purpose
The purpose of this action
is to clarify certain definitions and establish a new regulation for private
practice.
Estimate of Economic Impact
The proposed action has no economic impact.
Economic Impact on Small Businesses
The proposed action has minimal or no economic impact on small
businesses.
Impact on Individuals with Disabilities
The proposed action has no impact on individuals with disabilities.
Opportunity for Public Comment
Comments may be sent to Jordan Fisher Blotter, Director, Office of
Regulation and Policy Coordination, Maryland Department of Health, 201 West
Preston Street, Room 534 Baltimore, Maryland 21201, or call 410-767-0938, or
email to [email protected]. Comments will be accepted through August 11,
2025. A public hearing has not been scheduled.
.02 Definitions.
A. (text unchanged)
B. Terms Defined.
(1)—(7) (text unchanged)
(8) Independent Practice.
(a) "Independent clinical practice" means
the practice of licensed clinical social work without the requirement of
social work supervision.
(b) “Independent non-clinical practice” means the practice of
licensed non-clinical social work without the requirement of social work
supervision.
(9)—(11) (text unchanged)
(12) “Non-clinical social work” means assisting individuals,
groups, families, or communities in accessing critical services, locating
resources, negotiating and advocating on behalf of clients, community
organizing, teaching, researching, developing and analyzing policy, and other
non-clinical activities.
[(12)] (13)—[(20)] (21)
(text unchanged)
.06 Private Practice.
A. An LMSW, Board-approved for independent practice, may not
practice clinical social work without supervision in accordance with §B of this
regulation.
B. Supervision Requirements.
(1) An LMSW shall only practice clinical social work under the
supervision of a Board-approved LCSW-C supervisor for clinical practice
employed by the same practice as the LMSW.
(2) An LMSW or LBSW may not practice clinical social work under
the supervision of a:
(a) Psychiatrist;
(b) Psychologist; or
(c) Licensed clinical professional counselor.
C. An LCSW-C supervisor shall:
(1) Ensure the LMSW is:
(a) Properly licensed; and
(b) Knowledgeable of the laws and regulations as set forth in
Health Occupations Article, Title 19, Annotated Code of Maryland and this
subtitle;
(2) Assess the:
(a) LMSW’s:
(i) Knowledge;
(ii) Skills;
(iii) Experience;
(iv) Competence; and
(v) Training; and
(b) Client’s needs;
(3) Assign clients to the LMSW based on the assessment conducted
in §C(2) of this regulation;
(4) Participate in the initial intake and diagnostic assessment
of all clients served by the LMSW until the LMSW is determined to be competent;
(5) Be considered as having a professional/therapeutic
practitioner relationship with the clients served by the LMSW, as evidenced in
documents, such as invoices and client agreements, indicating the name of the
supervising LCSW-C;
(6) Maintain full responsibility for the LMSW’s practice and
professional conduct, including any disciplinary actions;
(7) Monitor and ensure effective and ethical services to
clients;
(8) Maintain full records of practice and communication, which
clearly establishes the LMSW is a supervisee and not an independent
practitioner; and
(8) Comply with the requirements and responsibilities set forth
in COMAR 10.42.08.
D. An LMSW supervisee shall practice within the scope of
practice set forth in Regulation .03B of this chapter.
E. LMSW supervisees may not:
(1) Receive payment directly from the client or client’s
insurance carrier;
(2) Be the owner or in charge of the practice;
(3) Be the lessor in a co-lease or sublease arrangement of
office space where the practice is based or delivered;
(4) Advertise for clients or patients without clearly
identifying the LMSW’s supervisor; and
(5) Directly or indirectly solicit clients or patients for:
(a) Themselves; or
(b) The supervising LCSW-C.
RYAN B. MORAN, DRPH, MHSA
Acting Secretary of
Health
Subtitle 65 BOARD OF MASSAGE THERAPY
EXAMINERS
Notice of Proposed Action
[25-105-P]
The Secretary of Health proposes to:
(1) Amend Regulation .02 under COMAR 10.65.07 Fees; and
(2) Adopt new Regulations .01—.05 under a new chapter, COMAR
10.65.12 Handheld Tools.
This action was considered by the Board of Massage Therapy
Examiners at a public meeting held on October 23, 2024, notice of which was
given by publication on the Board’s website at
health.maryland.gov/massage/Pages/home.aspx pursuant to General Provisions
Article, §3–302(c), Annotated Code of Maryland.
Statement of Purpose
The purpose of this action is to
add a new chapter for handheld tools pursuant to Ch. 788, Acts of 2024,
and a one-time registration fee for licensees trained and qualified for usage.
Estimate of Economic Impact
I. Summary of Economic Impact. The handheld tool
registration fee is for licensees who are trained/qualified for usage. This is
a new requirement and therefore the number of licensees who will register is
unknown. Nevertheless, while the full economic impact is unknown, the impact is
unlikely to be significant as the proposed fee is a one-time registration fee
of $100.
II. Types of Economic Impact.
|
Impacted Entity
|
Revenue
(R+/R-)
Expenditure
(E+/E-)
|
Magnitude
|
|
A. On issuing agency:
|
|
|
|
Board of Massage Therapy
Examiners
|
(R+)
|
Indeterminable
|
|
B. On other State agencies:
|
NONE
|
|
|
C. On local governments:
|
NONE
|
|
|
|
Benefit
(+)
Cost
(-)
|
Magnitude
|
|
D. On regulated industries or
trade groups:
|
|
|
|
Licensees of the Board of Massage Therapy
|
(-)
|
Indeterminable
|
|
E. On other industries or
trade groups:
|
NONE
|
|
|
F. Direct and indirect
effects on public:
|
NONE
|
|
III. Assumptions. (Identified by Impact Letter and Number
from Section II.)
A. The number of licensees who will register is unknown. The
proposed fee is a one-time registration fee of $100.
D. See A above.
Economic Impact on Small Businesses
The proposed action has minimal or no economic impact on small
businesses.
Impact on Individuals with Disabilities
The proposed action has no impact on individuals with disabilities.
Opportunity for Public Comment
Comments may be sent to Jordan Fisher Blotter, Director, Office of
Regulation and Policy Coordination, Maryland Department of Health, 201 West
Preston Street, Room 534 Baltimore, Maryland 21201, or call 410-767-0938, or
email to [email protected]. Comments will be accepted through August 11,
2025. A public hearing has not been scheduled.
10.65.07 Fees
Authority: Health Occupations Article, §§6-206 and 6-207, Annotated
Code of Maryland
.02 Fees for Massage Therapy Licensure and Registration.
The following fees are established by the Board and are
non-refundable:
A.—Q. (text unchanged)
R. Paper copy of laws and regulations . . . $40[.];
and
S. Handheld tool one-time registration fee. . . $100.
10.65.12 Handheld Tools
Authority: Health Occupations Article, §§6-101(f)(2)(ii) and
6-206(a)(1), Annotated Code of Maryland
.01 Scope.
Pursuant to Health Occupations Article, §6-101(f)(2)(ii),
Annotated Code of Maryland, this chapter establishes standards for the use of
instrument-assisted soft tissue manipulation techniques, also known as handheld
tools, by a licensed massage therapist or a registered massage therapist.
.02 Definitions.
A. In this chapter, the following terms have the meanings
indicated.
B. Terms Defined.
(1) “Board” means the State Board of Massage Therapy Examiners.
(2) “Good standing” means that the Board has not:
(a) Reprimanded the licensee, suspended or revoked the license
or registration of the licensee; or
(b) Placed the licensee on probation within 5 years before the
submission of a handheld tool registration application.
(3) Handheld Tool.
(a) “Handheld tool” means an instrument that is used by a
licensee in the practice of massage therapy to enhance or imitate manual
techniques.
(b) “Handheld tool” includes a:
(i) Mechanized vibration instrument; or
(ii) Muscle-scraping tool.
(c) “Handheld tool” does not include a tool exclusively used for
protective self-care, including a:
(i) Thumb-saver tool;
(ii) Trigger point tool; or
(iii) Still point inducer.
(4) “Licensee” means, unless the context requires otherwise, a
licensed massage therapist or a registered massage practitioner authorized by
the Board to practice massage therapy.
(5) “National Certification Board of Therapeutic Massage and
Bodyworkers (NCBTMB)” means the National Certification Board of Therapeutic
Massage and Bodyworkers.
(6) “Practice massage therapy” has the meaning stated in Health
Occupations Article, §6-101(f), Annotated Code of Maryland.
.03 Registration Required.
A. The Board shall register a licensee as qualified to use
handheld tools in the State if the licensee:
(1) Is in good standing as defined in Regulation .02 of this
chapter;
(2) Submits adequate documentary evidence that the licensee
meets the education and training requirements set forth in Regulation .04 of
this chapter;
(3) Submits an application for registration on the form provided
by the Board; and
(4) Pays the one-time registration fee as specified in COMAR
10.65.07.02.
B. A licensee may not use any handheld tool without first
registering as qualified with the Board in accordance with §A of this
regulation.
.04 Minimum Education and Training Requirements.
A. In order to be registered by the Board as qualified to use
handheld tools, a licensee shall meet the requirements of this regulation.
B. A licensee shall complete a minimum of 12 hours of
instruction in the following content areas:
(1) Philosophy and historical perspective of handheld tools and
massage therapy treatment;
(2) Indications, contra-indications, and qualifications for
handheld tools in the practice of massage therapy;
(3) Licensee and patient safety when using handheld tools;
(4) Case management and jurisprudence when using handheld tools;
(5) Recordkeeping, specifically detailing implementation and
specific location of instrument use; and
(6) The clinical use of muscle scraping and mechanized vibration
tools in the practice of massage therapy.
C. The instruction required by this regulation shall be approved
in advance by the Board or the NCBTMB.
D. Prior Instruction.
(1) The Board shall accept a continuing education course
completed before the effective date of this chapter, if the same course, in
substantially similar form, is sponsored by a continuing education provider
approved by the Board or the NCBTMB.
(2) Notwithstanding §D(1) of this regulation, the Board may not
accept a course completed before January 1, 2018.
E. The coursework required by this regulation shall be in
addition to the 750 contact hours of education required by Health Occupations
Article, §6-302, Annotated Code of Maryland.
.05 Standards of Practice.
A. A licensee registered to use handheld tools shall:
(1) Fully explain and demonstrate the use of the handheld tool
to the client in advance of the tool’s use;
(2) Obtain informed written consent specific to the handheld
tool and maintain that written consent within the client’s record;
(3) Utilize handheld tools in a manner consistent with the
standards set forth in the Maryland Occupational Safety and Health Act, Labor
and Employment Article, Title 5, Annotated Code of Maryland, and its associated
regulations;
(4) Document the use of handheld tool therapy in accordance with
COMAR 10.65.06;
(5) Be responsible for the ongoing evaluation, assessment, and
re-evaluation of client impairments;
(6) Only use handheld tools on parts of the body with
neuromuscular or musculoskeletal links to those impairments; and
(7) Maintain continuing competence for handheld tool usage.
B. Any violation of these standards of practice or of the
requirements of this chapter may subject the licensee
to discipline pursuant to Health Occupations Article,
§6-308, Annotated Code of Maryland.
LAURA HERRERA SCOTT
Secretary of Health
Title 11
DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION
Subtitle 14 MOTOR VEHICLE
ADMINISTRATION—VEHICLE INSPECTIONS
Notice of Proposed Action
[25-058-P]
The Administrator of the Motor Vehicle Administration and the
Department of State Police jointly propose to:
(1) Repeal existing Regulations .01—.18 and adopt new
Regulations .01—.16 under COMAR 11.14.01 General Inspection
Requirements and Provisions;
(2) Repeal existing Regulations .01—.26 and adopt new
Regulations .01—.29 under COMAR 11.14.02 Vehicle Inspection Standards;
(3) Repeal existing Regulations .01—.14 under COMAR
11.14.03 Safety Standards for Motorcycles;
(4) Repeal existing Regulations .01—.23 under COMAR
11.14.04 Safety Standards for Trucks, Truck Tractors, Commercial Buses, and
Type I School Vehicles;
(5) Repeal existing Regulations .01—.11 under COMAR
11.14.05 Safety Standards for Trailers; and
(6) Repeal existing Regulations .01—.07 under COMAR
11.14.06 Emissions Equipment Standards.
Statement of Purpose
The purpose of this action is to repeal the existing chapters of
regulations regarding the licensing of vehicle inspection stations, and the
registration of inspection mechanics, and adopt new chapters to address changes
in vehicle technologies, vehicle inspection test tools and equipment, and to
separate, organize, and clarify the existing regulations regarding vehicle
equipment safety inspection. The new proposed chapters remove unnecessary and
obsolete language, update references, address changes in automotive standards
and emerging technologies, and incorporate current policy and procedures for
the licensing and regulatory oversight of Maryland Vehicle Safety Inspection
program by the Maryland Department of State Police Automotive Safety
Enforcement Division (ASED).
This action also establishes the licensing of inspection mechanics
independent of an inspection station license. This will allow persons to be
examined and licensed as vehicle inspection mechanics prior to employment at
inspection stations and will facilitate the transfer of inspection mechanics
from one station to another without unnecessary delay and interruption of
employment.
In addition, the proposed new regulations make provision for the
inspection of vehicles which have been properly modified for operation by
persons with special needs. ASED will provide an examination of specially
modified vehicles and the related documentation at no cost to persons with
special needs. ASED personnel will then provide a form that identifies the
properly modified equipment, which will be presented to inspection stations and
inspection mechanics to allow vehicle safety inspections to be performed and
certified with certain authorized exemptions to regulated vehicle equipment.
Finally, the proposal addresses auxiliary equipment installed on
vehicles that potentially risk person, property, or environmental hazards which
is not currently regulated and makes provisions for current and emerging
automotive technologies for vehicle safety that are not currently regulated
such as supplemental restraint systems, anti-lock brakes and traction control,
and stability systems. eliminates requirements for obsolete or ineffective test
equipment and tools and allows the current test equipment and tools used in the
automotive industry to be approved for use during vehicle safety inspections.
Estimate of Economic Impact
I. Summary of Economic Impact. There is a positive economic
impact on the vehicle repair/service companies that are licensed inspection
stations in the Vehicle Safety Inspection Program and a positive impact on
members of the public.
II. Types of Economic Impact.
|
Impacted Entity
|
Revenue
(R+/R-)
Expenditure (E+/E-)
|
Magnitude
|
|
A. On issuing agency:
|
|
|
|
MVA
|
(E-)
|
None
|
|
B. On other State agencies:
|
|
|
|
No Impact
|
(E-)
|
None
|
|
C. On local governments:
|
|
|
|
None
|
(E-)
|
None
|
|
|
Benefit
(+)
Cost
(-)
|
Magnitude
|
|
D. On regulated industries or
trade groups:
|
|
|
|
Positive Impact
|
(+)
|
$2,500
|
|
E. On other industries or
trade groups:
|
|
|
|
None
|
(+)
|
0
|
|
F. Direct and indirect
effects on public:
|
|
|
|
Positive Impact
|
(+)
|
0
|
III. Assumptions. (Identified by Impact Letter and Number
from Section II.)
D. The implementation of the revised Vehicle Inspection Handbook,
COMAR Title 11 subtitle 14 will have a positive economic impact on the vehicle
repair/service companies that are licensed inspection stations in the Vehicle
Safety Inspection Program. The revised
regulations eliminate an expensive previously required tool, a headlight-aiming
machine, which saves the station between $1,500 and $2,500 depending on the
brand and model of tool they purchased.
The elimination of this tool provides for a quicker inspection process
that saves the station time and can increase their earning potential on a daily
basis. The stations will be required, as they currently are, to purchase the
new Vehicle Inspection Handbook, which has a cost of $50.00 plus $15.00 shipping
and handling.
F. There is a positive impact on members of the public as well, the
revised regulations have provisions to inspect and accommodate specialized and
or modified equipment installed in vehicles for persons with disabilities. Whether it is equipped for disabled
passengers and or disabled drivers.
Currently, there are no provisions to accommodate this equipment, and at
times the vehicles will need be converted back to a conventional vehicle for
inspection. This is cost-prohibitive.
An additional positive impact to the public in the revised
regulation is a provision to allow heavy-duty pickup style trucks over 10,000
GVWR not equipped with airbrakes to be inspected at a lower cost to the
citizen.
Economic Impact on Small Businesses
The proposed action has a meaningful economic impact on small
businesses. An analysis of this economic impact follows:
Economic Impact on Small Businesses: The proposed action has a
meaningful economic impact on small businesses. As stated in the summary the
revised regulations will have a positive economic impact on small businesses.
The elimination of a previously required tool will save businesses between
$1,500 and $2,500. This also allows for a streamlined, quicker, inspection
process, which may increase their daily earning potential. Lastly, the
availability of digital version of the Vehicle
Inspection Handbook at a reduced cost will have a positive impact.
Impact on Individuals with Disabilities
The proposed action has an impact on individuals with disabilities
as follows:
The proposed action has an impact on individuals with disabilities
as follows: Positive impact, the new regulations have provisions to inspect and
accommodate specialized and/or modified equipment installed in vehicles for
persons with disabilities. Whether it is equipped for disabled passengers and
or disabled drivers. Currently, there are no provisions to accommodate this
equipment, and many times the vehicles must be converted back to a conventional
vehicle for inspection. This is cost-prohibitive.
Opportunity for Public Comment
Comments may be sent to Tracey C. Sheffield, Regulations
Coordinator, MVA, 6601 Ritchie Highway NE, Room 200 Glen Burnie, MD 21062, or
call 410-768-7545, or email to [email protected]. Comments will be
accepted through August 11, 2025. A public hearing has not been scheduled.
11.14.01 General Inspection Requirements
and Provisions
Authority: Transportation Article, §12-104(b), §22-104, §23-101 –
23-109, §24-106.1, and § 25-110
Annotated Code of Maryland
.01 Definitions.
A. In this subtitle, the following terms have the meanings
indicated. . Terms Defined.
(1) “Administration” means the Maryland Motor Vehicle
Administration of the Maryland Department of Transportation.
(2) “Autocycle” means a motor vehicle that:
(a) Has two front wheels
and one rear wheel;
(b) Has a steering wheel;
(c) Has permanent seats
on which the operator or a passenger is not required to sit astride;
(d) Has foot pedals to
control acceleration, braking, and, if applicable, a clutch; and
(e) Is manufactured to
comply with federal safety standards for motorcycles.
(3) “Bed” means the load-carrying part temporarily or
permanently attached to a vehicle and separated from the passenger compartment
and fully enclosed on both sides by sideboards or side panels, on the front by
a board or panel or by the cab of the vehicle, and on the rear, by a tailgate,
board, or panel.
(4) “Commercial motor vehicle” means any self-propelled or towed
motor vehicle used on a highway for interstate or intrastate commerce to
transport passengers or property when the vehicle:
(a) Has a gross vehicle weight rating or gross combination
weight rating, or gross vehicle weight or gross combination weight, of 10,001
pounds (4,536 kg) or more, whichever is greater:
(b) Is designed or used to transport more than eight passengers
(including the driver) for compensation;
(c) Is designed or used to transport more than 15 passengers
(including the driver) and is not used to transport passengers for
compensation; or
(d) Is used in transporting material found by the Secretary of
Transportation to be hazardous under 49 U.S.C. §5103 and transported in a
quantity requiring placarding under regulations required by the Secretary under
49 CFR.
(5) “Conviction” has the meaning stated in Transportation
Article, §11-110, Annotated Code of Maryland.
(6) “Covert vehicle” means a vehicle used by the Division to
monitor compliance with COMAR 11.14, by inspection stations, or inspection
personnel.
(7) “Covert vehicle inspection” means the submission of a covert
vehicle as defined in §B(6) of this regulation to inspection stations, or
inspection personnel, for the investigation of compliance with COMAR 11.14
during inspection, or the presentation of a fictitious safety equipment repair
order.
(8) “Dealer” means a dealer who is licensed in this State under
Transportation Article, Title 15, Annotated Code of Maryland.
(9) “Division” means the Automotive Safety Enforcement Division
(ASED) of the Department of State Police.
(10) “DOT” means United States Department of Transportation.
(11) “Enclosures” means the front, rear, and sides of a vehicle
bed as defined in Transportation Article, §24-106.1(d)(1), Annotated Code of
Maryland.
(12) “Facility” means a vehicle dealer repair shop, vehicle
repair garage, or service station vehicle repair shop.
(13) “Fictitious safety equipment repair order” means a safety
equipment repair order that is an authentic document containing information
that may be fabricated, prepared by Division personnel for submission for
inspection and compliance with COMAR 11.14.
(14) “Fleet station” means an organization, company, business,
educational institution, or municipal facility that owns, operates, or controls
15 or more vehicles, and has been licensed and authorized by the Division to
inspect only those vehicles owned, operated, or controlled by the licensee.
(15) “GVWR” means the gross vehicle weight rating as determined
by the manufacturer.
(16) “Inspection certification” means a certification by an
inspector, in a format established by the Division, that:
(a) Certifies that as of the specified date, and mileage (if
applicable), at the time of certification, a vehicle, identified by the Vehicle
Identification Number (VIN), and having been subject to a vehicle safety
inspection, meets or exceeds the standards established in these regulations;
and
(b) Inspection includes initial inspections, inspection of vehicle
equipment rejected during a previous inspection, or inspection of vehicle
equipment due to the issuance of a safety equipment repair order.
(17) “Inspection station” means a facility that has been
authorized to allow the performance of vehicle safety inspections, the
certification of inspections of compliant vehicles, and the certification of
safety equipment repair orders for a specific class or classes of vehicles.
(18) “Inspector” means an individual who:
(a) Meets the requirements defined in Regulation .04 of this
chapter;
(b) Has passed the appropriate written and demonstrative ability
examinations;
(c) Is not under any type of administrative sanctions; and
(d) Has been licensed as an inspector by the Division to perform
vehicle safety inspections on specific classes of vehicles at a specific type
of inspection station.
(19) “Limousine” means a vehicle that:
(a) Has been modified or stretched for transportation of
passengers;
(b) Is driven as part of a service provided by a person that
advertises itself as a provider of limousine services or registers with the
Public Service Commission as a provider of limousine services; or
(c) Is equipped with additional amenities not normally provided
in passenger cars, for passenger convenience.
(20) “Load cover” means a device made of canvas or other type
material and used to enclose the open top of a vehicle bed, as defined in
Transportation Article, §24-106.1(a), Annotated Code of Maryland.
(21) “Loose material” means loose material as defined in
Transportation Article, §24-106.1(a), Annotated Code of Maryland, and COMAR
11.15.20.01.
(22) “Low-speed vehicle” means a four-wheeled motorized vehicle
that has a maximum speed capability that exceeds 20 miles per hour and not more
than 25 miles per hour on a paved level surface, and whose GVWR is less than
3,000 pounds.
(23) Manufacturer.
(a) “Manufacturer” means a person or entity in the business of
constructing or assembling vehicles of a type required to be registered under
Transportation Article, Title 13, Annotated Code of Maryland.
(b) “Manufacturer” includes a person or entity in the business
of constructing or assembling the first-stage manufacture of an incomplete
vehicle, and the second-stage manufacture of a two-stage vehicle so that it
becomes a completed vehicle, as these terms are defined in Transportation
Article, §13-113.2 Annotated Code of Maryland.
(24) “Maryland Safety Inspection System (MSIS)” means the
electronic reporting and certification system established by the Division to
facilitate the electronic submission of inspection certifications to the
Administration and provide an electronic database of vehicle inspection
records.
(25) “Modular home trailer” means a trailer manufactured solely
for transporting modular homes or portions of modular homes.
(26) “Motorcycle” means a motor vehicle that:
(a) Has motive power;
(b) Has a seat or saddle for the use of the rider;
(c) Is designed to travel:
(i) On not more than three wheels in contact with the ground;
and
(ii) At speeds exceeding 35 miles per hour; and
(d) Complies with all motor vehicle safety standards applicable
to motorcycles under federal law.
(27) “Multipurpose passenger vehicle” means:
(a) A motor vehicle that is designed primarily for carrying
persons which is constructed on a truck chassis or with special features for
occasional off-road operations; or
(b) A motor vehicle that is of unique design that does not meet
the requirements of any other class as determined by the Division, except
4-wheel drive passenger vehicles (sedans, convertibles, and station wagons).
(28) “NHTSA” means National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration.
(29) “OEM” means original equipment manufacturer.
(30) “Physical Disability Medical Exemption for Vehicle
Equipment” means a form issued by the Division to provide notification and
documentation to inspection station personnel performing an inspection of a
vehicle that:
(a) The vehicle has been properly modified and identified, to
enable a person with a disability to operate, or ride as a passenger in the
motor vehicle; and
(b) Is exempted from the “make inoperative” prohibition of 49
U.S.C. §30122 to the extent that those modifications affect the motor vehicle's
compliance with the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards or portions thereof
specified in 49 CFR §595.7.
(31) “Physician’s Written Certification of Necessity for Medical
Exemption from Maryland Window Tint Limitations Form” is a form issued by the
Division that enables a physician to render a signed statement indicating a
person meets all provisions for a medical exemption set forth in Transportation
Article, §22-406, Annotated Code of Maryland, and the applicable COMAR
governing post manufacture window tinting while being operated by the primary
owner/driver.
(32) “Police officer” means:
(a) A uniformed police officer as defined in Transportation
Article, §11-147, Annotated Code of Maryland; or
(b) A civilian employee of the Department of State Police as
defined in Transportation Article §23-101(g), Annotated Code of Maryland.
(33) “Post Manufacture Window Tint Inspection Report” means a
form that:
(a) Has been approved by the Division;
(b) Has been completed by an inspector; and
(c) Identifies the owner or agent, the vehicle information, and
light transmittance readings of regulated windows equipped with post
manufacture window tint.
(34) Post Manufacture
Window Tint Medical Exemption Form”.
(a) “Post Manufacture Window Tint Medical Exemption Form” means
a form issued by the Division upon presentation of a written certification from
a physician or optometrist licensed to practice medicine in the State of
Maryland that details the vehicle owner’s medical need for windows tinted to
less than 35 percent light transmittance.
(b) “Post Manufacture Window Tint
Medical Exemption Form” authorizes an inspector to exempt the vehicle’s windows
equipped with post manufacture window tint from meeting the light transmittance
requirement during a vehicle inspection, or during certification of a SERO
issued to an owner of a vehicle.
(35) “Rebuilding” means the restoring of a salvage vehicle as
set forth in Transportation Article, §13-506, Annotated Code of Maryland, or a
vehicle that is inoperable because of the need for major or extensive repairs
to the body, frame, suspension, engine, or drivetrain.
(36) “SAE” means the Society of Automotive Engineers.
(37) “Safety Equipment Repair Order (SERO)” means a hand-printed
or electronic directive ordering repair of defective equipment on a specified
vehicle.
(38) Second-Stage Manufacturer.
(a) “Second-stage manufacturer” means a licensed second-stage
manufacturer as defined in Transportation Article, §15-201, Annotated Code of
Maryland.
(b) “Second-stage manufacturer” includes a person who works on
an incomplete vehicle so that it becomes a complete vehicle in accordance with
COMAR 11.15.27 and Transportation Article, §15-201, Annotated Code of Maryland,
or retrofits an existing vehicle for dump service registration with the
Administration so that it becomes a complete vehicle in accordance with COMAR
11.15.27 and Transportation Article, §15-201, Annotated Code of Maryland; and
(c) A second-stage manufactured vehicle shall be identified as
such only if the vehicle is labeled in accordance with 49 CFR §567.5.
(39) “Securement hardware” means any device used to attach or
secure a cover on a vehicle bed.
(40) Specially Constructed Vehicle.
(a) “Specially constructed vehicle” means a vehicle that was not
originally constructed under a distinctive name, make, model, or type by a
generally recognized manufacturer of vehicles and has not been materially
altered from its original construction, including kit cars and replicas of
previously manufactured vehicles.
(b) “Specially constructed vehicle” does not include a vehicle
assembled from parts acquired from multiple vehicles or other sources that has
been assembled into a single vehicle, other than one which is constructed upon
an engineered and manufactured kit from a manufacturer as defined in this
regulation.
(41) “State Police” means the Maryland Department of State
Police.
(42) “Supervisor” means an individual who:
(a) Has supervisory authority within the business establishment;
(b) Has been designated by the applicant or licensee, and agrees
to be responsible for the daily operation of the inspection program at the
facility; and
(c) Has submitted a Division application, passed a written
examination administered by the Division, and has been approved by the Division
to act on behalf of a licensee.
(43) “Vehicle” means, except as otherwise provided in this
regulation, any vehicle registered or to be registered in this State as:
(a) Class A (passenger) vehicle;
(b) Class E (truck) vehicle;
(c) Class F (tractor) vehicle;
(d) Class G (trailer) vehicle;
(e) Class J (vanpool) vehicle;
(f) Class M (multipurpose) vehicle;
(g) Class B (for hire) vehicle;
(h) Class D (motorcycle) vehicle;
(i) Class Q (limousine) vehicle; and
(j) Class L (historic) applicable to a historic vehicle sold by
a licensed Maryland dealership, which was previously titled or registered in
another state or country, for initial registration in Maryland:
(i) For the purpose of load covers, required by Transportation
Article, §24-106.1, Annotated Code of Maryland, any vehicle as defined in
Transportation Article, §11-176, Annotated Code of Maryland;
(ii) For the purpose of SERO issuance, a motor vehicle, trailer,
semitrailer, Class L (historic) vehicle with the model year of 1986 or later,
and Class L truck, tractor, and multipurpose motor home over 10,000 GVWR,
except as provided in §B(43)(d) of this regulation; or
(iii) For the purpose of a SERO issuance, “Vehicle” does not
include any Class L (historic) vehicle with the model year of 1985 or earlier,
Class N (street rod) vehicle, or trailer which is a mobile home as defined in
Transportation Article, §11-134, Annotated Code of Maryland.
(44) “Vehicle Inspection Handbook” means a book of regulations
governing motor vehicle inspections, obtained from the Office of the Secretary
of State, Division of State Documents, for the State of Maryland, in a format
approved by the Division.
(45) “Vehicle Safety Inspection Bulletin” means a bulletin
released by the Division to supply an enforceable interpretation of the
regulation, or to provide guidance for procedures related to the vehicle safety
inspection program for specific circumstances not covered by the Vehicle
Inspection Handbook, and to address emerging automotive technical innovation which
may seem to conflict with current regulations.
.02 Administrative Penalties.
A. The inspection station license under Regulation .03 of this
chapter, or the inspector license under Regulation .04 of this chapter, may be
refused, revoked, or suspended if the station or inspector has
committed any of the offenses in this regulation:
(1) Falsification of facts shall result in revocation of the
license to protect the integrity of the Vehicle Safety Inspection Program;
(2) Failure to comply with any requirements of the regulations
contained in COMAR 11.14; or
(3) Materially altering, or knowingly allowing changing of
equipment on a vehicle:
(a) For which an inspection certification or a repair order
certification has been issued, that results in equipment not meeting or
exceeding the standards established under this subtitle; or
(b) For a vehicle registered in Maryland, or sold for
registration in Maryland which results in equipment not meeting or exceeding
the standards established under this subtitle.
B. Corrective action procedures are intended to establish an
equitable and effective process to correct unacceptable vehicle safety
inspection actions. The regulations contained within this chapter establish
corrective actions and administrative penalties through direct reference in the
regulation, or by the penalty assessment categories found in §C of this
regulation.
(1) Vehicle steering systems, suspension systems, brake systems,
and tire and wheel equipment are critical safety equipment systems that may
have a very high potential for loss of control of a vehicle during operation
and shall result in the application of severe penalties for unacceptable
vehicle safety inspection actions:
(a) A school vehicle, as defined in Transportation Article,
§11-154, Annotated Code of Maryland is also regulated for inspection under
COMAR 11.19.04 School Vehicle Inspection by Authority established in
Transportation Article, §§12-104(b) and 25-110, Annotated Code of Maryland.
(b) A school vehicle, due to the specific purpose of safely
transporting children, categorizes and identifies additional vehicle equipment
in this regulation as “School Vehicle Critical Safety Equipment”, and the
Administration may suspend the registration and confiscate the registration
plates of a school vehicle determined to be unfit or unsafe for the
transportation of passengers.
(2) When multiple offenses have been committed, all offenses
will be included in the Investigative Report as supporting documentation to
determine the corrective action to be taken.
(a) A combination of any three or more violations committed
during the same action or inspection will enhance the violation to a higher
category.
(b) Subsequent violations within 12 months enhance the penalty
to a higher category.
(c) Subsequent Category “II”, “III”, or “IV” violations within
12 months of reinstatement into the Inspection Program after a served penalty
will result in enhanced penalties for violations.
(3) All categories of offenses will apply uniformly to the
inspectors involved in the offenses and inspection station alike, where it is
revealed that inspection station supervision was involved in the matter or had
knowledge of its occurrence.
(4) Corrective disciplinary action for each category of offense
shall not be exceeded unless strong mitigating circumstances exist which
require escalation of charges, otherwise, the appropriate corrective action
will be taken.
C. Penalty assessment categories are divided into five groups of
offenses based on the seriousness as they pertain to vehicle safety. The
specified corrective disciplinary action for each category of offense shall not
be exceeded unless strong mitigating circumstances exist. A violation of any
regulation in the Vehicle Inspection Handbook or a procedure detailed in a
Vehicle Safety Inspection Program Bulletin issued by the Division shall be
addressed using the following categories of assessment of penalties. Multiple
incidents of violations of regulations or procedures shall escalate charges to
a higher category.
(1) Category I. Unacceptable vehicle safety inspection actions
that are less serious, but which require corrective action to maintain an
efficient and effective Vehicle Inspection Program, and unless designated
otherwise as required by this regulation shall result in:
(a) First offense – Documented in Station Compliance Check
Report or Investigative Report as applicable;
(b) Second offense – Documented in Station Compliance Check
Report or Investigative Report as applicable; and
(c) Third offense – Written reprimand – Issued by the Division
Commander.
(2) Category II. Unacceptable vehicle safety inspection actions
that are serious which require corrective disciplinary action to prevent unsafe
vehicle safety inspection actions and shall result in a suspension for 30 days.
(3) Category III. Unacceptable vehicle safety inspection actions
that are more serious which require corrective disciplinary action due to
multiple occurrences of offenses involving unsafe vehicle safety inspection
actions, and the associated safety risk to the public this creates, and shall
result in a suspension for 180 days.
(4) Category IV. Unacceptable vehicle safety inspection actions
that are very serious which require corrective disciplinary action due to
multiple occurrences of very serious offenses involving critically unsafe
vehicle safety inspection actions, and the escalation of the associated safety
risks to the public this creates, and shall result in a suspension for 2 years.
(5) Category V. Unacceptable vehicle safety inspection actions
that are critical safety violations and require immediate corrective action to
prevent serious vehicle safety incidents, and unless designated otherwise as
required by §B(4) of this regulation shall result in revocation from the
Maryland Vehicle Safety Inspection Program.
D. Reinstatement after Revocation under Administrative
Penalties.
(a) A revoked Inspector or Inspection Station may apply for
reinstatement after 5 years of revocation; and
(b) A revoked Inspector or Inspection Station, having served one
revocation period, and having made reapplication and been reinstated, commits
any subsequent Category “II”, “III”, or “IV” violation shall be subject to
permanent revocation.
E. Penalty Categories by Regulation. Sections not listed below
will be assessed on a case-by-case basis for an appropriate penalty as certain
regulations impose the penalty established by regulation.
(1) Category I. Violations of the following regulations are
Category I offenses:
(a) 11.14.01.04A(1)—(2);
(b) 11.14.01.04D;
(c) 11.14.01.05A(1)—(3);
(d) 11.14.01.05C;
(e) 11.14.01.06;
(f) 11.14.01.07C;
(g) 11.14.01.09D;
(h) 11.14.01.09H—J;
(i) 11.14.01.11A;
(j) 11.14.02.04A—B Tow Vehicle Hitches and Coupling Devices—(Except
for Truck-Tractors);
(k) 11.14.02.09C Auxiliary Equipment Exhaust Systems;
(l) 11.14.02.10 Emissions Control Systems;
(m) 11.14.02.12 Body Components;
(n) 11.14.02.13 Bumpers and Rear Metal Frame—(Except for School
Vehicles);
(o) 11.14.02.14 Floor, Trunk, Bulkhead, and Interior Engine
Cover— (Except for School Vehicles);
(p) 11.14.02.15 Rearview Mirrors;
(q) 11.14.02.16 Equipment for Operator, and Passengers;
(r) 11.14.02.17 Seat Belts, and Supplemental Restraint Systems;
(s) 11.14.02.18 Automatic Transmission Gear Indicator, and
Neutral Safety Switch for Starter;
(t) 11.14.02.19 Manual Transmission Neutral Safety and Clutch
Safety Starter Switch;
(u) 11.14.02.20 Speedometer, and Odometer;
(v) 11.14.02.21 Windshield Wipers and Washers—(Except for School
Vehicles);
(w) 11.14.02.22 Glazing—(Except for School Vehicles);
(x) 11.14.02.23 Lighting—(Except for School Vehicles);
(y) 11.14.02.24 Electrical Systems—(Except for School Vehicles);
and
(z) 11.14.02.25 Load Covers.
(2) Category II. Violations of the following regulations are
Category II offenses:
(a) 11.14.01.04B, C(5), (6);
(b) 11.14.01.05B;
(c) 11.14.01.09A—C;
(d) 11.14.01.09E—G;
(e) 11.14.02.02 Steering, Alignment, and Suspension (Critical
Safety Equipment);
(f) 11.14.02.03 Vehicle Frame and Unibody Construction (Critical
Safety Equipment);
(g) 11.14.02.04C Fifth Wheels for Truck-Tractors (Critical
Safety Equipment);
(h) 11.14.02.05 Trailer Towing Attachment Devices (Critical
Safety Equipment);
(i) 11.14.02.06 Brake System (Critical Safety Equipment);
(j) 11.14.02.07 Wheels, Tire Pressure Monitoring, and Tires
(Critical Safety Equipment);
(k) 11.14.02.08 Fuel Systems (Critical Safety Equipment);
(l) 11.14.02.09A Motor Vehicle Powertrain Exhaust Systems
(Critical Safety Equipment);
(m) 11.14.02.09B Commercial Vehicle Exhaust Systems (Critical
Safety Equipment);
(n) 11.14.02.09D School Vehicle Exhaust Systems (Critical Safety
Equipment);
(o) 11.14.02.11 Powertrain and Powertrain Components (Critical
Safety Equipment);
(p) 11.14.02.13F Bumpers and Rear Metal Frame School Vehicles
(Critical Safety Equipment);
(q) 11.14.02.14 Floor, Trunk, Bulkhead, and Interior Engine
Covers (Critical Safety Equipment for School Vehicle);
(r) 11.14.02.15E School Vehicle Mirrors (Critical Safety
Equipment for School Vehicle);
(s) 11.14.02.16A—E Equipment for Operator, and Passengers
(Critical Safety Equipment for School Vehicle);
(t) 11.14.02.21 Windshield Wipers and Washers (Critical Safety
Equipment for School Vehicle);
(u) 11.14.02.22 Glazing—Critical Safety Equipment (Critical
Safety Equipment for School Vehicle);
(v) 11.14.02.23H School Vehicle Warning Lights (Critical Safety
Equipment for School Vehicle);
(w) 11.14.02.24 Electrical Systems (Critical Safety Equipment
for School Vehicle);
(x) 11.14.02.26 School Vehicle Color and Identification
(Critical Safety Equipment for School Vehicle);
(y) 11.14.02.27 School Vehicle Emergency Equipment (Critical
Safety Equipment for School Vehicle);
(z) 11.14.02.28 School Vehicle Approved Optional Systems
(Critical Safety Equipment for School Vehicle); and
(aa) 11.14.02.29 Type I School Vehicle for Transporting Special
Needs Children (Critical Safety Equipment for School Vehicle).
(3) Category III. Violations of the following regulations are
Category III offenses:
(a) 11.14.01.02A(2) and (3);
(b) 11.14.01.03B;
(c) 11.14.01.04B(1)(g)—(l);
(d) 11.14.01.04B(2) and (3);
(e) 11.14.01.13A; and
(f) 11.14.01.14.
(4) Category IV. Violations of the following regulations are
Category IV offenses:
(a) 11.14.01.08; and
(b) 11.14.01.11B.
(5) Category V. Violations of 11.14.01.02A are Category V
offenses.
.03 Licensing Requirements for Facilities.
A. An application for an inspection station license or license
renewal shall be submitted in a format established by the Division, and be
signed by a principal officer of the organization applying for the license
under penalty of perjury, as provided by Criminal Law Article, §9-1, Annotated
Code of Maryland. This application shall be accompanied by the fee set forth in
COMAR 11.11.05, as follows:
(1) Private business—identifies the owner;
(2) Partnership—identifies all partners; and
(3) Corporation—identifies a corporate officer or other person
with written power of attorney that shall either accompany the application or
be on file with the Division.
B. Any facility as defined in Regulation .01B(12) of this
chapter may apply to the Division to be licensed or otherwise authorized as an
inspection station. A dealer who is licensed in this State under the
Transportation Article, Title 15, of the Annotated Code of Maryland for the
sale of vehicles shall not be licensed as a fleet station. Applications shall
not be accepted from a facility owned or operated by a person or persons if any
administrative actions authorized under this subtitle, including suspension,
revocation, refusal, or fines have been imposed, or are pending against any
license held or applied for by those parties, and subject to the following
conditions:
(1) Vehicle sales and repair, vehicle repair, or vehicle service
shall remain the primary business of the facility;
(2) The application shall identify the person or persons who
shall routinely be on-site and will supervise and be responsible for the daily
operation of the inspection station activities; and
(3) Corporate officers, owners, and partners not routinely
on-site at the establishment shall delegate inspection station responsibility to
an approved supervisor, as defined in Regulation .01B(42) of this chapter,
within the business establishment as permitted in this regulation.
C. Applications will not be accepted from any applicant who has
been in business at that location for less than 6 months except:
(1) Previously appointed facilities which have changed location;
(2) Additional locations of existing or established businesses
that have one or more locations licensed as inspection stations; or
(3) A dealer licensed by the Administration.
D. The Division Commander may waive the 6-month waiting period
when adequate documentation of previous business operational experience is
presented.
E. “License” may also refer to “registration”, “appointment”,
“authorization”, or similar terms used regarding inspection station facilities
in this chapter.
.04 Personnel Requirements.
A. Each inspection station open to the public shall have the
following personnel available during Division approved hours as specified
below:
(1) At least one Vehicle Safety Inspector licensed to perform
inspections at the specific types of station; and
(2) An approved inspection station supervisor, as applicable.
(3) If the inspection station does not employ a licensed
inspector for a period of 90 days, the inspection station license shall be
canceled.
B. Inspector Licensing and Requirements. Applications shall not
be accepted from a person if any administrative actions authorized under this
subtitle, including suspension, revocation, refusal, or fines have been
imposed, or are pending by those parties.
(1) Each new applicant, or renewing inspector shall:
(a) Submit an application for a vehicle safety inspector
license, or for renewal of a license in a format established by the Division,
as follows:
(i) The application or renewal shall identify the applicant, the
person applying for the license;
(ii) The application shall indicate whether the applicant has
been convicted of a crime other than a traffic violation;
(iii) The application shall indicate if any administrative
actions, including suspension, revocation, refusal, or fines are pending
against any license held or applied for; and
(iv) The application shall indicate the type of vehicle safety
inspector license being applied for;
(b) Be at least 18 years old, and have a minimum of 12 months
general motor vehicle repair experience;
(c) Be at least 17 years old and possess a certificate of
satisfactory completion of an automotive mechanic's course from an accredited
Maryland high school or its equivalent;
(d) Be thoroughly familiar with the contents of the Vehicle
Inspection Handbook; and
(e) Possess a valid driver's license issued in the applicant's
name for the class of motor vehicle to be driven in the course of inspection.
(2) Applicants shall be capable of passing written examinations,
and demonstrative ability examinations as required by the Division.
(a) Applicants shall register, complete, and receive a grade of
at least 80 percent within a 30-day period, on the written general inspection
knowledge examination, and on the vehicle equipment knowledge examinations for
each type of station and associated vehicle class of which the applicant will
be performing inspections; and
(b) Applicants shall take and pass a demonstrative ability
examination for each type of station and vehicle type the applicant will be
performing inspections upon, after the written examinations are successfully
completed.
C. Examination Requirements. Written and Demonstrated Ability
Examinations shall be successfully completed within the same 6-month period
which shall begin on the initial date of the registration for written
examinations.
(1) Three consecutive failures of a written examination shall
require a 6-month waiting period before any additional examinations may be
taken. The 6-month period start date shall begin on the initial date of
registration for written examinations.
(2) Three consecutive failures of a demonstrated ability
examination shall require a 6-month waiting period before any additional
examinations may be taken.
(3) A licensed inspector wishing to add an additional type of
inspection license shall be required to pass the specific vehicle equipment
knowledge and demonstrated ability examinations for the types of vehicles
approved to be inspected by the type of station.
(4) A licensed inspector shall be subject to reexamination as
required by the Division.
(a) A tools knowledge and ability examination may be
administered to an inspector transferring to a station to ensure that the
inspector can calibrate and properly use the station’s brand/make of tools and
equipment before the inspector is placed active at the station.
(b) A tools knowledge and ability examination may be
administered to an active inspector with justifiable cause indicated by
improper use or maintenance of the required tools and equipment. Any two
failures of this examination shall require a 6-month waiting period before any
subsequent examination.
(c) Written examinations may be re-administered to an active
inspector with the approval of a Division supervisor when reasonable grounds
exist. Any two failures of this examination shall require a 6-month waiting
period before any subsequent examination.
(d) A Demonstrative Ability Examination may be re-administered
to an active inspector with the approval of a Division Supervisor when
reasonable grounds exist. Any two failures of this examination shall require a
6-month waiting period before any subsequent examination.
(e) Re-examinations as a result of failures will be conducted
upon the next station visit or sooner depending on the availability of Division
personnel.
(5) An inspector shall only perform inspections of vehicles for
which they are licensed to perform:
(a) Only in designated inspection areas; and
(b) Only on the property of their assigned inspection stations.
(6) An inspector shall complete all regulated aspects of vehicle
inspection. An assistant may help raise the vehicle and remove and replace
tire/wheel assemblies, but the inspector shall perform all regulated inspection
procedures, and properly tighten all fasteners and reinstallation of all
equipment removed or disassembled for inspection.
(a) An inspector shall be capable of road testing the motor
vehicle as part of the inspection procedure.
(b) An inspector shall be responsible for and capable of
completing all aspects of an inspection including:
(i) Performing vehicle inspections, and inspections for
certification of defects identified by SEROs only at the inspection station;
(ii) Maintaining accurate and factual records pertaining to all
inspections that the inspector performs; and
(iii) Maintaining strict security of username and password
access to MSIS.
(c) An inspector shall only use approved tools and equipment for
vehicle inspection, and be capable of calibrating all tools and equipment used
for vehicle safety inspection procedures.
(d) An inspector shall not use, or be under the influence of
alcoholic beverages or controlled dangerous substances (CDS) while performing
any action as an inspector.
(e) An inspector shall be required to renew the inspector
license every 5 years, or as otherwise required by the Division.
D. Inspection Station Supervisor Requirements. Applications
shall not be accepted from a person if any administrative actions authorized
under this subtitle, including suspension, revocation, refusal, or fines have
been imposed, or are pending by those parties.
(1) The applicant/licensee shall designate supervisory personnel
within their business establishment who shall:
(a) Hold a supervisory/management position within the
established business with authority over personnel employed by the business;
(b) If not a licensed inspector, the inspection station
supervisor shall submit an application, and pass a supervisor general
inspection knowledge examination before being approved to function in that
capacity; and
(i) Be responsible for, and supervise the daily operation of the
inspection program at the licensee's facility on behalf of the
applicant/licensee;
(ii) Assure inspection certifications and SERO certifications
are properly completed after the conclusion of the inspection for compliance
with the regulations in this subtitle, and before the vehicle leaves the
inspection station premises;
(iii) Have all records of inspections available at the facility
during normal working hours that may be examined or removed by Division
personnel as needed;
(iv) Be employed on a full-time basis at the inspection station;
and
(v) Maintain strict security of username and password to access
the MSIS, if applicable.
(2) The station supervisor shall not use, or be under the
influence of alcoholic beverages or CDS while performing any action as a
station supervisor.
.05 Facility Requirements.
A. The building and location of a facility shall conform to
established requirements in these regulations to be approved as an inspection
station of any type, or combination of types. Inspection area requirements for
a combination of types at the same facility may be met by multiple approved
inspection areas, or by a single inspection area, if the single inspection area
meets all the requirements for all the specific types applied for, or approved
at the facility and shall be open and accessible to the public for inspections
except for those facilities with a Type F
designation.
(1) Inspection stations shall have regular operating hours
Monday through Friday from at least 8 a.m. to 4 p.m. for inspection-related
activities unless otherwise authorized by the Division.
(2) Inspection stations may adjust their operating days or hours
for inspection-related activities in the best interest of the State and the
public after submission of a request in a format approved by the Division and
shall not adjust them until the request is approved by the Division.
(3) Inspection stations shall display the trading name on the
facility, or on a sign on the premises, that can be clearly read from the
street in front of the business.
(4) Inspection stations shall comply with all applicable laws,
ordinances, and regulations for the jurisdiction in which it is located.
B. The facility shall be appropriate for the types of inspection
to be conducted as described below, including an entrance to the inspection
area of sufficient height and width to accommodate the maximum legal height and
width of vehicles to be inspected.
(1) Type A—passenger vehicles, limousines, trucks, vans,
multipurpose passenger vehicles, motor homes, 10,000 pounds and under GVWR,
trailers not equipped with air brakes, and autocycles. Type A inspection
station inspection bays shall be at least 12 feet wide and 24 feet long. Type A
inspection stations may allow, but shall not require, an inspector to inspect a
vehicle with a GVWR of more than 10,000 pounds provided;
(a) The vehicle is not equipped with an air brake system;
(b) The vehicle can be physically accommodated inside a
designated Type A inspection bay, (12 feet wide x 24 feet long); and
(c) The facility shall have sufficient means of safely lifting
and supporting the vehicle for inspection.
(2) Type C—trucks, truck tractors, buses, motor homes, converted
buses, and limousines over 10,000 pounds GVWR. Type C inspection station
inspection bays shall contain an area at least 15 feet wide and 45 feet long.
(3) Type F—fleet station (must own, operate, or control at least
15 vehicles operated in a commercial venture, service application, or repair
enterprise – not applicable to automotive dealers). Type F inspection station
contains an inspection area meeting the requirements established for the
classes of vehicles owned or controlled by this facility.
(4) Type M—motorcycles, and trailers not equipped with air
brakes. Type M inspection station inspection bays shall be at least 10 feet
wide and 15 feet long.
(5) Type R—only motor homes and converted buses. Type R
inspection station inspection bays shall be at least 12 feet wide and 40 feet
long.
(6) Type T—any trailer, including those equipped with air
brakes. Type T inspection station inspection bays shall be at least 12 feet
wide and at least 60 feet long. This area may be outside.
(7) Type TL—any trailer not equipped with air brakes. Type TL
inspection station inspection bays shall be at least 12 feet wide and at least
60 feet long. This area may be outside.
C. If the inspection bay cannot be cleared for an inspection at
the time a vehicle is presented, an appointment shall be given to accommodate
an inspection of the vehicle within three business days of the request for
inspection.
D. All inspection areas of an authorized station shall be at the
same location of the premises of the business establishment.
.06 Inspection Area Requirements.
A. An inside inspection area shall have a smooth, level
hard-surfaced concrete or cement floor which:
(1) Shall have no more than a 1 percent slope from front to
rear, rear to front, or side to side;
(2) May not have a four-way slope;
(3) Shall be free of permanently located workbenches, displays,
machinery, stairways, shelves, car washing equipment, or any other obstructions
which would create a hazard; and
(4) Shall have an entrance that will allow a vehicle of the
authorized class to enter the inspection bay for inspection.
B. An outside inspection bay shall have a level surface that is
capable of being used to lift and support the applicable type of vehicle the
station is authorized to inspect which shall be free of permanently located
equipment or other obstructions that would create a hazard or prohibit the
parking of the vehicle in the area in any manner.
C. Type A, C, or R inspection stations shall be designed and
equipped with two convex mirrors viewable from the driver position, a minimum
of 12 inches in diameter each, one mounted facing forward from the rear to
observe the rear lights of a vehicle, and one facing rearward to observe the
front lights of a vehicle in the inspection bay. Alternatively, mirrors may be
mounted on portable stands to be appropriately positioned during inspection.
Oversize mirrors positioned to provide the same viewing areas are also
acceptable.
D. Type A inspection stations shall be equipped with:
(1) A vehicle lift that has frame lift capability capable of
raising vehicles, except for oversized vehicles, at least 5 feet off the floor;
and
(2) A jack and jack stands capable of lifting and supporting
oversized vehicles too large for the frame contact lift to accommodate.
.07 Inspection Tools and Equipment.
A. Station applicants and station licensees shall have the
following tools, equipment, and reference specification materials approved by
the Division, except as specified in this regulation:
(1) Two jack stands, capable of supporting the types of vehicles
subject to inspection;
(2) One roller floor jack, capable of lifting the types of
vehicles subject to inspection; and
(3) One window tint meter meeting the following requirements
which shall be maintained on the ASED website (not required for Type T, M, or
TL):
(a) Manufactured as a two-piece device, portable and compact,
with digital readout to the nearest percent;
(b) Suitable for measuring standard automotive glazing on
roll-down and fixed windows;
(c) Designed to be operated by one person;
(d) Equipped with an alignment aid feature to assist in
obtaining and maintaining accuracy throughout measurement;
(e) Equipped with an activation switch or button, off switch or
button, or self-deactivation;
(f) Equipped with the manufacturer’s reference sample
calibration standards that are labeled with the manufacturer’s name, serial
number (if equipped), and percentage of light transmittance; and
(g) Equipped with a light transmittance meter which shall
maintain unit accuracy within plus or minus 2 percentage points (certified by
an independent testing laboratory):
(i) Designed to maintain repeatability within plus or minus 1
percentage point; and
(ii) Manufacturers shall provide information to the Division
regarding any change in specifications of any approved products used for tint
inspection and certification in Maryland.
(4) Reference material for the appropriate type of station:
(a) Brake specifications Type A, Type C, and Type R stations,
current by July 1st of the year;
(b) Ball joint specifications Type A, Type C, and Type R
stations, current by July 1st of the year;
(c) Emission guide specifications Type A, Type C, and Type R
stations, current within 2 years by July 1st of the year;
(d) Tire guide specifications Type A station, current by July
1st of the year;
(e) The required specifications may take the form of a printed
or electronic reference source from a computerized system, provided the
reference material contains required specifications by July 1st of that year;
and
(f) Type F stations shall have the appropriate specification
reference material for the types of vehicles the station is licensed to
perform.
B. The following tools and equipment approved by the Division
shall be available as specified in this regulation.
(1) A disc brake measuring tool, with a pointed anvil, capable
of accurately measuring for the appropriate type of vehicle, the thickness of
discs or rotors in increments of at least 0.001 of an inch or 0.0254 of a
millimeter;
(2) One disc measuring tool calibration gauge or standard
compatible with the brake disc measuring tool;
(3) A drum brake measuring tool, capable of accurately measuring
for the appropriate type of vehicle the inside diameter of brake drums in
increments of at least 0.001 of an inch or 0.0254 of a millimeter;
(4) One drum measuring tool calibration gauge or standard
compatible with the brake drum measuring tool;
(5) One brake disc pad thickness gauge, capable of accurately
measuring for the types of vehicles subject to inspection, in fractions of an
inch, or decimals of millimeters, the remaining usable bonded brake disc pad
lining or the thickness of brake disc pad lining remaining above rivet heads;
(6) One brake shoe lining thickness gauge, capable of accurately
measuring, for the types of vehicles subject to inspection, in fractions of an
inch, or decimals of millimeters, the remaining usable bonded brake lining or
the thickness of brake lining remaining above rivet heads;
(7) One dial indicator with an adjustable mount, capable of
accurately measuring ball joint or kingpin movement in increments of 0.001 of
an inch or 0.0254 of a millimeter (not required for Type T or TL);
(8) One tire tread depth gauge, capable of accurately measuring
tire tread depth 1/32 of an inch or 0.79375 of a millimeter;
(9) One tire pressure gauge, capable of measuring air pressure
in pounds per square inch (psi), or kilopascal (kPa), for type of vehicle being
inspected;
(10) One minimum 25-foot, or 7.62-meter tape measure, with
clearly legible SAE or metric figures and markings; and
(11) Miscellaneous hand tools necessary to perform mechanical
disassembly of vehicle components to conduct inspections, including one
screwdriver, capable of spreading tire cuts and breaks to determine severity of
damage.
C. Care, Calibration, and Certification of Inspection Tools and
Equipment.
(1) Inspection tools and equipment shall be maintained in proper
working order at all times.
(2) Inspection tools and equipment shall be kept together and
available for use within close proximity to the inspection bay.
(3) Inspection tools and equipment requiring calibration shall
be calibrated as required by the manufacturer, or a minimum of once each month,
whichever is more frequent.
(a) The on-site licensee or designated supervisor of the
inspection station shall ensure that inspection tools and equipment calibration
is performed by a licensed inspector as required in §(5) of this regulation.
(b) The calibration of inspection tools and equipment owned or
used by an inspector is the responsibility of the inspector who owns or uses
the tool or equipment for inspections.
(4) The calibration and certification data specified in this
regulation shall be:
(a) Recorded with respect to the calibration date specified in
§C(3) of this regulation, in a format designated by the Division;
(b) Made available to Division personnel;
(c) Retained for at least 1 year or until released by the
Division; and
(d) Supplied to Division personnel at the time of the station
progress check, or upon request of a Division representative.
(5) The calibration and maintenance of the tools and equipment
required in this regulation is the responsibility of the inspector utilizing
the tools and equipment. Any required tools and equipment used for regulated
functions within the station are subject to the same requirements regardless of
the actual ownership.
(6) Maryland manufacturers, second-stage manufacturers, or
authorized dealers:
(a) May calibrate the standard automotive air pressure gauge
specified in §G(1) of this regulation daily;
(b) Shall certify the standard automotive air pressure gauge
specified in §G(1) of this regulation at least semiannually; and
(c) Shall certify the scale or scales specified in §G(2) of this
regulation at least semiannually.
D. Inspectors may use personal tools and equipment or inspection
station-owned inspection tools and equipment provided that sufficient
quantities of inspection tools and equipment are available at all times for the
number of inspectors employed at the station.
E. The Division may add or delete inspection tools and equipment
from those set forth in this regulation by notifying inspection stations.
Inspection stations are required to obtain the additional equipment within 90
days of the official notification.
F. If any inspection tool or equipment is found to be
inoperative, and there are no other approved tools or equipment available
within the station, the supervisor shall have the equipment repaired or
replaced within 72 hours. During this time, access to MSIS shall be suspended.
Other issued materials may be retained by the inspection station. Vehicle
inspections shall not be performed. SEROs not requiring the use of the
inoperative tool or equipment may be inspected and certified if found to be
compliant with the applicable regulations.
(1) If the inoperative equipment or tool is repaired or replaced
within 72 hours, access to the MSIS shall be reinstated.
(2) If the equipment or tool is not repaired or replaced within
72 hours, access to the MSIS shall remain suspended. The inspection station
shall remove the inspection station sign from public view. All other issued
materials shall be retained by the inspection station. During this period, no
inspections or repair order certifications may be performed.
(3) If the equipment or tool is not repaired or replaced within
a total of 90 days, the inspection station license shall be canceled and all
issued materials returned to the Division, except where a valid backorder
receipt is in evidence. If the tool is not replaced within 6 months the station
license will be canceled.
G. Maryland manufacturers, second-stage manufacturers, or
authorized dealers operating in COMAR 11.15.27.08 and State-operated weight
facilities shall be equipped with a:
(1) Standard automotive air pressure gauge as specified by the
State Police in concurrence with the Maryland Department of Transportation; and
(2) Scale or scales capable of accurately measuring the weight
of a lift axle on a vehicle equipped with a lift axle.
.08 Licensing Agreements.
A. Licensure as an inspection station is contingent upon
compliance with the regulations contained in COMAR 11.14, and the licensee:
(1) Agrees to act in the best interest of the State and the
general public and comply with these regulations and procedures of the
Division;
(2) Acknowledges that actions or obligations of the inspection
station are the direct responsibility of the inspection station licensee or the
designated inspection station supervisor as stipulated in Regulation .03B of
this chapter;
(3) Acknowledges that the inspection station supervisor has the
responsibility and the authority within the business operation to supervise all
activities related to the inspection program;
(4) Acknowledges that properly licensed inspectors assigned to
the station are the only personnel allowed to perform vehicle inspections or
inspection of defects identified on a SERO;
(5) Acknowledges that reference to actions or obligations of the
inspection station have the same meaning and responsibilities as that of
licensee or supervisor, as applicable to the inspection station;
(6) Acknowledges that the license may be revoked, suspended, or
refused for the reasons provided in these regulations and, upon revocation,
suspension, or refusal, the inspection station shall surrender the license and
all related materials issued or supplied by the Division;
(7) Acknowledges that the Division reserves the right, in the
interest of public safety and in determining compliance with the subtitle, to
conduct covert vehicle inspections at inspection stations;
(8) Acknowledges that noncompliant action taken by inspection
station personnel during a covert vehicle inspection is subject to the same
administrative penalties as during an actual vehicle inspection;
(9) Acknowledges that all vehicles presented shall be fully
inspected to satisfy the requirements of these regulations, and that
certification shall not be applied to a vehicle unless:
(a) A vehicle inspection for the purpose of registration in the
State of Maryland, or required to satisfy any other Maryland law or regulation,
shall have all regulated and approved equipment inspected;
(b) A vehicle reinspection due to rejection during a previous
inspection shall have all rejected equipment and any observed non-compliant
equipment inspected; and
(c) A vehicle inspection for the purpose of certification of a
SERO or Notice of Suspension shall have all the non-compliant equipment
identified on the order inspected; and.
(10) Acknowledges that the “Vehicle
Safety Inspection Bulletins” supply interpretation of a regulation, or provide
guidance for procedures related to the vehicle safety inspection program for
specific circumstances not covered by the Vehicle Inspection Handbook; and
(11) Acknowledges that the “Vehicle
Safety Inspection Bulletins” are posted online and shall be referenced as
required.
B. The licensee or their representative shall create and
maintain an account in the MSIS after being placed active by the Division and
acknowledges that:
(1) Electronic certification of vehicle inspection shall only be
performed by the licensed inspector who performed the inspection under the
unique login and password that electronically identifies the person in the
MSIS; and
(2) The unique login and password that electronically identifies
individual station personnel in the MSIS shall be protected and shall not be
shared or otherwise revealed to anyone other than the person authorized under
the unique login and password.
C. The licensee or their representative acknowledges that access
to the MSIS may be denied for revocation or suspension of the station license,
and if applicable, for non-payment of the account until the account is made
current.
(1) Access to MSIS will cease upon the inspection station
license being canceled, or the inspection station being placed inactive.
(2) Access to MSIS records for a business denied access shall
require submission of a request for specific records to the Division.
D. Licensure as an inspector is contingent upon compliance with
the regulations contained in COMAR 11.14, and the licensed inspector:
(1) Agrees to act in the best interest of the State and the
general public and comply with these regulations and procedures of the
Division;
(2) Acknowledges that the inspection station supervisor has the
responsibility and the authority within the business operation to supervise all
activities related to the inspection program;
(3) Acknowledges that the licensed inspector shall create and
maintain an account in the MSIS after being placed active by the Division and
that:
(a) Electronic certification of vehicle inspection shall only be
performed by the licensed inspector who performed the inspection under the
unique login and password that electronically identifies that person in the
MSIS;
(b) The unique login and password that electronically identifies
the licensed inspector in the MSIS shall be protected, and shall not be shared
or otherwise revealed to anyone other than the licensed inspector authorized
under the unique login and password; and
(c) Access to the MSIS may be denied
by the inspection station due to termination of employment or other business
requirements of the facility;
(4) Acknowledges that the inspector license may be
revoked, suspended, or refused for falsification of facts or noncompliance with
any of these regulations.
(5) Acknowledges that the Division reserves the right, in the
interest of public safety and in determining compliance with the subtitle, to
conduct covert vehicle inspections;
(6) Acknowledges that noncompliant action taken by inspection
station personnel during a covert vehicle inspection is subject to the same
administrative penalties as are during actual vehicle inspection;
(7) Acknowledges that all vehicles presented shall be fully
inspected to satisfy the requirements of these regulations, and that
certification shall not be applied to a vehicle unless:
(a) A vehicle inspection for the purpose of registration in the
State of Maryland, or required to satisfy any other Maryland law or regulation,
shall have all regulated and approved equipment inspected;
(b) A vehicle reinspection due to rejection during a previous
inspection shall have all rejected equipment and any observed non-compliant
equipment inspected; and
(c) A vehicle inspection for the purpose of certification of a
SERO or Notice of Suspension shall have all non-compliant equipment identified
on the order inspected; and
(8) Acknowledges that all materials
issued by the Division, along with access to MSIS shall be denied if licensure
as an inspector is revoked, suspended, or refused for falsification of facts or
any other noncompliance with the regulations of this subtitle.
.09 Obligations of Inspection Stations and Inspectors.
A. Inspections.
(1) The inspection station shall have an inspector perform an
inspection of a vehicle presented for inspection. If an inspection cannot be
performed when a vehicle is presented, an appointment shall be set for no more
than 3 business days from the date the vehicle is presented, and a scheduled
appointment shall be honored.
(2) Upon completion of a failed vehicle inspection, a Maryland
State Vehicle Safety Inspection Receipt shall be provided listing all rejected
equipment.
(3) Upon completion of a passed vehicle inspection, a Maryland
State Vehicle Safety Inspection Receipt shall be provided.
(4) Upon request for any inspection, a complete Maryland State
Vehicle Safety Inspection Report of all equipment inspected shall be provided
to the person who presented the vehicle for inspection.
B. Inspection of Previously Rejected Equipment.
(1) A vehicle rejected during an initial inspection is subject
to another inspection after repairs have been made before a certification of
inspection may be submitted. A rejected vehicle shall be re-inspected within 30
days and within 1,000 miles of the initial inspection or the vehicle is
ineligible to continue the previous inspection process and a new, separate
inspection shall be performed. A prorated fee may be charged for inspection of
equipment requiring lifting or disassembly to be inspected, based upon the
inspection fees shown in §I of this regulation. If the vehicle cannot be
re-inspected on the day presented, an appointment shall be scheduled within 3
business days of the day the vehicle was presented for re-inspection.
(a) If a vehicle is presented for inspection of previously
rejected equipment, the inspector who performed the initial inspection shall
re-inspect the rejected equipment, and any equipment visually observed, that
fails to meet minimum safety standards.
(b) The inspector may charge a prorated fee, if applicable for
the requested re-inspection.
(2) If the inspector who performed the initial inspection is not
available, another licensed inspector at the station shall perform a new
vehicle inspection. The prorated fee, which would have been applicable for the
requested re-inspection, may be charged.
(3) If there is not a licensed inspector available at the
inspection station to perform a new pro-rated inspection, the original
inspection fee shall be immediately refunded to the owner or agent for the
vehicle.
(4) If the facility's inspection station license is suspended or
revoked, the initial inspection fee shall be refunded to the owner or agent for
the vehicle.
(5) If the inspector’s license is suspended or revoked, the
initial inspection fee shall be refunded to the owner or agent for the vehicle.
C. Inspection and Certification of SERO, and Notice of
Suspension.
(1) The inspection station shall have an inspector perform a
complete inspection of the defective equipment which is indicated on a SERO.
Certification of a SERO shall only be completed after the rejected equipment
has been inspected for compliance with the applicable regulations for minimum
safety standards.
(2) The inspection station shall have an inspector perform a
complete inspection of the defective equipment which is indicated on a Notice
of Suspension issued to a vehicle. Certification of a Notice of Suspension
shall only be completed after the rejected equipment has been inspected for
compliance with the applicable regulations for minimum safety standards.
(3) Certification of a fictitious SERO as defined in Regulation
.01B(13) of this chapter or any other document approved, issued, or required by
the Division; that is an authentic document, prepared by Division personnel,
containing information that may be fabricated for the purpose of submission for
inspection and compliance is subject to the same administrative penalties as an
official document. The inspection station or the inspection station personnel
may not use as a defense, to a charge of violating any provision of this
subtitle, that a fictitious document was presented to the inspector as part of
a covert vehicle inspection.
D. The inspection station shall have available for use by all
inspection personnel the Vehicle Inspection Handbook.
E. The inspection station shall permit only inspectors to
perform inspections and only within the inspection bays. Certification of defects on SEROs may be
performed outside the inspection bays but only on the premises of the business.
F. The inspection station shall notify the Division of any of
the following circumstances, and may be required to cease all
inspection-related activities until authorized to resume by the Division:
(1) Loss of an inspector for any reason and no other inspector
is actively employed at the station;
(2) Change in ownership, partnership, corporate representatives,
or trade name;
(3) Change in location of the facility;
(4) Any remodeling or significant change to the inspection bays
which shall be subject to Division approval;
(5) Request to cancel the license or application for license; or
(6) Any circumstance which prevents an inspection, the
certification of an inspection, or the certification of a repair order.
G. Notifying the Division.
(1) The Division shall immediately be notified of the following
circumstances:
(a) Change of inspection or supervisory personnel;
(b) Stolen, lost, or damaged sign, or records pertaining to
inspection;
(c) Arrest or conviction of station personnel for any crime;
(d) Arrest or conviction of any motor vehicle laws, causing
restrictions to be imposed on their driver's license, or loss of driving
privileges of any inspector, including the issuance of a temporary license
resulting from a DUI arrest;
(e) Any circumstance which may affect an inspector’s ability to
conduct inspections, certify inspections or SEROs;
(f) The VIN is illegible or any indication of tampering is
present;
(g) Any unauthorized access or use of MSIS is detected or
suspected; or
(h) Any absence of inspection station personnel which would
result in the inability of the inspection station to perform inspection-related
activities for a period of time that exceeds 5 business days:
(2) The inspection station representative shall notify the
Division immediately if the inspection station does not employ a licensed
inspector to perform inspections on the type of vehicle or vehicles that the
inspection station is authorized to inspect. If the inspection station does not
employ an inspector, the inspection station shall remove the inspection station
sign from public view, cease all vehicle safety inspection activities, and the
inspection station status in MSIS shall be placed inactive by the Division.
H. The inspection station shall prominently display, so that it
may be read by the public, the following Division issued and required items:
(1) Inspection station sign:
(a) The inspection station, when applicable, shall display the
issued authorized inspection station sign on the property in a manner, visible
to the public on the main thoroughfare where the business is located;
(b) An inspection station sign may not be displayed other than
at a licensed inspection station;
(c) An inspection station sign may not be duplicated; and
(d) A facsimile or likeness of an inspection station sign shall
not be displayed by an unlicensed facility;
(2) The inspection procedure chart in a frame and under clear
glass or plastic; and
(3) The approved inspection fees list in a frame and under clear
glass or plastic.
I. Inspection Fees.
(1) A licensed inspection station open to the public may
establish a fee for a complete inspection based on the times listed in this
section at the hourly rate charged for similar mechanical repairs. When
additional disassembly is directed or required by the regulations contained in
this subtitle to complete an inspection, appropriate fee increases may be
authorized:
(a) Motor vehicles 10,000 pounds and under GVWR with 2 axles—1.5
hours;
(b) Motor vehicles 10,000 pounds and under GVWR with 2 axles
which require bearing or axle removal to inspect brakes—1.5 hours, and add 0.5
hours for each wheel position removed;
(c) Motor vehicles over 10,000 GVWR with 2 axles equipped with
hydraulic brakes, and which do not require bearing or axle removal to inspect
brakes—1.5 hours, and add 0.5 hours for each wheel position equipped with dual
wheels which are removed;
(d) Motor vehicles over 10,000 pounds GVWR with 2 axles which
require bearing or axle removal to inspect brakes—3.0 hours, and add 0.5 hours
for each additional axle wheel position removed;
(e) Motor vehicles over 10,000 GVWR with 2 axles equipped with
air brake systems that do not require disassembly to inspect brake components—2.0
hours, and add 0.25 hours for each additional axle;
(i) With outboard brake drums or disc brakes requiring
disassembly add 0.5 hours for each axle wheel position removed; and
(ii) With inboard brake drums requiring bearing or axle
disassembly add 1.0 hour for each axle wheel position removed;
(f) Trailers under 10,000 pounds GVWR without brakes—0.5 hours;
(g) Trailers under 10,000 pounds GVWR with brakes—1.0 hour and
add 0.5 hours for each additional axle;
(h) Trailers over 10,000 pounds GVWR with 2 axles;
(i) Without air brakes with outboard brake drums or disc brakes—1.0
hour and add 0.5 hours for each additional axle;
(ii) With inboard brake drums requiring bearing or axle
disassembly—2.0 hours and add 0.5 hours for each wheel position removed;
(iii) Trailers with air brake systems that do not require
disassembly to inspect brake components—1.25 hours, and add 0.25 hours for each
additional axle;
(iv) Trailers with air brake systems equipped with outboard
brake drums or disc brakes requiring disassembly add 0.25 hours for each wheel
position removed; and
(v) Trailers with air brake systems equipped with inboard brake
drums requiring bearing or axle disassembly add 1.0 hour for each wheel
position removed;
(i) Motorcycles:
(i) Motorcycles with 2 wheels—0.75 hours and add 0.5 hours for
each wheel position required to be removed; and
(ii) Motorcycles with 3 wheels—1.0 hour;
(j) School vehicle inspections required by the Motor Vehicle
Administration shall have all wheel positions disassembled for inspection,
measurement, and recording of brake component readings. Inspection Fees shall
be based upon the hourly rate established in this regulation;
(k) Vehicles with post manufacture window tint applied to
windows required to meet at least 35 percent light transmittance and compliant
with all other post manufacture window tinting regulations under this subtitle—0.2
hours of hourly rate in addition to applicable inspection fees established
under this section; and
(l) Vehicles with petroleum-powered auxiliary equipment subject
to inspection—0.2 hours of hourly rate for each type of auxiliary equipment in
addition to applicable inspection fees established under this section.
(2) A vehicle rejected during an initial inspection is subject
to a reinspection after repairs have been made before a certification of
inspection may be submitted. A prorated
inspection fee may be charged for the reinspection of those defects requiring
jacking, lifting, or measuring to perform the inspection procedure. Defects
that are repaired during the initial inspection may not be charged a
reinspection fee but may be charged for the repair with the approval of the
owner/agent for the vehicle. An inspection fee, if charged, will be based on
defects inspection as set forth in this regulation. However, an additional fee
may not be charged for the reinspection of those defects that may be visually
inspected and do not require the use of inspection equipment.
(3) SERO Certification Procedures. Certification of a fictitious
SERO as defined in Regulation .01B(13) of this chapter is subject to the same
administrative penalties as an official document. A fee for certification of
defects on a SERO may be charged as follows and based on the prevailing hourly
labor flat rate at the inspection station. Those defects that can be merged
shall be charged at the single highest rate, for example, tires and steering,
0.2 hours of the facility's hourly labor flat rate, or tires and wheel
alignment, 0.3 hours of the facility's hourly labor flat rate. The inspection
fee for multiple defects that can be merged may not be higher than the highest
single time increment. Those which cannot be merged may be charged separately
provided the total inspection fee is not exceeded. The inspection and
certification for the defect “tint” for a vehicle that has had the tint
removed, and therefore does not require the use of a window tint meter shall be
performed without charge by an inspection station or by a police officer of an
agency participating in the SERO program. An inspection fee may not be charged
for the certification of a SERO with defects that may be visually inspected.
These visual defects are noted with an asterisk on the SERO and do not require
the use of inspection equipment. The inspection station may establish a fee for
certification of a SERO that cannot be visually inspected based on the
following fee charged for inspections:
(a) Defect #50 Brakes.
(i) Vehicles requiring wheel removal—0.5 hours of the facility's
hourly labor rate per axle for removing each wheel and inspecting the brakes on
each axle;
(ii) Vehicles under 10,000 pounds GVWR that require bearing or
axle removal to inspect brakes—0.5 hours of the facility's hourly labor rate
per wheel position;
(iii) Vehicles over 10,000 pounds GVWR that require bearing or
axle removal to inspect brakes—0.75 hours of the facility's hourly labor rate
per each wheel position; and
(iv) Vehicles with air brakes not requiring wheel removal for
inspection—0.5 hours of the facility's hourly labor rate per axle.
(b) Other defects:
(i) Defect #51 Tires—0.2 hours of the facility's hourly labor
rate per axle;
(ii) Defect #52 Steering—0.2 hours of the facility's hourly
labor rate;
(iii) Defect #53 Exhaust system—0.3 hours of the facility's
hourly labor rate;
(iv) Defect #54 Windshield wipers*;
(v) Defect #55 Headlights*—0.3 hours of the facility's hourly
labor rate to check for aim, and an additional 0.1 hours may be added if an
adjustment is needed;
(vi) Defect #56 Tail lights*;
(vii) Defect #57 Horn*;
(viii) Defect #58 Driver's seat—0.2 hours of the facility's
hourly labor rate;
(ix) Defect #59 Suspension/shocks — 0.2 hours of the facility's
hourly labor rate per axle;
(x) Defect #60 Bumper or bumpers*;
(xi) Defect #61 Glass* Tint—0.2 hours of the facility’s hourly
labor rate to measure the light transmittance of windows equipped with post
manufacture window tint that is required to have at least 35 percent light
transmittance that is compliant with post manufacture window tinting
regulations under this subtitle, excepting the light transmittance of the
window;
(xii) Defect #62 load cover*;
(xiii) Defect #64 stop lights*;
(xiv) Defect #65 tag light or lights*;
(xv) Defect #66 dash lights*;
(xvi) Defect #67-wheel alignment—0.3 hours of the facility's
hourly labor rate per axle;
(xvii) Defect #68 rearview mirrors*;
(xviii) Defect #69 door latch or door handle*;
(xix) Defect #70 fuel system—0.2 hours of the facility's hourly
labor rate, except fuel cap*;
(xx) Defect #71 turn signals*;
(xxi) Defect #72 wheel or wheel lugs—0.2 hours of the facility's
hourly labor rate per axle;
(xxii) Defect #73 hood catch or hood catches*;
(xxiii) Defect #74 floor/trunk pan or pans—0.2 hours of the
facility's hourly labor rate;
(xxiv) Defect #76 fenders or flaps*;
(xxv) Defect #77 speedometer/odometer—0.2 hours of the
facility's hourly labor rate;
(xxvi) Defect #78 hazard warning lamps*;
(xxvii) Defect #79 parking lamps*;
(xxviii) Defect #80 side marker lamps*;
(xxix) Defect #81 fog/auxiliary lamps*—0.3 hours of the
facility's hourly labor rate to check for aim; and an additional 0.1 hours may
be added if an adjustment is needed;
(xxx) Defect #82 emergency warning lamps*;
(xxxi) Defect #83 back-up lamp or lamps*;
(xxxii) Defect #84 reflectors*;
(xxxiii) Defect #85 external air brake components—0.3 hours of
the facility's hourly labor rate per axle;
(xxxiv) Defect #86 low air warning device*;
(xxxv) Defect #87 clearance lamp*;
(xxxvi) Defect #88 identification lamps*;
(xxxvii) Defect #89 safety belts—0.3 hours of the facility's
hourly labor rate;
(xxxviii) Defect #90 lift axle air/weight ratio—0.5 hours of the
facility's hourly labor rate per lift axle; and
(xxxix) Defect #91 diesel emission—0.5 hours of the facility's
hourly labor rate.
(4) Any type of inspection station open to the public may
certify any defect on a SERO that is indicated as visually certifiable. Defects
that can be visually certified are indicated by an asterisk after the defect on
a SERO and as indicated above.
(5) A request for an inspection fee increase shall be submitted
in a format approved by the Division and shall not be charged until the request
is approved by the Division.
(6) No inspection fee may be charged without the associated
record of the inspection being on file as applicable to the station's
inspection reporting and certification process.
J. Division personnel shall have access to the inspection
station facilities, inspection areas, all required records, and inspection
station personnel during regular business hours to ensure the integrity of the
vehicle safety inspection program.
K. A fictitious SERO as defined in Regulation .01 B(13) of this
chapter or any other document approved, issued, or required by the Division;
that is an authentic document, prepared by Division personnel that contains
information that may be fabricated for the purpose of submission for inspection
and compliance is subject to the same administrative penalties as an official
document. The inspection station or the inspection station personnel may not
use as a defense, to a charge of violating any provision of this subtitle, that
a fictitious document was presented to the inspector as part of a covert
vehicle inspection.
.10 Obligations of Maryland Manufacturers, Second-Stage
Manufacturers, and Dealers.
A. Maryland manufacturers, second-stage manufacturers, or
authorized dealers certifying SEROs under COMAR 11.15.27 are responsible for
supplying a list of individuals authorized to certify SEROs to ASED and shall
notify ASED of changes to the list within 10 days.
B. Fees for inspection or certification of SEROs under COMAR
11.15.27 shall meet the requirements for approved fees listed in Regulation .09
of this chapter.
.11 Records.
A. Vehicle inspection records are maintained electronically in
MSIS for each station. Each inspection station shall create and maintain a
pre-numbered or electronically generated shop management work order that
cross-references an internal work order to the inspection, or any
inspection-related repair action performed by the station, and have those work
orders available to the Division for at least 1 year. Other vehicle inspection
information shall be maintained for each vehicle inspection as follows:
(1) Station copies of completed Post Manufacture Window Tint
Inspection Reports shall be maintained for at least 1 year from the date of
certification;
(2) Station copies of completed Division issued Post Manufacture
Window Tint Medical Exemption Forms shall be maintained for at least 1 year
from the issue date of the form;
(3) Station copies of completed Division issued Physical
Disability Medical Exemption Inspection Vehicle Equipment Forms shall be
maintained for at least 1 year from the issue date of the form; and
(4) The Division may require the inspection station to maintain
certain other administrative records pertaining to the inspection process.
B. Vehicle Inspection Data.
(1) The Inspector shall accurately record the required owner or
owner’s agent information, the specific vehicle identification and information,
and the status of the vehicle equipment at the time of inspection in MSIS for
each vehicle safety inspection.
(2) All vehicle inspection data shall be entered in MSIS by the
licensed inspector who performed the inspection under their unique MSIS login.
(3) MSIS automatically saves all the data for each inspection,
and the status of the vehicle equipment at the time of inspection.
(4) MSIS may generate a complete record of the inspection upon
request.
C. Permission shall be obtained from the vehicle owner/agent
before any repair resulting from an inspection is performed at the authorized
inspection station. If any such repair work over $50 is necessary, this
permission should be in writing. All the requirements of the auto repair
facilities law, Commercial Law Article, Title 14, §10, Annotated Code of
Maryland, shall be complied with by each authorized inspection station.
.12 Vehicle Sale or Transfer of Ownership.
A. An inspection is required when a used vehicle is sold or
ownership is transferred or when a used vehicle is to be titled and registered
in the State. As requested by a vehicle owner, the owner's agent, or dealer, an
inspector at an inspection station shall perform a complete inspection, as set
forth in this subtitle.
B. An inspection is not required for:
(1) Sales or transfers of used vehicles to a licensed or foreign
dealer;
(2) Sales or transfers accompanied by a signed statement by the
purchaser or transferee that the sale or transfer is made for rebuilding, as
defined in Regulation .01B(35) of this chapter, or dismantling the vehicle;
(3) Transfers between spouses or former spouses when the
transfer occurs as a result of a settlement or court order predating the
divorce;
(4) Transfers between parent and child;
(5) Transfers of co-owned vehicles when a co-owner's name is
being removed from the title;
(6) Sales or transfers of used vehicles which are not to be both
titled and registered in the State;
(7) Transfers of used vehicles among State agencies;
(8) Transfers of used vehicles as described in Transportation
Article, §13-503.2, Annotated Code of Maryland;
(9) The transfer of a used vehicle into a written inter vivos
trust in which the transferor is the primary beneficiary;
(10) The transfer of a used island vehicle, as defined in
Transportation Article, §13-935, Annotated Code of Maryland, registered, or to
be registered, as a Class K (farm area/island) vehicle; or
(11) The transfer of a leased used vehicle to the lessee at the
end of the lease term.
C. If a used vehicle is transferred other than by voluntary
transfer or is transferred by a political subdivision of the State after that
subdivision obtains the vehicle by proceedings under Criminal Procedure
Article, Title 12, Annotated Code of Maryland, the transferee shall obtain the
inspection certificate from an authorized inspection station.
.13 Inspection Certification.
A. Upon successful completion of an inspection of a vehicle that
has met or exceeded minimum safety standards as set forth in these regulations,
and before the vehicle leaves the licensed inspection station, the inspector
who performed the inspection shall certify the vehicle by accurately and
factually recording all data required in a format established by the Division.
(1) The inspection certification shall include the following
vehicle information;
(a) The VIN, either the manufacturer's or if applicable, a
state-assigned VIN obtained from the vehicle;
(b) The model year of the vehicle;
(c) The make (manufacturer name) of the vehicle;
(d) The model of the vehicle;
(e) The major color of the vehicle;
(f) The odometer reading obtained from the vehicle at the
beginning of the inspection; and
(g) The odometer reading obtained from the vehicle on the date
of certification of the inspection.
(2) The inspection certification may be electronically
transmitted, or printed and supplied to the owner or agent of the vehicle.
(3) The inspection certification shall be electronically
transmitted to the Administration by MSIS when submitted by the Inspector.
B. The inspection certification shall remain valid for 90
calendar days from the date of the vehicle inspection certification.
C. An inspection certification for a used vehicle owned and held
in inventory by a dealer licensed under Transportation Article, Title 15,
Annotated Code of Maryland, shall remain valid for 6 months or 1,000 miles from
the date of certification, whichever occurs first.
D. A vehicle titled and registered with the Administration may
be transferred and retitled to another owner within 30 days from the date of
the inspection certification without another inspection certification being
performed.
.14 Safety Equipment Repair Orders (SERO).
A. Hand Written SERO. The vehicle owner/agent shall present the
No. 3, 4, and 5 copies of the SERO to an inspection station, or to a police
officer, as applicable. If the defects have been corrected and meet or exceed
established safety standards, the inspector, or police officer shall complete,
sign, and certify the SERO using the method required for SERO inspection
certification contained in Regulation .09 of this chapter in the space provided
and copies shall be distributed as follows:
(1) Number 3 (inspection station/police department) copy—may be
retained on file as required;
(2) Number 4 (owner/agent) copy—returned to the vehicle/agent
for his records; and
(3) Number 5 (State Police compliance copy— returned to the
vehicle owner/agent to be forwarded to the Division.
(4) Important instructions for the vehicle owner and authorized
inspection station are on the reverse sides of the owner's and inspection
station copies.
B. Electronic Safety Equipment Repair Order (E-SERO). The
vehicle owner/agent shall present both part 1 Vehicle Owner/Agent copy and part
2 State Police Compliance copy of the E-SERO to an inspection station, or
police officer, as applicable. Important instructions for the vehicle owner and
licensed vehicle inspector are on part 2 of the E-SERO. If the defects have
been corrected and meet or exceed established safety standards, the inspector,
or police officer shall complete, sign, and certify the E-SERO using the method
required for inspection certifications contained in Regulation .09 of this
chapter in the space provided and copies shall be distributed as follows:
(1) Part 1, Vehicle Owner/Agent Copy—returned to the vehicle
owner/agent for their records; and
(2) Part 2, State Police Compliance Copy—returned to the vehicle
owner/agent to be forwarded to the Division.
C. If a notice of suspension is presented for certification, the
procedures set forth in §A of this regulation will apply and the copies shall
be distributed as follows:
(1) Letter, white copy—returned to vehicle owner/agent to be
forwarded to the Division;
(2) Yellow, inspection station/police department copy—may be
retained on file as required; and
(3) Goldenrod, owner/agent copy—returned to vehicle owner/agent.
D. A dump service registration vehicle registered under COMAR
11.15.27 that receives a SERO for an inaccurate lift axle air/weight ratio
shall be inspected during normal business hours by:
(1) A Maryland manufacturer;
(2) A Maryland second-stage manufacturer;
(3) An authorized dealer; or
(4) A State-operated weight facility.
E. A vehicle owner/agent receiving a SERO under COMAR
11.15.27.08C shall present for certification the No. 3, 4, and 5 copies of the
SERO to:
(1) A Maryland manufacturer;
(2) A Maryland second-stage manufacturer;
(3) An authorized dealer; or
(4) A State-operated weight facility.
F. A diesel vehicle as defined in COMAR 11.21.02.01 that
receives a SERO for violating emissions standards under COMAR 11.21.02.06 shall
be inspected during normal operating hours by:
(1) A Maryland emissions inspector; or
(2) A diesel emissions inspector in Maryland as required in
COMAR 11.21.02.08.
G. A vehicle owner/agent receiving a SERO under COMAR 11.21.02
shall present for certification copies 3, 4, and 5 of the SERO to a:
(1) Maryland emissions inspector; or
(2) A diesel emissions inspector in Maryland as required in
COMAR 11.21.02.08.
.15 Suspension of Vehicle Registration.
A. Whenever the owner of a vehicle fails to comply with a SERO
within the time required by law, a notice of suspension of the registration of
the vehicle shall be issued.
B. Whenever the owner of a vehicle fails to comply with a notice
of suspension that requires the registration plates to be returned to the
Administration within 10 days, a tag pick-up order shall be issued. The
registration plates are subject to confiscation by a police officer, as defined
in Transportation Article, §23-101(g), Annotated Code of Maryland, following
procedures established by the Division, and shall be forwarded to the
Administration upon confiscation.
C. The Administration, upon confirmation from ASED, or
satisfactory proof of correction of defective equipment, shall remove the order
of suspension and issue new registration plates to the owner of the vehicle if
applicable.
.16 Administrative Actions.
A. Violations of the regulations contained in this subtitle will
be investigated by the Division. The Division will provide written notification
of any sustained administrative action to the representative for the Inspection
Station License and the Licensed Inspector of record in the investigation.
(1) The written notification will contain a proposed resolution
for any sustained violation under Regulation .02 of this chapter.
(2) Failure to submit a written appeal within 30 calendar days
of receipt of the written notification of violation and the proposed resolution
will be deemed as having waived all rights to appeal, and the proposed action
shall become accepted and final.
B. Violations of the regulations contained in this subtitle that
involve critical vehicle equipment or multiple violations of the regulations as
established in Regulation .02 of this chapter shall result in emergency
suspension action in accordance with State Government Article, §10-226,
Annotated Code of Maryland if:
(1) The Division finds that the public health, safety, or
welfare imperatively requires emergency action; and
(2) The Division promptly provides the representative for the
Inspection Station License and the Licensed Inspector:
(a) Written notice of the emergency suspension which includes
the finding and the reasons that support the finding; and
(b) An opportunity to be heard in appeal.
C. Appeals will be handled in accordance with State Government
Article, §10-205, Annotated Code of Maryland, and COMAR 29.01.01.
11.14.02 Vehicle Equipment
Inspection Standards
Authority: Transportation
Article, §12-104(b), §22-104, §23-101-23-105, §24-106.1, and §25-110,
Annotated Code of Maryland
.01 Applicability.
A. The standards,
requirements, and procedures outlined in this chapter are applicable to
regulated equipment required by federal and state regulations on vehicles
registered or to be registered by the administration for on-road use that are
subject to a vehicle safety inspection. Equipment not designed for on-road
vehicle operation shall not be approved for use during on-road vehicle
operation. Equipment installed for off-road operation shall not be in use while
the vehicle is operated on-road. Any questions regarding these standards,
requirements, or procedures shall be referred to the Automotive Safety
Enforcement Division (ASED) of the State Police. Any person constructing or
reconstructing a vehicle shall ensure the vehicle meets or exceeds all applicable
Federal and State safety standards.
B. Commercial vehicles may have other specific regulations
due to the nature of their intended use and Federal Motor Carrier Safety
Administration (FMCSA) regulations contained in 49 CFR §393. The FMCSA
requirements are not fully provided by the regulations contained in this
chapter and may place additional requirements for vehicle inspections by
enforcement agencies during the operation of commercial vehicles.
C. Damage, deterioration, wear, modification, or missing
vehicle equipment that adversely impacts the proper operation and function of
the equipment shall be cause for rejection of the equipment or component.
Conditions that do not adversely impact the function of the equipment are not
cause for rejection of the equipment or component provided documented support
from the manufacturer is referenced.
D. A vehicle not
manufactured or constructed as a complete vehicle by a generally recognized
vehicle manufacturer (specially constructed vehicle) shall be required to meet
or exceed all applicable established minimum standards for a vehicle of the
same model year in which the vehicle was constructed and titled as established
in COMAR 11.14.
E. A motor vehicle
modified to enable a person with a disability to operate, or ride in as a
passenger is exempted from the “make inoperative” prohibition of 49 U.S.C.
§30122 to the extent that those modifications do not affect the motor vehicle's
compliance with the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards (FMVSS) or portions
thereof specified in 49 CFR §595.7. Modifications that would take a vehicle out
of compliance with any other FMVSS, or portions thereof, are not covered by
this exemption.
(1) A motor vehicle
that has been modified for operation by persons with a physical disability
under the authority of 49 CFR §595.7 must be equipped with the permanent label
affixed to the vehicle by the modifier which contains the statement, “This
vehicle has been modified in accordance with 49 CFR §595.7 and may no longer
comply with all FMVSS in effect at the time of its original manufacture.” The
modifier is required to supply documentation to the vehicle owner which shall:
(a) Identify the
vehicle that has been modified;
(b) Contain a list of
the FMVSS which the vehicle is no longer in compliance with;
(c) Indicate any
reduction in the load-carrying capacity of the vehicle of more than 100 kg (220
lb.) after the modifications are completed; and
(d) State whether the
weight of a user's wheelchair is included in the available load capacity.
(2) Upon the request of
a vehicle owner with a physical disability, ASED personnel shall examine the
documentation and the vehicle VIN to determine compliance with 49 CFR §595.7.
(a) If the
documentation and the vehicle label properly identify the vehicle safety
equipment that was decertified under 49 CFR §595.7 and matches the VIN of the
vehicle presented, ASED personnel shall complete the form, Physical Disability Medical Exemption for Vehicle
Equipment.
(b) The form shall be
delivered to the vehicle owner for presentation at a licensed inspection
station, to authorize an inspector to perform a modified vehicle safety
inspection of the vehicle with the decertified equipment on the form exempt
from compliance with the specified regulations. The Division shall retain a
copy of the form.
(3) A vehicle that has
been properly equipped to allow operation by persons with a physical disability
and presented with a Physical Disability Medical Exemption for Vehicle
Equipment form, issued by ASED personnel, will have all regulated equipment as
required by the regulations contained in COMAR 11.14. The decertified equipment
which has been identified by the label and documentation described in this
regulation are still subject to inspection for broken, missing, or otherwise
unsafe conditions.
F. A vehicle specially
constructed as a replica of a previously manufactured vehicle does not qualify
as a historic vehicle or a vehicle of unique interest as defined by the Motor
Vehicle Administration for registration. A vehicle as described in this regulation
shall meet all applicable established minimum standards for a vehicle of the
same model year in which the replica vehicle was actually constructed and
titled with the following exceptions.
(1) Regulation .23§C(1)
of this Chapter. If the original counterpart of the specially constructed
vehicle was manufactured without side marker lamps, side marker lamps are not
required on the replica.
(2) Regulation .12B of
this Chapter. If the original counterpart of the specially constructed vehicle
was manufactured without fenders or with fenders that do not meet current
established minimum standards, the specially constructed vehicle need only conform
to the exact design of its original counterpart to meet the requirements for
fenders.
(3) Regulation .13 of
this Chapter. If the original counterpart of the specially constructed vehicle
was manufactured without bumpers, with concealed bumpers, or with bumpers that
do not meet current established minimum standards, the specially constructed
vehicle need only conform to the exact design of its original counterpart to
meet the requirements for bumpers.
(4) Regulation
.23§A(13) of this Chapter. If the original counterpart of the specially
constructed vehicle was manufactured without a center high mounted stop lamp. A
center high mounted stop lamp is not required on the replica.
G. Recommended
procedures for the inspection of vehicles are provided in the Inspection
Procedure Chart which is established in COMAR 11.14.01.09§H(2)(a)
and issued by the Division. These procedures are guidelines rather than
required order of operations, however, performing vehicle safety inspections
following these procedures will help develop a logical system for consistency
in the vehicle safety inspection program.
H. All motor vehicles
shall be subject to a minimum of at least a one-mile road test during vehicle
safety inspections, inspections due to the issuance of a SERO, or a previous
rejection during an inspection as applicable. The steering, suspension, braking,
and handling characteristics of motor vehicles will be inspected during this
actual road operation.
I. Type 1 and Type 2
School Vehicles may have other specific regulations due to the nature of their
intended use, and as required by federal and State requirements. Type I and
Type II school vehicle construction standards are established by COMAR 11.19.02 and 11.19.03. Additional requirements for
vehicle inspection by enforcement agencies during operation of school vehicles
may be required. Any questions regarding these standards or specifications
shall be referred to the School Vehicle Safety Section of the Maryland Motor
Vehicle Administration.
J. Fluid leakage shall
be inspected and identified by class level as listed in the following table:
|
Leakage
|
Conditions
|
Actions
|
|
Class-1
|
Seepage of fluid, as indicated by
wetness or discoloration, but does not form drops
|
No Action Required
|
|
Class-2
|
Fluid leakage forms drops but does not
cause drops to fall from the item being inspected
|
Advise Owner/Agent
|
|
Class-3
|
Leakage
of fluid that causes drops to fall from the item being inspected
|
Reject
Equipment
|
K. Threaded fasteners,
shall engage the threads to ensure proper retention. This thread engagement
shall be to a depth of at least:
(1) Steel fasteners – 1
to 1 ½ times the diameter of the fastener; and
(2) Aluminum fasteners –
1 ½ to 2 times the diameter of the fastener.
.02 Steering,
Alignment, and Suspension.
A. Inspect the entire
steering system for missing, loose, damaged, or unapproved components that may
adversely affect the proper operation or function of the steering system.
Consult the applicable manufacturer’s procedures for the correct method of lifting
all vehicles for steering and suspension inspection. Motor vehicles shall be
test-driven as a part of the safety inspection to ensure that adverse or
undesirable steering or handling conditions are not present.
(1) Vehicle equipment
that has been decertified from compliance with all FMVSS, as authorized under
49 CFR §595.7, may be exempt from meeting the requirements of the regulations
specific to that equipment, provided the proper documentation from the Division
is presented with the vehicle.
(2) Steering Wheel. The
steering wheel shall be inspected to determine if it is circular (complete rim)
and free of cracks, breaks, objects, or conditions that will interfere with the
safe steering of the vehicle. The steering wheel shall be equivalent to
original equipment in material strength and diameter but shall be no less than
13 inches in diameter under any condition.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The steering
wheel rim is broken or altered to the point it is not continuous, or there is
loose covering material.
|
|
(b) There are cracks
that could catch or snag on clothing, hands, or jewelry.
|
|
(c) The steering
wheel is not equivalent to original equipment in material, strength,
diameter, or is less than 13 inches in diameter.
|
|
(d) The steering
wheel has object attached which interferes with safe steering, except as
provided for in §(3) of this regulation.
|
(3) Hand Controls. Hand
controls or other special equipment for physical disability are acceptable
provided that the requirements defined in Regulation .01E(3) of this chapter
have been met. If the vehicle cannot be operated by the inspector due to authorized
modifications, the owner/agent of the vehicle may operate the vehicle for the
inspector. A steering knob is acceptable
equipment for operation by a person with a physical disability without having
to meet the requirements defined in Regulation .01E(3) of this chapter.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The hand controls
or other special equipment for physical disability are not readily accessible
to the operator or are binding, damaged, or jammed. Consult the equipment
operating manual if needed during inspection.
|
|
(b) The hand controls
or other special equipment interfere with the normal function of regulated
vehicle equipment, and the vehicle does not meet the requirements defined in
Regulation .01E of this chapter.
|
(4) Energy Absorbing
Steering Column and Steering Coupling. Passenger cars, multipurpose passenger
vehicles, trucks, and buses up to 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg) GVWR built on or
after January 1, 1968, are required to be equipped with energy absorption systems,
and some vehicles over 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg) GVWR may also be equipped with
these systems. If so equipped, the column shall be inspected for objects
attached that would prevent collapse under impact, and for indications of
improper column mounting or defective shear capsule. Disassembly of the vehicle
dash for inspection of this equipment is not required unless there are
indications of improper column mounting or a defective shear capsule. An
under-hood inspection of the collapsible steering shaft, shear pins, or
mesh-type material shall be performed. Steering couplings shall be inspected
for any unsafe condition. Modifications to the energy absorbing steering column
shall not be permitted.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Inside passenger
compartment:
|
|
(i) Objects
(tachometer, etc.) are mounted on steering column equipped with an energy
absorption system; or
|
|
(ii) The column is
improperly mounted, shear capsule is separated from bracket, or wheel and
column are not properly secured or mounted.
|
|
(b) Under
Hood/Vehicle Exterior:
|
|
(i) The shear pins or
other collapsible components of the column assembly are damaged, loose,
missing, modified, or otherwise not as originally designed and adversely
affect the operation of the vehicle; or
|
|
(ii) The steering
coupling component is damaged, loose, missing, modified, or otherwise not as
originally designed.
|
(5) Steering Lash.
Inspect the steering system lash to determine whether any condition exists that
would adversely affect the steering of the vehicle. The vehicle shall be on a
dry surface. Inspect with the front wheels in the straight-ahead position. Steering
lash on a vehicle equipped with a steering box is inspected based on the
diameter of the steering wheel. Turn the steering wheel until the turning
motion can be observed at the road wheels and note the steering wheel position.
Next, turn the steering wheel in the opposite direction until the turning
motion can be observed at the road wheels and note the second position of the
steering wheel. Measure the distance between the noted positions of the
steering wheel and use the steering wheel diameter if applicable to determine
the maximum allowable lash of the steering (unless the manufacturer specifies
less movement allowed) as listed in this regulation.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) A vehicle
equipped with a steering box:
|
|
(i) The steering lash
measured on a steering wheel diameter up to 16 inches exceeds 2 inches;
|
|
(ii) The steering
lash measured on a steering wheel diameter up to 18 inches exceeds 2 ¼
inches;
|
|
(iii) The steering
lash measured on a steering wheel diameter up to 20 inches exceeds 2 ½
inches; or
|
|
(iv) The steering
lash measured on a steering wheel diameter up to 22 inches exceeds 2 ¾
inches.
|
|
(b) A vehicle
equipped with rack and pinion steering has steering lash measured on a
steering wheel that exceeds 0.4 inches (10mm).
|
(6) Steering Travel.
Inspect the steering system travel by turning the steering wheel through a full
right and a full left turn. There shall be no binding, jamming, inconsistent
steering effort, excessive play, or other condition that adversely affect steering
operation during this inspection.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
Any roughness,
jamming, binding, inconsistent steering effort, excessive play, or other
condition which adversely affect steering operation is present when turning
the wheels from full right to full left.
|
(7) Steering Linkage.
Lift the vehicle according to the manufacturer’s procedure and grasp the front
and rear of the tire and attempt to move the assembly, feel and observe for
excessive movement. Grasp the steering linkage components by hand to detect any
physical or visual looseness in ball and socket joints or misalignment of
steering linkage. Misalignment of steering linkage that results in alignment
angles that cannot move in the same “arc” of movement up and down as the
suspension may cause binding or unacceptable steering and handling. Inspect the
steering box or the rack and pinion assembly, as applicable.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Movement is in
excess of the manufacturer’s recommendation;
|
|
(b) There is any
looseness that can be felt by hand in tie rod or drag link balls and sockets;
|
|
(c) A ball and socket
joint has missing or torn boot;
|
|
(d) A joint is not
secured with cotter pins or other locking devices;
|
|
(e) The steering
stops allow tire to rub frame, metal, or other chassis parts;
|
|
(f) The tie rods, tie
rod ends, center link, drag link, pitman arm, or idler arm are misaligned;
|
|
(g) Linkage movement
is restricted or impeded by any condition; or
|
|
(h) Steering linkage
angles have been altered to the extent that component function is adversely
affected.
|
(8) Manual Steering.
Manual steering units contain fluid for internal lubrication. Inspect the
steering box or rack and pinion, as applicable, for proper mounting, damage,
leakage, and proper function. Rack and pinion steering is equipped with bellows
covering the ends of the rack to prevent debris from contaminating the rack and
pinion teeth and damaging the fluid seals. Fluid visible in or from the bellows
indicates fluid seal failure.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The steering box
or steering rack is not properly mounted;
|
|
(b) The steering box
or steering rack is damaged to adversely affect function;
|
|
(c) The steering box
or steering rack has Class-3 leakage;
|
|
(d) The manual
steering box or rack and pinion assembly, as applicable, is damaged, loose,
leaking, or proper steering movement is restricted or impeded by any
condition;
|
|
(e) A steering rack
bellows are missing, damaged, or not secured to prevent the bellows from
shifting position; or
|
|
(f) Fluid is present
or leaking from rack and pinion bellows indicating a fluid seal leak is
active.
|
(9) Power Steering.
Inspect the operation and condition of the power steering. Integral power
steering systems are lubricated by the power steering fluid rather than having
a separate lubrication fluid. Inspect the fluid reservoir and reservoir cap
condition, fluid level, component mounting, belt condition, or the condition of
electrical components for electrical power steering. Surface corrosion on metal
components is not a cause for rejection. Visual indications of system leakage
shall be confirmed by inspection with the engine running. Power steering
systems that function properly and are filled to the manufacturer’s recommended
fluid levels that do not have visual indications of leakage are not required to
be inspected for leakage with the engine running. Rubber power steering hoses
shall be inspected to ensure they are firm but flexible, not hard and brittle,
or soft and spongy.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The power
steering does not function properly;
|
|
(b) The steering
component has Class-3 leakage;
|
|
(c) The fluid level
is less than the manufacturer's recommendation, or is contaminated;
|
|
(d) The belts are
frayed, loose, missing, or damaged;
|
|
(e) The fluid
reservoir or cap is damaged, loose, or missing;
|
|
(f) A hose, tubing,
fitting, or connection has been chafed or rubbed by moving parts, rubber is
cracked to expose cords, are not secured against damage, are leaking,
cracked, chafed, bulging, flattened, restricted, or are rusted to a point of
flaking or pitting. Surface rust is not a cause for rejection;
|
|
(g) A rubber power
steering hose is hard and brittle, or soft and spongy indicating severe
deterioration;
|
|
(h) Electrical
components are disconnected, missing, damaged, or not secured against damage;
|
|
(i) A mount or parts
are missing, loose, or broken;
|
|
(j) The steering rack
bellows are damaged, or not secured to prevent the bellows from shifting
position; or
|
|
(k) The power
steering box or rack and pinion assembly, as applicable, is damaged, loose,
leaking, or proper steering movement is restricted or impeded by any
condition.
|
|
(l) Fluid is present
or leaking from rack and pinion bellows indicating a fluid seal leak is
active.
|
Agency Note: Bellows protect the rack and the fluid
seals. Fluid visible in or from the bellows indicates fluid seal failure.
(10) Motorcycle
Steering Head, and Handlebars. With the front end of the motorcycle raised,
grasp both fork legs and apply forward and backward force to inspect for loose
adjustment or play in steering head bearings or bushings. Turn handlebars from
side to side and inspect for roughness in bearings or bushings. Inspect for the
presence of stops to prevent the handlebars, forks, or triple tree from
contacting other parts of the vehicle. Inspect handlebars for cracks,
deformation, proper alignment, mounting height, width, and hand grips. Apply
upward and downward force to handlebars to inspect for excessive flexing.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) There is
noticeable play or roughness in the steering head bearings or bushings, or
there is obstructed rotation to the left and the right. Drag from a steering
damper is not cause for rejection;
|
|
(b) Stops are missing
or do not prevent contact of the handlebars, forks, or triple tree with the
fuel tank or other equipment;
|
|
(c) The handlebars
are cracked, deformed, improperly aligned, not constructed of adequate
material, or show excessive flexure other than flexure from rubber mounts;
|
|
(d) Handlebars are
less than 18 inches in overall width at the handgrips;
|
|
(e) Handgrips are
missing or loose; or
|
|
(f) Handgrips are
positioned more than 20 inches above the lowest portion of the operator's
seat position.
|
B. Electronic Stability
Control (ESC).
(1) Beginning on or
after September 1, 2008, a certain percentage of passenger cars, multipurpose
passenger vehicles, trucks, and buses with a GVWR of 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg)
or less, are required to be equipped with ESC according to the phase-in schedule
specified in of 49 CFR §571.126.S8. All such vehicles manufactured on or after
September 1, 2011, must comply with this standard. The system may include an
“ESC Off” or other control that places the system in “default” mode, or normal
steering.
(2) All buses with a
GVWR greater the 33,000 pounds (14,969 kilograms) manufactured on or after June
24, 2018, and all buses manufactured on or after August 1, 2019, are required
to be equipped with ESC according to the 49 CFR §571.136.S8.
(3)
ESC systems use computer-controlled augmentations to enhance vehicle
directional stability by applying and adjusting the vehicle brakes and
modifying engine torque to induce a correcting yaw movement to a vehicle based
upon driver input. The system may include an “ESC Off” or other control that
places the system in “default” mode, or normal steering. A vehicle required to
be equipped with ESC shall be inspected to ensure that the ESC is present and
functioning as designed. Some vehicles are equipped with a Traction Control
System (TCS) which utilizes the anti-lock system to control wheel spin during
acceleration.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The electronic
stability control system warning light does not self-check;
|
|
(b) The electronic
stability control system warning light remains lit indicating a possible
system fault or failure;
|
|
(c) The electronic
stability control system warning light activates during normal operation of
the vehicle;
|
|
(d) The electronic
stability control system malfunction adversely affects vehicle's normal
operation;
|
|
(e) The electronic
stability control system has missing, loose, damaged, worn, or improperly
mounted components; or
|
|
(f) The electronic
stability control system is disconnected, disabled, or removed.
|
C. Wheel Alignment.
Wheel alignment settings are adjusted in degrees or fractions of an inch and
cannot be properly adjusted visibly, and require specific alignment equipment
to correct a misalignment. Wheel misalignment severe enough that it can be detected
visibly requires special attention. Undesirable steering or handling conditions
during a required test drive are indications of a misalignment condition. The
use of alignment equipment for the inspection of wheel alignment during any
inspection may not impose a fee without prior approval from the owner/agent of
the vehicle.
(1) Abnormal tire wear
may also indicate misalignment. Abnormal tire wear shall be determined by a
comparison of the tread depth measurements taken in the outermost major tread
groove and the innermost major tread groove of each tire being inspected. Tread
depth measurements that result in a difference of 4/32 of an inch or more shall
indicate wheel misalignment.
(2) Motorcycle
alignment includes inspection of the steering fork tubes and front tire
alignment and rear suspension systems alignment to the vehicle. Move the
vehicle at least the length of the wheelbase and observe if the rear tire
follows in a straight line with the front tire.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Excessive
alignment angles are measured or observed during the inspection;
|
|
(b) Abnormal tire
wear indicates misalignment as described in this regulation;
|
|
(c) Adverse steering
or handling conditions are evident during the test drive; or
|
|
(d) Rear wheel
alignment has any of the following:
|
|
(i) Rear wheel track
does not follow the front wheel track in “straight-ahead” operation;
|
|
(ii) The left-side
wheelbase is more than one inch in difference from the right-side wheelbase
unless specified by the manufacturer to indicate otherwise;
|
|
(iii) The front tire
is not properly aligned to the forks or tubes of the steering head assembly;
or
|
|
(iv) The swingarm or
rear tire/wheel assembly is not properly aligned to the vehicle, or front to
rear wheel alignment exceeds one inch of misalignment.
|
D. Suspension. Inspect
the suspension system for missing, damaged, worn, corroded, or modified
equipment components that would adversely affect vehicle stability. Movement
observed in ball joints, kingpins, or other suspension joints designed to allow
articulation or turning motion in the suspension, found to have movement shall
be measured, recorded, and rejected for excessive movement as required. It is
not required to measure the amount of observed movement of ball joints or other
components specified by the manufacturer for rejection. Ball joints, kingpins,
and other articulating suspension joints specified for no observed play allowed
shall be recorded as “0” for specification and measurement of ball joints.
(1) Front Axle Ball
Joints (Without Wear Indicators). Inspect ball joints per the manufacturer's
procedures and specifications. If the
vehicle manufacturer specifies ball joint inspection for vertical movement,
only use moderate force to exert upward pressure during the inspection.
Excessive force may falsely generate excessive movement. Ball joint boots that
are damaged or missing shall be rejected. Ball joints shall be rejected if the
ball joints do not turn freely. Unless specified otherwise, a ball joint is
normally unloaded by lifting the vehicle to remove the weight and tension from
the ball joint.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The ball joint
movement is in excess of the manufacturer's specifications;
|
|
(b) The ball joint
movement is restricted or impeded by any condition;
|
|
(c) The ball joint is
equipped with a tightener or repair kit. Ball joint alignment or control
bushings are not to be considered repair kits or tighteners;
|
|
(d) The ball joint
has been repaired by heating or bending the socket assembly to eliminate
excessive movement;
|
|
(e) The ball and
socket joint has missing or torn boot; or
|
|
(f) The joints are
not secured with cotter pins or other locking devices.
|
(2) Front Axle Ball
Joints (With Wear-Indicators). Wear-indicating ball joints shall be inspected
per the manufacturer's procedures and specifications. Ball joint boots that are
damaged or missing shall be rejected. Ball joints shall be rejected if the ball
joints do not turn freely.
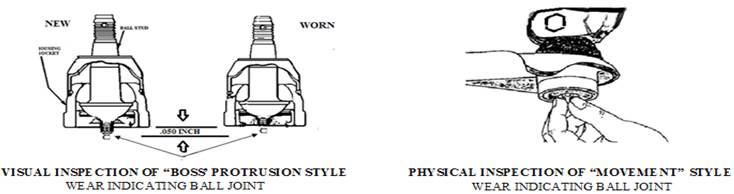
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The ball joint
manufacturer's wear indicator does not meet the manufacturer’s
specifications;
|
|
(b) The ball joint
movement is in excess of the manufacturer's specifications;
|
|
(c) The ball joint
movement is restricted or impeded by any condition;
|
|
(d) The ball joint is
equipped with a tightener or repair kit. Ball joint alignment or control
bushings are not to be considered repair kits or tighteners;
|
|
(e) The ball joint
has been repaired by heating or bending the socket assembly to eliminate
excessive movement;
|
|
(f) The ball and
socket joint has missing or torn boot; or
|
|
(g) The joints are
not secured with cotter pins or other locking devices.
|
(3) MacPherson Strut
Upper Bushing or Bearing. The upper bushing or bearing (as equipped), is the
load-carrying component of a steerable (front axle) MacPherson Strut suspension
system and shall be inspected unloaded for missing, frozen, damaged, worn, corroded,
or modified conditions.
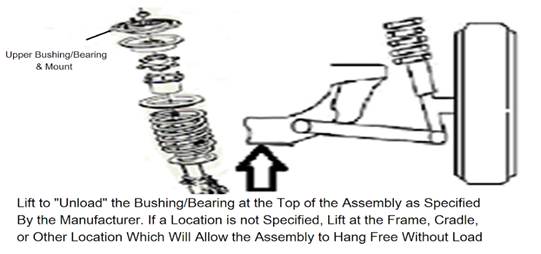
|
Reject
Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The strut upper
bushing or bearing has excessive movement;
|
|
(b) The strut
movement is restricted or impeded by any condition; or
|
|
(c) The strut mount
has any damaged, worn, rusted, modified condition, or missing parts.
|
(4) Kingpins. Inspect
kingpins to determine if there are any missing, rusted, broken, or worn parts
that may adversely affect the steering or suspension of the vehicle. Hoist the
vehicle under the axle or control arm and grasp the top and bottom of the tire
and attempt to move the assembly in and out to inspect for horizontal movement.
Lift the tire/wheel assembly to inspect for vertical movement using a pry bar
or other means to overcome the weight of the wheel assembly during the
inspection. Record any horizontal movement measured, or vertical movement
measured at the spindle. Kingpins shall be rejected if the kingpins do not turn
freely.
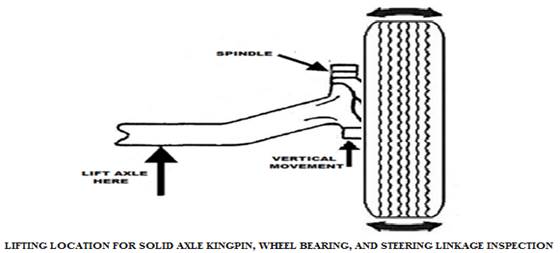
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Movement exceeds
the manufacturer's specification, or when manufacturer specification is not
available, movement measured at the sidewall of the tire based upon wheel
diameter exceeds:
|
|
(i) Wheels under 20
inch, lateral movement is more than 1/8 inch or 3 mm; or
|
|
(ii) Wheels 20
inches, or larger, lateral movement is more than 3/16 inch or 5 mm;
|
|
(b) Kingpin vertical
movement exceeds 3/32 inch or 2.5 mm; or
|
|
(c) Kingpin movement
is restricted or impeded by any condition.
|
(5) Control Arms, Locator Bars, Stabilizer
Bars, Track Bars, Rear Axle Ball Joints, and Rear Axle Linkage. These
components and their associated mounting hardware and bushings shall be
inspected for loose, damaged, missing, corrosion, deterioration, modifications,
or other conditions that could adversely affect the safe operation of the
vehicle. Autocycles may be equipped with “motorcycle type” swingarm rear
suspension systems which must be properly inspected for operation and
condition.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) A control arm,
locator arm/bar, stabilizer bar, track bar, or other suspension control
component is loose, broken, missing, rusted, deteriorated, modified, or has
any other condition which could adversely affect the operation of the
vehicle;
|
|
(b) A control arm,
locator arm/bar, stabilizer bar, track bar, or other suspension bushing is
damaged, deteriorated, oil-soaked, heat damaged, or dry rotted to a point
that the bushing is loose, frozen, or will not move as designed;
|
|
(c) A rear axle ball
joint is loose, frozen, or will not move as designed;
|
|
(d) A rear axle
linkage is loose, frozen, or will not move as designed; or
|
|
(e) Swingarm does not
articulate as designed to allow suspension movement, has excessive lateral
movement, excessive wear or deterioration is present in the bushings, or
bearings as equipped.
|
(6) Wheel Bearings.
Wheel bearings shall be inspected on all wheel positions for looseness, damage,
leaking seals, or any condition that could adversely affect the safe operation
of the vehicle. Wheel bearing noise detected during a road test requires a physical
inspection to properly identify the defective wheel bearing. With the vehicle
lifted, grasp the top and bottom of the tire and rock it in and out. Measure
any movement and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications. Rotate the
tire and inspect for rough, galled, or otherwise defective bearings. To
determine if excess movement observed is wheel bearing movement or ball joint
movement, it may be necessary to lift the vehicle to load the ball joints, if
applicable.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Wheel bearing
noise detected during a road test;
|
|
(b) Wheel bearing
movement exceeds the manufacturer’s specifications;
|
|
(c) Wheel bearings
are rough, galled, missing parts, or otherwise defective; or
|
|
(d) Wheel bearings
are not properly lubricated, or wheel seals have Class-3 leakage.
|
(7) Suspension Ride
Height Control Equipment. The different suspension systems may be composed of
equipment such as springs, torsion bars, airbags, electronic ride control,
hydraulic ride control, or a combination of components that properly support
the vehicle weight, control ride height, and cushion the ride of a vehicle.
Observe the ride height of the vehicle for unlevel conditions, and measure at
the corners of the vehicle if necessary. Ride control systems shall be
inspected for damaged, missing, improperly installed components, or equipment
not designed for on-road operation. All related mounting and hardware
associated with suspension equipment components shall be inspected for
excessively worn or deteriorated conditions, corrosion, suspension modifications,
or having other conditions that could adversely affect the safe operation of
the vehicle.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Springs, torsion
bars, airbags, electronic ride control devices, hydraulic ride control
devices, or other ride control components are loose, damaged, modified, or
has any other condition that adversely affects the safe operation of the
vehicle;
|
|
(b) Spring shackles,
bushings, fasteners, insulators, cushions, or other mounting components for
ride control devices are loose, damaged, modified, or has any other condition
which could adversely affect the safe operation of the vehicle;
|
|
(c) Air or electronic
suspension control system module, line, wiring, or other component is
missing, not functioning, is damaged or deteriorated to affect proper
function;
|
|
(d) U-bolts are
loose, damaged, or not of sufficient length to fully engage the threads of
the fasteners;
|
|
(e) Lift kits, lift
blocks, or other modifications to the suspension system components are loose,
sagging, damaged, or use multiple lift blocks;
|
|
(f) Spacers are
installed within the coils of a coil spring; components do not align the
suspension system properly, or for other condition which adversely affects
the safe operation of the vehicle;
|
|
(g) Any object or
equipment extends below the bottom edge of any wheel rim;
|
|
(h) Vehicle ride
height when measured on the left and the right side exceeds:
|
|
(i) One-inch
difference on a vehicle up to 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg) GVWR; or
|
|
(ii) Two inches
difference on a vehicle over 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg) GVWR;
|
|
(i) Ride height
allows tire to contact vehicle;
|
|
(j) Ride height
allows the suspension to contact suspension bump stops or bottom out during
normal vehicle operation; or
|
|
(k) Air leaks from
anywhere in an air suspension system.
|
(8) Lift Axle. Vehicles
equipped with axles that can be raised and lowered while in motion as needed to
support additional weight shall be inspected for function and condition. The
steering and suspension shall be inspected using the manufacturer’s procedures
and specifications.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Toe is not within
the manufacturer’s specifications, or plus or minus 1/16, whichever is the
least;
|
|
(b) Ball joint or
kingpin movement is restricted or impeded by any condition;
|
|
(c) Ball joint or
kingpin movement is in excess of manufacturer's specifications;
|
|
(d) Suspension
bushings, bearings, mounts, control arms, or other mounting components are
improperly installed, damaged, or do not function as designed;
|
|
(e) Axle fails to
respond properly to the axle lift control switch;
|
|
(f) Axle engages
before the axle is fully down; or
|
|
(g) Axle air pressure
indicated on the axle air pressure gauge does not measure equal to, or
greater than the psi indicated on the manufacturer’s certification when the
axle is deployed.
|
(9) Shock Absorbers,
Struts, and Front Forks. Shock absorbers, strut cartridges, and front forks may
be gas-charged, oil-filled, air-charged, electronically controlled, hydraulic
controlled, or use a combination of designs to dampen the spring rebound of the
suspension. These components shall be inspected for condition, mounting, and
function. The vehicle shall be inspected for insufficient dampening action
during a road test. Free rocking motion for more than two cycles while driving,
the front end diving excessively during braking, or rises excessively under
acceleration during a road test indicates defective equipment. Inspect shock
absorbers, struts, or front forks for wear, damage, or leakage that could
adversely affect vehicle stability.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Vehicle continues
free rocking motion for more than two cycles during operation, the front-end
dives excessively during braking or rises excessively under acceleration, or
otherwise does not function as designed;
|
|
(b) Mounting bolts,
bushings, or mounts are missing, damaged, or deteriorated to a point that
adversely affects the function of the component;
|
|
(c) Class-3 leakage
is present on hydraulic or gas-filled shocks, struts, or front forks if
equipped;
|
|
(d) Air leaks from
anywhere in an air suspension system;
|
|
(e) Lines or tubing
are leaking, improperly routed or mounted, or are not protected from damage;
|
|
(f) Electrical
components or wiring is improperly routed or mounted, or are not protected
from damage; or
|
|
(g) Front fork tubes
are damaged preventing full travel, or free action of front forks.
|
.03 Vehicle Frame and
Unibody Construction.
A. Full Frame. The
vehicle frame, body to frame mounting points, and mounting points for
suspension equipment components shall be inspected for corroded, damaged, or
modified conditions that could adversely affect the safe operation of the
vehicle. Body mounts shall not be stacked (multiple blocks or bushings). The
frame shall be inspected for improper materials or improper repairs. Frame side
rail height (excluding arches or kick-up areas at vehicle axles) shall be
measured at the highest portion of the frame. School vehicle frame alterations
shall be designed and guaranteed by the original chassis manufacturer or the
body manufacturer, and shall not extend the wheelbase. Type I School Vehicle
frame alterations may only be made behind the rear spring hangers. Type II
School Vehicle frame alterations may only be made behind the rear spring
hangers or in front of the front spring.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Frame is
corroded, damaged, or modified to adversely affect the safe operation of the
vehicle;
|
|
(2) Frame body
mounting points or mounting points for suspension or drivetrain components
are corroded, damaged, or modified and adversely affect the safe operation of
the vehicle;
|
|
(3) Body mount
bushings or other attachment devices are missing, damaged, modified, stacked,
or loose and adversely affect the safe operation of the vehicle;
|
|
(4) Frame has been
improperly repaired or cannot properly support attached components; or
|
|
(5) Frame side rail
height at the side or rear is higher than:
|
|
(a) 20 inches on a
passenger vehicle;
|
|
(b) 28 inches on an
MPV, SUV, or pickup truck up to 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg) GVWR; or
|
|
(c) 30 inches on a
vehicle except for a trailer, between 10,001 – 18,000 pounds GVWR.
|
B. Unitized Body. The
strength of unibody construction is dependent upon the thickness, type, and
shape of the material used in the construction of body components. Therefore,
any damage, improper repair, or modification that decreases the strength by altering
the thickness, type, or shape of the body construction material shall be
rejected during the inspection. Unibody vehicles shall be inspected for
corroded, damaged, improperly repaired, or modified conditions that could
adversely affect the safe operation of the vehicle. Body to subframe, cradle
mounting points, and mounting points for suspension components shall be
inspected for corroded, broken, damaged, or modified conditions that could
adversely affect the safe operation of the vehicle.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Unibody or
subframe is corroded, damaged, or modified to adversely affect the safe
operation of the vehicle;
|
|
(2) Unibody or
subframe is constructed of improper materials, has been improperly repaired,
or repaired using improper material;
|
|
(3) Subframe, cradle
mounting points, or mounting points for suspension components are corroded,
damaged, or modified and adversely affect the safe operation of the vehicle;
|
|
(4) Subframe, cradle
mount bushings, or other attachment devices are missing, damaged, modified,
or loose and adversely affect the safe operation of the vehicle; or
|
|
(5) Subframe or
unibody main support side rail height is higher than:
|
|
(a) 20 inches on a
passenger vehicle; or
|
|
(b) 28 inches on an
MPV, SUV, or pickup truck up to 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg) GVWR.
|
C. Motorcycle and
Autocycle Frame. The frames of motorcycle and autocycle vehicles are often
constructed with a central tubular frame to which the steering, suspension, and
drivetrain components are attached. The frame shall be inspected for corroded,
damaged, or modified conditions that could adversely affect the safe operation
of the vehicle. Mounting points for steering, suspension, and drivetrain
components shall be inspected for corroded, broken, damaged, or modified
conditions that could adversely affect the safe operation of the vehicle.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Frame is
corroded, damaged, or modified and adversely affects the safe operation of
the vehicle;
|
|
(2) Frame has been
improperly repaired, or repaired using improper material;
|
|
(3) Frame has cracks,
improper welds, fatigue points or work hardening, or other structural damage;
|
|
(4) Frame has flexure
or is bent to cause wheel misalignment; or
|
|
(5) Engine mounting
area or brackets are damaged.
|
.04 Tow Vehicle Hitches
and Coupling Devices.
A. Hitch Mounts and
Receivers. Inspect for damage or deterioration of the hitch structure, which
would adversely affect the safe towing capability of the vehicle. Inspect the
hitch attachment to the vehicle, and the vehicle attachment area for missing or
loose fasteners, cracks, improper welds, or inadequate or improper materials.
Agency Note: Hitches and Coupling Devices are not
required equipment for motor vehicles other than truck tractors, therefore they
may be removed if rejected and are not required to be replaced on vehicles
other than fifth wheels on truck tractors.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Hitch is damaged
or deteriorated and is unsafe for operation;
|
|
(2) Hitch attachment
has missing or loose fasteners, cracks, or improper welds; or
|
|
(3) Hitch is
constructed or repaired using improper materials.
|
B. Hitch Ball, and
Pintle Hook. Inspect the hitch ball or pintle hook for flat spots, pits, or
cracks. Inspect the hitch ball for wear exceeding 1/8 inch or 3.0 mm from its
original dimension. Inspect the pintle hook horn section for wear exceeding 20
percent. The latch on a pintle hook shall latch and unlatch as designed. Weld
repairs to a hitch ball or pintle hook shall not be permitted. Mounting
fasteners or welds shall be inspected for proper integrity.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Hitch ball has
flat spots, pits, or cracks;
|
|
(2) Hitch ball is
worn more than 1/8 inch or 3.0 mm from original dimension;
|
|
(3) Pintle hook
assembly has cracks;
|
|
(4) Pintle hook horn
has wear exceeding 20 percent;
|
|
(5) Pintle hook latch
does not function as designed;
|
|
(6) Hitch ball or
pintle hook has been repaired by welding; or
|
|
(7) Mounting
fasteners are missing, loose, damaged, or have improper welds.
|
C. Fifth Wheels.
Inspect the fifth wheel for proper alignment, distortion, deformation, cracks,
or missing parts.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Any frame
mounting fastener is missing or ineffective;
|
|
(2) Any movement
between mounting components;
|
|
(3) Mounting plate or
pivot bracket fastener is missing or ineffective;
|
|
(4) Mounting plate or
pivot bracket weld or metal is cracked, or any mounting angle iron is cracked
or broken;
|
|
(5) Pivot bracket pin
is missing or unsecured, or horizontal movement of pivot pin exceeds ⅜
inch;
|
|
(6) Horizontal
movement between the upper and lower fifth wheel halves exceeds ½ inch;
|
|
(7) Fifth wheel
slider has missing or ineffective latching fasteners, or fifth wheel slider
stops missing or unsecured;
|
|
(8) Movement between
slider bracket and slider base exceeds ⅜ inch;
|
|
(9) Any slider
component cracked in parent metal or weld;
|
|
(10) Cracks in the
fifth wheel plate contact area; (Not applicable to cracks in approach ramps
and casting shrinkage cracks in the ribs of the body of a cast fifth wheel.)
|
|
(11) Operating handle
does not function as designed;
|
|
(12) Locking
mechanism part is missing, broken, or deformed to the extent the kingpin is
not securely held; or
|
|
(13) Fifth wheel has
been removed from a truck tractor.
|
.05 Trailer Towing
Attachment Devices.
A. Trailer Kingpin.
Inspect for wear or damage that would adversely affect the proper coupling to a
fifth wheel.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Kingpin is
excessively worn, bent, or not securely attached;
|
|
(2) Kingpin bearing
plate is damaged, distorted, or not securely attached to the trailer; or
|
|
(3) Kingpin collar is
damaged or excessively worn.
|
B. Drawbars, Tongues,
and Hitches. Inspect for missing parts, improper alignment, damage,
deformation, deterioration, or constructed with inadequate materials or
welding.
Agency Note:
Drawbars, Tongues, and Hitches are required equipment on trailers, therefore,
if rejected, shall be properly repaired or replaced before certification of the
vehicle may be completed.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Parts are
missing, or constructed with inadequate materials or welding;
|
|
(2) Drawbar, tongue,
or hitch is improperly aligned to the vehicle, damaged, deformed, or
deteriorated and adversely affects safe operation; or
|
|
(3) Coupler has
cracks or deformations, or the inside of the coupler has worn spots or pits.
|
C. Safety Chains and
Cables. Trailers equipped for ball and hitch, pintle hook, or drawbar for
towing are required to be equipped with at least two safety chains or cables of
sufficient strength to support the loaded capacity of the trailer in the event of
separation from the towing unit.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Safety chains or
cables are not present on vehicles equipped for ball and hitch, pintle hook,
or drawbar for towing;
|
|
(2) Safety chains or
cables are not of sufficient strength to support the trailer in the event of
separation from the towing unit; or
|
|
(3) Safety chains or
cables are missing when required, broken, or excessively worn.
|
D. Landing Gear,
Trailer Jack, Trailer Drop Leg. Equipment used to support the trailer for
coupling and uncoupling from the towing vehicle shall be inspected for missing
parts, deterioration, damage, or construction with inadequate materials or
welded repairs to components.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Parts are
missing, constructed with inadequate materials, or repaired by welding;
|
|
(2) Landing gear,
trailer jack, or trailer drop leg is damaged, deformed, or corroded that will
adversely affect safe operation; or
|
|
(3) Landing gear,
trailer jack, or trailer drop leg will not properly deploy to support the
vehicle or will not properly stow away to allow vehicle operation.
|
.06 Brake Systems.
A. Service Brake
Performance Tests. The service brake is the primary driver input used for
slowing, stopping, and controlling the vehicle under normal operating
conditions. The stopping ability of the vehicle shall be tested at a speed of
20 mph by applying the service brakes firmly. This test may be performed during
the vehicle road test required for the steering and suspension inspection. The
service brake performance test shall be conducted on a hard, smooth surface
road or area that is free from loose material, oil, standing water, ice, snow,
or grease. While maintaining firm control of the steering wheel, observe
whether the vehicle comes to a smooth stop, without pulling to the right or
left, within the distance prescribed in this regulation. Brake pull or
vibration that adversely affects proper brake action during any operation of
the vehicle, shall be rejected. These procedures are also applicable to
vehicles equipped with hand controls for the physically disabled. A vehicle
modified for physically disabled operation, which does not allow conventional
operation, may require the owner/agent to drive the vehicle into the inspection
area and demonstrate the braking application to the satisfaction of the
inspection mechanic. A vehicle built to meet the standards for a motorcycle may
have both a hand-operated lever and foot-operated pedal for the application of
the service brakes on both wheel positions. Motorcycles manufactured before
January 1, 1974, were not required to be equipped with brakes on all wheels.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The vehicle does
not come to a smooth stop from a speed of 20 mph within the distance
established by the type of vehicle:
|
|
(a) 20 feet –
Motorcycle;
|
|
(b) 25 feet –
Passenger vehicles seating 10 persons or less with a GVWR of 10,000 lbs. or
less;
|
|
(c) 30 feet– Light
trucks, vans, and multipurpose passenger vehicles;
|
|
(d) 35 feet – Single
unit vehicles with a GVWR of more than 10,000 lbs. except truck tractors; or
|
|
(e) 40 feet – Truck
tractors.
|
|
(2) There is obvious
vibration caused by a warped brake rotor or an out-of-round brake drum;
|
|
(3) Vehicle pulls to
the right or left upon brake application; or
|
|
(4) There is
inadequate brake action on any wheel.
|
B. Hydraulic Brake
Application Systems.
(1) Inspect hydraulic
brake systems for function, condition, leakage, and proper installation. Any
hydraulic brake fluid leakage is cause for rejection of the brake equipment.
Brake components designed and intended for non-street applications such as “racing”
or other “off-road use only” shall not be allowed. Split service brake systems
consist of two or more subsystems actuated by a single control, designed so
that a single failure in any subsystem does not impair the operation of any
other subsystem. A motorcycle split service brake system may consist of a
single split brake service system actuated by a single control, or two separate
brake systems with separate controls, one of which may be a parking brake
system. Inspect brake systems equipped with a “RED” warning light which
illuminates if a malfunction exists that is related to fluid pressure,
reservoir fluid level, or fluid pressure imbalance to ensure that the warning
light is operating properly. Inspect split service brake systems for function
of the “RED” brake warning light, and illumination of the warning light during
operation. Do not remove or pull back wheel cylinder or caliper dust boots
during the inspection. Inspect hydraulic hoses and brake lines for leaks,
cracks, chafing, restrictions, improper installation, or support. Inspect metal
lines or fittings for corrosion with obvious pitting that reduces the wall
thickness, or for improper material not intended for vehicle brake systems.
Copper/nickel hydraulic brake line that is manufactured for use with automotive
hydraulic brake systems is acceptable material. Rubber brake hoses shall be
inspected to ensure that they are firm but flexible and shall not be hard and
brittle, or soft and spongy. Inspect master cylinder fluid level and all brake valves
for leakage. Inspect the brake warning light for presence and function.
Agency Note:
Vehicles with hydraulic brake application systems on which the wheel/tire
assembly mounts over the brake assembly shall have all wheels removed to
inspect all brake components. Conventional motorcycle disc brake equipment is
accessible for inspection without wheel removal.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Service brake
pedal, lever, or other brake input device is improperly positioned or
misaligned, or there is excessive friction present;
|
|
(b) Red brake warning
light function and operation:
|
|
(i) Fails to perform
self-check when the ignition system is activated; or
|
|
(ii) Comes on when
the brake pedal or hand lever is depressed, or at any time while the vehicle
is in operation, indicating a hydraulic brake defect or low fluid level.
|
|
(c) Wheel cylinder or
brake caliper fails to operate, leaks, or is not properly installed;
|
|
(d) Wheel cylinder or
caliper dust boots are missing or damaged;
|
|
(e) Brake line has
been repaired or replaced with tubing or material that is not designed for
vehicle hydraulic brake systems;
|
|
(f) Brake hose or
line is improperly supported, or not mounted to prevent contact with wheels
or body during steering or suspension movement;
|
|
(g) Brake hose,
rubber line, or fitting, is cracked to expose cords, leaking, chafed,
flattened, bulging, restricted, or metal line is rusted to a point of
flaking, bulging, or pitting, or has re-welded sections. Surface rust is not
a cause for rejection;
|
|
(h) Rubber brake hose
is hard and brittle, or soft and spongy;
|
|
(i) Master cylinder
leaks, or is not securely mounted;
|
|
(j) Master cylinder
reservoir fluid level is not within the manufacturer's range, or any section
is less than 1/2 full if range is not specified;
|
|
(k) Brake fluid is of
the incorrect type or is contaminated;
|
|
(l) Master cylinder
reservoir cap or cover is missing or leaking; or
|
|
(m) A motorcycle
manufactured after January 1, 1974, is not equipped with brakes on all
wheels.
|
(2) Hydraulic System
Leakage Test and Brake Pedal or Hand Lever Reserve. The engine shall be running
when checking vehicles with power-assisted brake systems. While the vehicle is
stopped, activate the service brake pedal, lever, or other brake input device
under moderate force. The service brake applied position shall remain constant
for 1 minute to ensure that there is no hydraulic external or internal leakage.
Brake pedal or lever travel reserve shall be no less than 1/3 of the total
travel. An inability to maintain a consistent brake application position
indicates a hydraulic pressure loss. A
low reserve capability indicates improper brake adjustment or a mechanical
failure in the brake system.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The service brake
pressure, brake pedal, or hand lever position cannot be maintained for at
least 1 minute while the service brake is applied; or
|
|
(b) Less than 1/3 of
the total pedal or hand lever travel reserve remains while the vehicle is
stopped and the service brake pedal or lever is depressed with moderate
force.
|
(3) Power Assist Brake Units. Inspect power
assist brake systems for reserve assist with the engine off, and for power
assist with the engine running for vehicles that use engine-driven sources of
power. Electrically powered systems may require different inspection
procedures. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the procedures for
inspection of electrically powered systems.
(a) Vacuum Brake Assist
Unit. Stop the engine and apply service brake several times to deplete all
vacuum in system. Depress the brake pedal with approximately 50 pounds of force
and while maintaining that force, start the engine. If the brake pedal does not
move slightly when the engine starts, there is a malfunction in the power
assist unit. The vacuum brake assist unit shall demonstrate integrity as
indicated by a decrease in pedal height when the engine is started and force is
maintained on the pedal. The vacuum brake system shall provide sufficient
vacuum reserve to permit one service brake application with a brake pedal force
of approximately 50 pounds after the engine is turned off without actuating the
low vacuum indicator.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(i) System reserve
does not retain vacuum with the engine off;
|
|
(ii) Brake pedal does
not move slightly under force when the engine starts with all vacuum reserve
depleted;
|
|
(iii) Vacuum reserve
is not sufficient to permit at least one service brake application with the
engine off without actuating the low vacuum warning indicator;
|
|
(iv) Brake booster
hose or line is improperly supported, or not mounted to prevent contact with
wheels or body during steering or suspension movement; or
|
|
(v) Brake booster
hose, rubber line, or fitting, is cracked to expose cords, leaking, chafed,
flattened, bulging, restricted, or metal line is rusted to a point of
flaking, bulging, or pitting, or has re-welded sections. Surface rust is not a cause for rejection.
|
(b) Hydraulic Brake
Assist Unit. Stop the engine and apply service brake several times to deplete
all hydraulic reserve pressure in system. Depress the brake pedal with
approximately 50 pounds of force and while maintaining that force, start the
engine. If the brake pedal does not move slightly when the engine starts, there
is a malfunction in the power assist unit. The hydraulic brake assist unit
shall demonstrate integrity as indicated by a decrease in pedal height when the
engine is started while approximately 50 pounds of force is maintained on the
pedal. The hydraulic brake system shall provide sufficient hydraulic reserve to
permit at least one service brake application with a brake pedal force of
approximately 50 pounds after the engine is turned off.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(i) System reserve
does not retain hydraulic reserve pressure with the engine off;
|
|
(ii) Brake pedal does
not move slightly under force when the engine starts with all hydraulic
reserve pressure depleted;
|
|
(iii) Hydraulic
reserve pressure is not sufficient to permit one service brake application
with the engine off;
|
|
(iv) Class-3 Leakage
of Hydraulic fluid leakage is present;
|
|
(v) Brake booster
hose or line is improperly supported, or not mounted to prevent contact with
wheels or body during steering or suspension movement; or
|
|
(vi) Brake booster
hose, rubber line, or fitting, is cracked to expose cords, leaking, chafed,
flattened, bulging, restricted, or metal line is rusted to a point of
flaking, bulging, or pitting, or has re-welded sections. Surface rust is not a cause for rejection.
|
(c) Electrically
Powered Brake Assist System. Some vehicles may be equipped with
electric-powered systems to develop vacuum or pressure for power assist brake
systems. Some systems use electrically powered sources to develop vacuum or
pressure rather than engine sources for power and are subject to inspection for
condition and function.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(i) Electrical power
is not being supplied to the system when the service brake is applied;
|
|
(ii) Power assist
brake fails to apply when the proper voltage is applied or fails to release
when the voltage is removed from the system; or
|
|
(iii) Electrical
wiring, terminal, plug, or connection has a loose connection, excessive
corrosion, damage, is improperly supported, or is exposed to damage.
|
C. Air Brake Application Systems. Inspect Air
Brake Systems for function, condition, and leakage.
(1) Air Brake System
Function Compressor, Governor, Low Air Warning Indicator. With the air system
at zero pressure, run engine at fast idle and note the time required to build
air pressure from 50 – 90 psi. Continue building air pressure and note pressure
at which governor cut-out occurs. Make a series of brake applications until
governor cuts in and note pressure. Continue lowering air pressure until the
low air warning activates and note the pressure when the warning activates.
(2) Air Activated (Air
Over Hydraulic) Brake Systems. A brake system in which the operator’s braking
effort is reduced utilizing compressed air acting on the hydraulic system which
actuates the wheel brakes. These systems use an air operated foot valve to
provide operator input to the hydraulic service brakes. If an air actuated
hydraulic brake system loses its air supply, the service brake will not
operate. The air system components shall be inspected in the same manner as a
full air brake system. The parking brake does not use air spring chambers,
therefore does not function as an emergency brake system.
(3) Air Assisted
Hydraulic Brake Systems (Hydraulic Over Air). A brake system in which the
operator’s braking effort is reduced through an air chamber booster acting on
the hydraulic system which actuates the wheel brake. These systems use a
hydraulic master cylinder to provide operator input to activate the hydraulic
service brakes. Compressed air is used to power brake boosters to increase
brake efficiency and reduce operator effort. If the system loses air pressure,
the service brake system would continue to work at reduced effectiveness. The
air system components shall be inspected in the same manner as a full air brake
system. The parking brake does not use air spring chambers, therefore does not
function as an emergency brake system.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Time required to
build pressure from 50 – 90 psi at fast idle exceeds 2 minutes;
|
|
(b) Governor cut-out
pressure is higher than 135 psi, or lower than 100 psi;
|
|
(c) Governor cut-in
pressure is lower than 80 psi;
|
|
(d) Low pressure
warning fails to function when pressure is lowered to 55 psi, or 1/2 the
governor cut-out pressure, whichever is less;
|
|
(e) Air activated
hydraulic brake system does not function as designed; or
|
|
(f) Air assisted
hydraulic brake system does not function as designed.
|
(4) Air Brake Control
Valves and Tractor Protection. Full air
brake systems utilize compressed air as the sole source of energy for
application of brakes at the vehicle’s wheels. Air brake control valves apply
and release the parking brake, and supply air for towed air brake units. The
parking brake valve should not stay in the released position unless there is 60
psi in the air system, and should “pop out” before air pressure is reduced to
“zero”. The tractor protection valve protects the tractor from air loss
associated with the trailer air supply system.
To inspect the air brake control valves for proper function, release the
parking brake (valve pushed in) without applying the trailer air supply valve;
no air should escape from the trailer supply hose, and at this time with the
service brakes applied (no air should escape from the trailer service hose.)
Apply the trailer air supply (valve pushed in), air should discharge from the
trailer supply hose, and at this time, application of the service brake or the
hand valve should discharge air from the service brake hose. To inspect the
tractor protection valve, apply the trailer supply valve with the trailer
supply hose disconnected, and observe the pressure at which the trailer supply
valve automatically closes to prevent total loss of brake air pressure from the
tractor. Trailer air supply valve should “pop out” to protect the vehicle from
total air loss between 20 – 45 psi.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Air is discharged
from the trailer air supply or service hose with the trailer air supply valve
pulled out or disengaged;
|
|
(b) Air does not
discharge from the trailer air supply hose when the trailer air supply valve
is pushed in or engaged;
|
|
(c) The service brake
hose does not discharge air when the service brake or the trailer hand valve
is applied with the trailer air supply valve button pushed in or engaged;
|
|
(d) Tractor
protection valve does not close to prevent service brake air loss during an
“air loss” or disconnect of the trailer supply hose; or
|
|
(e) Trailer air
supply valve does not “pop out” during an “air loss” or disconnect of the
trailer supply hose.
|
(5) Air Brake Leakage.
Any audible air leak is a rejection during inspection. Air leakage shall also
be inspected for inaudible leakage that exceeds the allowable pressure loss
during timed inspection. The spring parking brake must be released to perform
the leak-down tests required by this regulation. With a fully charged system,
and the engine off, note the pressure drop in the psi per minute with park and
service brakes released. Next, with a fully charged system, and the engine off
apply the service brake and note the pressure drop in the psi per minute with
the service brakes fully applied. Trailers (towed vehicles) receive compressed
air from a towing vehicle; therefore, the air system shall be tested on the
uncoupled towing vehicle before inspecting the air systems on a trailer.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Air loss with the
park and service brakes released is:
|
|
(i) Truck or truck
tractor – more than 2 psi per minute on a single unit; or
|
|
(ii) Trailer attached
to towing vehicle – more than 3 psi per minute on a combination unit;
|
|
(b) Air loss with the
service brakes applied is:
|
|
(i) Truck or truck
tractor – more than 3 psi per minute on a single unit; or
|
|
(ii) Trailer attached
to towing vehicle – more than 4 psi per minute on a combination unit.
|
(6) Compressed Air
Reserve. The air system shall also be inspected for brake air reserve
pressure. Note the full air pressure
indicated on the air gauges with the engine off, make a full-service brake
application and measure the drop in reservoir pressure. Inspect the air reserve
function by lowering air pressure until the low air warning device is
activated, with the engine off apply the service brake while observing
operation of the brakes.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Air reserve
pressure is lowered more than 20 percent of the full pressure reading when
the service brake is fully applied; or
|
|
(b) Air reserve
pressure with low air warning device activated is not sufficient to permit a
full-service brake application.
|
(7) Air Brake
Components, General Condition. Inspect all air brake components, air hoses,
tubes, and connections for damage or deterioration that adversely affects the
safe operation of the vehicle and for improper installation of components. Inspect for audible leaks, attachment of all
connecting lines, and look for proper mounting and support of components. Be
sure lines are free from contact with frame, axles, exhaust system, or other
lines. Rubber impregnated fabric cover is not a reinforcement ply. Thermoplastic
nylon may have braid reinforcement or color difference between cover and inner
tube. Exposure of the second color is cause for rejection. Brake chambers and
slack adjuster shall match by design or type on the same axle but may be
different by axle.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Air compressor
drive belts in a condition of impending or probable failure;
|
|
(b) Air compressor
has cracked, broken, or loose pulley;
|
|
(c)
Loose air compressor mounting bolts, cracked or broken mounting brackets,
braces, or adapters;
|
|
(d) Air compressor
inlet filter is clogged or restricted to prevent proper operation of the air
compressor;
|
|
(e) Air brake valve
or other air brake components is not properly and securely installed;
|
|
(f) Air pressure
relief valve is rated for more than 150 psi, is not present, or is not
operational;
|
|
(g) Brake tubing is
not approved for on-road vehicle usage, is cracked, damaged by heat, broken
or crimped;
|
|
(h) Any audible leak;
|
|
(i) Brake hose or
tubing bulges or swells when air pressure is applied;
|
|
(j) Brake hose
improperly joined with hose clamps over tubing;
|
|
(k) Brake hose is not
approved for on-road vehicle usage, cracked to expose cords, broken, or
crimped;
|
|
(l) Brake hose has
any damage extending through the outer reinforcement ply;
|
|
(m) Brake chamber is
a different design or type on the same axle; or
|
|
(n) Slack adjuster is
a different design or length on the same axle.
|
(8) Air Brake Park and
Emergency Brake Systems. The parking brake shall be able to hold the vehicle
motionless on any grade. The emergency brake system shall be capable of
stopping from 10 miles per hour in the distance, equal to that specified for
service brake performance.
(a) With the air
pressure in the braking system at 90 psi or more, set and release the parking
brake control and observe functioning of the spring brake
chamber at each wheel position equipped; and
(b) Drain the system
air pressure to “zero” and attempt to move the vehicle. Vehicle should remain
stationary.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(i) Spring
parking/emergency brake fails to release the vehicle brakes for operation
when released;
|
|
(ii) Spring
parking/emergency brake fails to hold the vehicle stationary when applied;
|
|
(iii) Vehicle can be
moved with “zero” air pressure in the system; or
|
|
(iv) Parking brake
valve does not “pop out” before air pressure is reduced to “zero”.
|
(9) Actuator (Pushrod
Stroke) Reserve.
(a) The maximum pushrod
stroke shall not be greater than the values given in this regulation. Any brake
stroke exceeding the readjustment limit will be rejected. Stroke must be
measured with engine off, parking brake released, and reservoir pressure of 80
to 90 psi with the service brakes fully applied;
(b) Pushrod/slack
adjuster angle shall not be more or less than 90 degrees with the service brake
applied. Commercial motor vehicles
manufactured on or after October 20, 1994, with air brakes using slack
adjusters shall be equipped with automatic slack adjusters;
(c) For actuator types
not listed in these tables, the pushrod stroke shall not be greater than 80
percent of the rated stroke marked on the actuator by the actuator
manufacturer, or greater than the readjustment limit marked on the actuator by
the actuator manufacturer; and
(d) Wedge brake systems
shall be inspected for brake shoe movement during service brake application.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(i) Slack adjusters
are not adjusted equally;
|
|
(ii) Not equipped
with automatic slack adjuster when required;
|
|
(iii) Manual slack
adjuster will not maintain adjustment;
|
|
(iv) Automatic slack
adjuster is not functioning properly (out of adjustment);
|
|
(v) Pushrod travel on
BF Goodrich Air Actuated Disc Brakes exceeds manufacturer’s specification;
|
|
(vi) Pushrod/slack
adjuster angle is more than 90 degrees with the service brake applied;
|
|
(vii) Brake shoe
movement on wedge brake systems exceeds 1/16 inch (shoe to drum clearance);
or
|
|
(viii) The pushrod
stroke exceeds the limit by design and type of chamber.
|
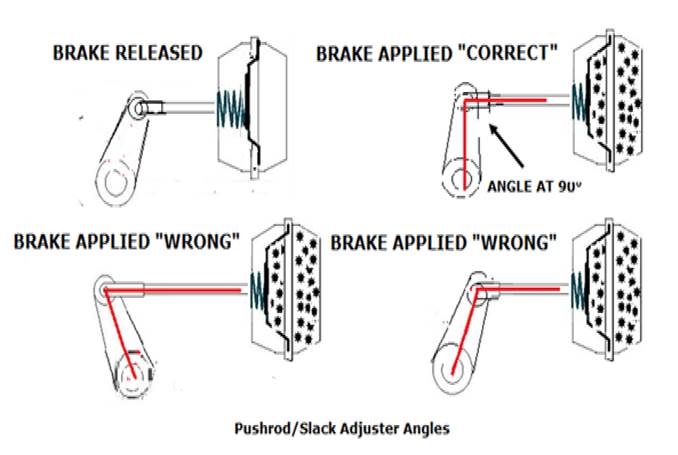
|
Clamp
Type Brake Chamber Pushrod Strokes
|
|
Type
|
Outside
Diameter
|
Standard
Chamber Stroke
|
Long
Stroke Chamber Stroke
|
|
6
|
4 1/2 in. (114
mm)
|
1 1/4 in.
(31.8 mm)
|
Note: Long Stroke Chambers are identified by a “Square
Boss” at the airline connection of the chamber.
|
|
9
|
5 1/4 in. (133
mm)
|
1 3/8 in
(34.9 mm)
|
|
|
12
|
5 11/16 in. (145
mm)
|
1 3/8 in.
(34.9 mm)
|
1 3/4 in.
(44.5 mm)
|
|
16
|
6 3/8 in. (162
mm)
|
1 3/4 in.
(44.5 mm)
|
2 in.
(50.8 mm)
|
|
20
|
6 25/32 in. (172
mm)
|
1 3/4 in
(44.5 mm)
|
2 in.
(50.8 mm)
2 1/2 in.
(63.5 mm) 1
|
|
24
|
7 7/32 in. (184
mm)
|
1 3/4 in.
(44.5 mm)
|
2 in.
(50.8 mm)
2 1/2 in.
(63.5 mm) 2
|
|
30
|
8 3/32 in. (206
mm)
|
2 in.
(50.8 mm)
|
2 1/2 in.
(63.5 mm)
|
|
36
|
9 in.
(229 mm)
|
2 1/4 in.
(57.2 mm)
|
|
|
1 For type 20
chambers 3-inch (76 mm) rated stroke. 2 For type 24 chambers 3-inch (76 mm)
rated stroke
|
|
Bendix
DD-3 Brake Chambers Pushrod Strokes
|
|
Type
|
Outside
Diameter
|
Brake
Readjustment Limit
|
|
30
|
8 1/8 in.
(206 mm)
|
2 ¼ in.
(57.2 mm)
|
|
Bolt-Type
Brake Chambers Pushrod Strokes
|
|
Type
|
Outside
Diameter
|
Brake
Readjustment Limit
|
|
A
|
6 15/16 in. (176
mm)
|
1 3/8 in.
(34.9 mm)
|
|
B
|
9 3/16 in. (234
mm)
|
1 3/4 in.
(44.5 mm)
|
|
C
|
8 1/16 in. (205
mm)
|
1 3/4 in.
(44.5 mm)
|
|
D
|
5 1/4 in.
(133 mm)
|
1 1/4 in.
(31.8 mm)
|
|
E
|
6 3/16 in. (157
mm)
|
1 3/8 in.
(34.9 mm)
|
|
F
|
11 in.
(279 mm)
|
2 ¼ in.
(57.2 mm)
|
|
G
|
9 7/8 in.
(251 mm)
|
2 in.
(50.8 mm)
|
|
Rotochamber-Type
Brake Chambers Pushrod Strokes
|
|
Type
|
Outside
Diameter
|
Brake
Readjustment Limit
|
|
9
|
4 9/32 in. (109
mm)
|
1 ½ in.
(38.1 mm)
|
|
12
|
4 13/16 in. (122
mm)
|
1 ½ in.
(38.1 mm)
|
|
16
|
5 13/32 in. (138
mm)
|
2 in.
(50.8 mm)
|
|
20
|
5 15/16 in. (151
mm)
|
2 in.
(50.8 mm)
|
|
24
|
6 13/32 in. (163
mm)
|
2 in.
(50.8 mm)
|
|
30
|
7 1/16 in. (180
mm)
|
2 ¼ in.
(57.2 mm)
|
|
36
|
7 5/8 in.
(194 mm)
|
2 ¾ in.
(69.9 mm)
|
|
50
|
8 7/8 in.
(226 mm)
|
3 in.
(76.2 mm)
|
|
For types not listed in these
tables, the pushrod stroke must not be greater than 80 percent of the rated
stroke marked on the actuator by the manufacturer, or greater than the
readjustment limit marked on the actuator by the manufacturer.
|
D. Mechanical Brake
System. Some model year vehicles used full mechanical brake systems (cables and
rods) rather than hydraulic, electric, or air for brake application. Inspect
Mechanical Brake Systems for function and condition. Motorcycle mechanical brake
systems with external brake lining wear indicators do not require disassembly
for inspection unless a defect or brake issue is discovered during road
testing. Inspect all mechanical components of the brake system for high
friction, wear, and broken or missing parts.
Agency Note:
Motorcycles manufactured before January 1, 1974, were not required to be
equipped with brakes on all wheels.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Brake system
spring, retainer, linkage, rod, pivot bushing or bearing, mount, or other
mechanical brake component is missing, frozen, excessively worn, broken, or
corroded and adversely affects proper brake function;
|
|
(2) Pins or clevises
are worn more than 25 percent of the original diameter, or cotter pins are
missing;
|
|
(3) Any cables are
frayed (two or more broken strands), there is any roughness, binding, or
jamming in levers or pedals, or brake cable is pinched, damaged, or is routed
to become so;
|
|
(4) Any brake
adjustment mechanism that will not maintain an adjusted position or is
adjusted to its maximum extent;
|
|
(5) Brake adjustment
changes under any steering or loading conditions;
|
|
(6) Brake cam
operating lever has been repositioned on the shaft as a means of avoiding
replacement of worn cam, shoes, or lining;
|
|
(7) Less than 1/3 of
travel remains in hand or foot brake when brakes are applied, or
modifications make the pedal inaccessible for adequate leverage or operation;
or
|
|
(8) A motorcycle
manufactured after January 1, 1974, is not equipped with brakes on all
wheels.
|
E. Electric Brake
Application Systems. Inspect Electric Brake Systems for function, and
condition.
(1) Electric brake
application is a brake system that utilizes electromagnetic forces to attract
the brake shoe magnet to the brake drum. The rotation of the wheel assembly
then forces the arm, the magnet is attached to, to move as a lever which forces
the brake shoes out against the brake drums, and is the sole source of energy
for application of brakes at the vehicle’s wheels. Application of the wheel
brake does not occur until the wheel assembly is rotated while current is being
applied to the brake magnet. Electric brake function may be inspected either by
connection to a towing vehicle or an external power supply for activation. When
proper voltage is applied, and the wheel assembly is rotated in either
direction, the electric brakes shall apply and remain applied while rotational
pressure is being applied to the assembly. Brake magnets shall be inspected for
proper installation, uneven or abnormal wear, or any part of the magnet coil
visible through the friction material of the magnet. The drum’s armature
surface, for the magnet, shall also be inspected for uneven or abnormal wear,
friction, or other conditions that would adversely affect the operation of the
brake system. Vehicles with electric brake application systems shall have all
wheels removed for inspection.
(2) Electrical brake
wiring, terminals, plugs, or connections shall be inspected for loose
connections, excessive corrosion, damage, and improper support or routing.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Brake fails to
apply when the proper voltage is applied while rotating the wheel assembly or
fails to release when the voltage is removed from the wheel assembly;
|
|
(b) Brake magnet is
improperly installed, worn abnormally, or magnet coil is visible through the
friction surface of the magnet;
|
|
(c) The magnet
armature surface on the brake drum is worn abnormally or has any other
condition that adversely affects the operation of the brake system; or
|
|
(d) Electrical
wiring, terminal, plug, or connection has a loose connection, excessive
corrosion, damage, is improperly supported, or is exposed to damage.
|
F. Vacuum Brake
Application Systems. A vacuum over hydraulic brake system in which the
operator’s braking effort is reduced through a vacuum booster acting on the
hydraulic system which actuates the wheel brake.
(1) Trailer vacuum over
hydraulic brake system components include a vacuum storage tank, a control
valve, a vacuum chamber/master cylinder assembly, hydraulic lines, and
hydraulic disc or drum brakes. The trailer brakes may be applied independently
of the tow vehicle service brakes. Maximum braking effort is applied to the
trailer brakes in the event the trailer becomes uncoupled from the tow vehicle.
Inspect vacuum brake systems for function, condition, and leakage:
(a) The towing vehicle
supplies vacuum for the trailer storage tank and a modulated control signal to
operate a trailer unit through quick connects mounted on the tow vehicle and
trailer. The control signal is sent from a control valve connected to the towing
vehicle's vacuum source and hydraulic brake system. When the operator applies
the tow vehicle service brakes, the control valve produces a vacuum signal in
direct proportion to the tow vehicle service brake pressure; and
(b) The trailer control
valve receives this signal and produces a control vacuum signal that is applied
to a vacuum chamber/master cylinder assembly producing a corresponding
hydraulic pressure in the trailer brake system.
(2) Vacuum Brake Unit
Integrity. With the engine off, apply service brake several times to deplete
all vacuum in system. Depress the brake pedal with approximately
50 pounds of force and while maintaining that force, start the engine. If the
brake pedal does not move slightly when the engine starts, there is a
malfunction in the power assist unit. The vacuum brake assist unit shall
demonstrate integrity as indicated by a decrease in pedal height when the
engine is started and approximately 50 pounds of force is maintained on the
pedal. The vacuum brake system shall provide a vacuum reserve to permit at
least one service brake application with a brake pedal force of approximately
50 pounds after the engine is turned off without actuating the low vacuum indicator.
Trailer vacuum brakes shall operate in conjunction with the truck or truck
tractor brake pedal.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Vacuum supply
system does not maintain more than 8 inHg of vacuum, or the reserve does not
retain vacuum with the engine off;
|
|
(b) Brake pedal does
not move slightly under force when the engine starts with all vacuum reserve
depleted; or
|
|
(c) Vacuum reserve is
not sufficient to permit at least one service brake application with the
engine off without actuating the low vacuum warning indicator.
|
(3) Low Vacuum
Indicator. Run the engine to evacuate the system fully. Shut off the engine and
slowly reduce the vacuum in the system by moderate brake applications until the
vehicle vacuum gauge reads 8 inHg of vacuum and observe the functioning of the low-vacuum
indicator. The indicator shall activate no lower than
8 inHg of vacuum.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Low vacuum
warning indicator does not self-check with ignition activation or actuates
while the vehicle is being operated; or
|
|
(b) Low vacuum
warning indicator does not actuate with vacuum reduced to 8 inHg of vacuum.
|
(4) Vacuum System
Hoses, Tubes, and Connections. Vacuum hoses, tubes, and connections shall be in
place, properly supported, and protected from damage. Vacuum hoses shall not be
collapsed, cracked, or abraded. Inspect hoses and tubes for the conditions indicated,
broken or missing fasteners or clamps.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Vacuum hoses,
tubes, or connections are not of the proper materials, or not properly
supported or protected from damage; or
|
|
(b) Vacuum hose or
tube is damaged or has broken, missing fasteners or clamps.
|
(5) Trailer Vacuum
Brake Inspection. Check the trailer vacuum system by coupling trailer(s) to
truck, truck tractor, or independent vacuum supply, and opening trailer shutoff
valves. With adequate vacuum, at least 9 inHg of vacuum, apply and release the trailer
brakes. In the case of trailer brakes equipped with brake chamber rods, observe
the chamber rod movement. Reestablish maximum vacuum, then shut off the vacuum
source and apply the brakes fully. Note the brake application and ensure that a
low-vacuum condition (8 inHg of vacuum or less) is not present.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Brake does not
apply and release; or
|
|
(b) System will not
apply brakes or low-vacuum condition is indicated during brake application
with vacuum source shut off. Will not function using reserve vacuum or will
not maintain more than 8 inHg of vacuum.
|
G.
Brake Drums and Disc Brake Rotors. Inspect for condition and for wear in
excess of the manufacturer's specifications. Manufacturer’s brake drum and
rotor specifications shall be referenced during inspection, and these
specifications and the actual measurements taken during inspection shall be
recorded in MSIS. The manufacturer’s specifications and procedures for brake
inspection may not use physical size specifications for inspection and may
specify alternative component inspection methods. A station that does not
possess the test equipment to perform this inspection may direct the vehicle to
an inspection station that has access to the proper equipment to inspect brake
components that are not measured for size thickness or diameter. Brake
equipment marked with the wear specifications shall be inspected using the
marked specifications on the equipment rather than published specifications.
Replacement high-performance brake equipment approved for on-road operation may
have different specifications from the vehicle manufacturer’s published
specifications. These specifications shall be referenced during equipment
inspection. Vehicles other than school vehicles, which are equipped with
an air brake system with inspection ports, or without backing plates to allow
measurement of brake lining and visual inspection of the friction components,
may be inspected without removal of the wheels. Vehicles not so equipped shall
have all wheels removed to inspect all brake components.
(1) Inspect the
friction surface for cracks extending to the edge of disc or drum. Inspect the
entire disc or drum for cracks that can be felt when physically touched. Short
hairline heat check cracks that cannot be felt by hand shall not be considered
defects. Inspect for mechanical damage or rust to the extent that pitting is
present. Inspect for contaminated friction surface. Measure the disc brake
rotor thickness, or brake drum diameter, and record the measured readings as
required. Compare the recorded readings to the manufacturer's minimum or
maximum specifications as applicable. Brake components designed and intended
for non-street applications such as “racing” or “off-road use only” shall be
prohibited.
(2) Air Brake
Systems. Air brake systems with exposed
friction components, without backing plates, or with inspection ports/slots,
may be inspected without removal of the wheel assemblies. Brake adjustment
slots are not to be used as inspection ports. Brake drums and brake discs
without visual indications of wear or machining that would exceed
manufacturer’s specifications may be inspected without wheel removal for drum
or disc measurement and the nominal size may be entered on the inspection
report. Any defect observed shall require disassembly of the wheel/brake
assembly for further inspection and measurement, and additional fees may be
applied.
Agency Note:
An excessive “lip” (area at the extreme inner or outer friction surface edge
that is higher than the rest of the surface) present on a brake rotor or brake
drum, is a visual indication of disc or drum wear, which would require
disassembly for measurement.
(3) Motorcycle
Mechanical Type Drum Brakes. These types
of brake systems are not required to be disassembled for inspection unless,
during a road test, a brake malfunction is indicated. If disassembly is
required, the brake systems shall be inspected utilizing the procedures
required in this regulation.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Disc brake rotor:
|
|
(i) Has a crack on
the friction surface extending to the inner or outer edge of the rotor;
|
|
(ii) Has a
substantial crack anywhere on the disc that can be felt by hand when
physically touched;
|
|
(iii) Has mechanical
damage, or rust to the extent that pitting is present;
|
|
(iv) Friction surface
is contaminated with oil, grease, brake fluid, or other friction-reducing
substances;
|
|
(v) Thickness of disc
is less than the manufacturer's recommended specification. If the
manufacturer does not provide a “discard” specification, the “machine to”
specification shall be used as the minimum thickness specification;
|
|
(vi) Disc is warped
or has excessive runout causing brake pulsation;
|
|
(vii) Disc is
designed for “racing”, or “off-road use”; or
|
|
(viii) Has a ceramic
disc brake rotor that does not meet the manufacturer’s minimum specification.
|
|
(b) Brake drum:
|
|
(i) Is cracked on the
friction surface extending to the inner or outer edge of the drum;
|
|
(ii) Has any external
crack;
|
|
(iii) Has any
substantial crack anywhere on the drum that can be felt by hand when
physically touched;
|
|
(iv) Has mechanical
damage or corrosion to the extent that pitting is present;
|
|
(v) Has a friction
surface contaminated with oil, grease, brake fluid, or other
friction-reducing substances;
|
|
(vi) Inside drum
diameter is greater than the manufacturer's specifications. If the
manufacturer does not provide a “discard” specification, the “machine to”
specification shall be used as the maximum diameter;
|
|
(vii) Is warped or has excessive runout causing
brake pulsation; or
|
|
(viii) Is designed
for “racing”, or “off-road use”.
|
H. Brake Shoe and Disc
Pad Lining. Inspect the condition, and measure the thickness of disc brake pad
lining, or drum brake shoe at the thinnest visible area of the material. Air
drum brake shoe lining is measured at the center of the brake shoe. Inspect
disc pad lining or brake shoe lining material for loose attachment to the
backing material. Corrosion of the backing material may cause the lining to
lift away from the backing material (lining jacking), which causes the lining
to not be firmly attached. Inspect for broken linings or cracks that can be
felt when physically touched by hand, contamination, or visible excessive
uneven lining wear. Heat cracks in bonded linings that cannot be felt when
physically touched by hand are not cause for rejection if the lining is
securely attached to the backing material. Inspect wire-backed lining for wire
showing on the surface of the lining. School vehicle brake inspection requires
that all wheels be removed for visual inspection and measurement of brake shoe
linings. Vehicles that are equipped with an air brake system with inspection
ports, or without backing plates to allow measurement of brake lining and
visual inspection of the friction components, may be inspected without removal
of the wheels. Conventional motorcycle disc brake equipment is accessible for
inspection without wheel removal. Vehicles not so equipped shall have all
wheels removed to inspect all brake components.
(1) Hydraulic,
Electric, and Mechanical Brake Shoe and Disc Pad Lining. The manufacturer’s
minimum thickness shall be used if available, however, under no circumstance
may a disc pad lining be less than 4/32 of an inch, or a riveted disc pad be
less than 4/32 of an inch above a rivet head. A brake shoe lining shall be not
less than 2/32 of an inch or less than 2/32 of an inch above a rivet head.
Inspect riveted disc pad or brake shoe lining for loose or missing rivets.
(Excludes motorcycle mechanical drum brakes that perform satisfactorily during
performance brake test)
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The thinnest
point of a bonded disc pad lining is less than manufacturer’s specification,
or less than 4/32 of an inch over a rivet head of a riveted lining;
|
|
(b) The thinnest
point of a bonded brake shoe lining is less than 2/32 of an inch or less than
2/32 of an inch above a rivet head on a riveted lining unless the thickness
is specified as greater by the manufacturer;
|
|
(c) A rivet is loose
or missing in disc pad or shoe lining material;
|
|
(d) A bonded disc pad
or shoe lining material is not firmly attached to the backing material;
|
|
(e) The brake lining
material is contaminated by oil, grease, brake fluid, or other
friction-reducing substances;
|
|
(f) A disc brake pad
or brake shoe lining is cracked and the crack can be physically felt when
touched by hand; or
|
|
(g) A disc brake pad
or brake shoe lining is worn excessively uneven.
|
(2) Air Brake Shoe and
Disc Pad Lining. The minimum thickness of an air disc pad lining can be no less
than 4/32 (1/8) of an inch. A steering axle air brake shoe lining with a
continuous strip of lining shall be no less than 6/32 (3/16) of an inch, or a steering
axle air brake shoe lining with separated lining material be no less than 8/32
(¼) of an inch at the center of the shoe. Non-steering axle air brake shoe
lining with separated lining material can be no less than 8/32 (¼) of an inch
at the center of the shoe.
|
Reject
Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The thinnest
point of an air brake disc pad lining is less than 1/8 (4/32) of an inch;
|
|
(b) The thinnest
point of an air brake shoe lining measured at the center of the shoe is:
|
|
(i) A steering axle
air brake shoe with a continuous lining is less than 3/16 (6/32) of an inch;
|
|
(ii) A steering axle
air brake shoe with separated linings is less than ¼ (8/32) of an inch; or
|
|
(iii) A non-steering
axle air brake shoe is less than ¼ (8/32) of an inch;
|
|
(c) An air disc brake
pad or air brake shoe lining is worn excessively uneven;
|
|
(d) An air-bonded
disc pad or air shoe lining material is not firmly attached to the backing
material;
|
|
(e) A rivet is loose
or missing in an air brake lining material;
|
|
(f) An air disc brake
pad or air brake shoe lining is cracked so that the crack can be physically
felt by hand; or
|
|
(g) The air brake
lining material is contaminated by oil, grease, brake fluid, or other
friction-reducing substances.
|
(3) Motorcycle Brake
Shoe and Disc Pad Lining. The manufacturer’s published minimum thickness shall
be used if available, however, under no circumstance may a bonded disc pad or
brake shoe lining be less than 2/32 of an inch. A riveted disc pad or a riveted
brake shoe lining shall not be less than 2/32 of an inch above a rivet head.
Motorcycles equipped with brake wear limit indicators shall be inspected using
the replacement reference mark indicators. Motorcycle type drum brakes are not
required to be disassembled for inspection unless, during a road test, a brake
malfunction is indicated. Three-wheeled multipurpose vehicles and motorcycles
equipped with automotive type brake systems shall be inspected utilizing the
procedures required for hydraulic brake systems as detailed in these
regulations.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The thinnest
point of a riveted disc pad lining is less than 2/32 of an inch over a rivet
head unless the minimum thickness is specified as greater by the
manufacturer;
|
|
(b) The thinnest
point of a bonded disc pad lining is less than 2/32 of an inch unless the
minimum thickness is specified as greater by the manufacturer;
|
|
(c) A disc brake pad
or brake shoe lining is worn excessively uneven;
|
|
(d) Drum brake wear
reference marks indicate unsafe or replacement needed;
|
|
(e) The thinnest
point of a bonded brake shoe lining is less than 2/32 of an inch unless the
minimum thickness is specified as greater by the manufacturer;
|
|
(f) The thinnest
point of a riveted brake shoe lining is less than less than 2/32 of an inch
above a rivet head unless the thickness is specified as greater by the
manufacturer;
|
|
(g) A bonded disc pad
or shoe lining material is not firmly attached to the backing material;
|
|
(h) A rivet is loose
or missing in disc pad or shoe lining material;
|
|
(i) A brake lining
material is contaminated by oil, grease, brake fluid, or other
friction-reducing substances; or
|
|
(j) A disc brake pad
lining or brake shoe lining is cracked so that the crack can be physically
felt by hand.
|
I. Brake Mechanical
Components. Brake mechanical components include the service brake mechanical
linkage, parking brake mechanical linkage, and all manual controls on vehicles
equipped for physically challenged persons. Inspect for missing, damaged, rusted,
inoperative, or otherwise defective linkage components. Inspect for restriction
of disc brake pad or brake shoe movement. Inspect the service and parking brake
pedals for missing, damaged, or worn non-slip surfaces, or rubber pads, as
applicable. Inspect the pedal shaft and bushings or bearings for high friction
or excessive wear. Vehicles with brake application systems other than air
brakes shall have all wheels removed to inspect all brake components. Air brake
systems equipped with backing plates, or without inspection ports/slots to
allow for visual inspection of brake components shall have all wheels removed
to inspect all brake components.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) A brake spring,
retainer, linkage, rod, cable or cable housing, pivot bushing or bearing,
mount, or other mechanical brake component is missing, damaged, rusted, or
otherwise inoperative or defective;
|
|
(2) The disc brake
pad or brake shoe movement is restricted due to mechanical component defect;
|
|
(3) The service or
parking brake pedals are missing rubber pads, or are not otherwise equipped
with a non-slip contact surface when applicable; or
|
|
(4) The pedal shaft,
bushings, or bearings have high friction or are worn excessively.
|
J. Parking Brakes. A parking brake is not an emergency brake
although the two functions may use the same brake equipment. Parking brakes
function to hold a vehicle stationary when the vehicle is not in motion. Set the
parking brake firmly and check the ability of the parking brake to hold the
vehicle. A parking brake shall hold a stopped vehicle firmly on any road grade
and remain applied until released. Vehicles that are equipped with parking
brake systems separate from the service brake system are not required to be
disassembled for inspection. If equipped with a parking brake warning light, it
shall function as designed.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The brake fails
to hold the vehicle on any road grade on which it is operated;
|
|
(2) The parking brake
does not remain applied, or will not properly release;
|
|
(3) The parking brake
components are damaged, loose, or worn out;
|
|
(4) The parking brake
friction components are contaminated with grease, or coated with other
friction-reducing substances; or
|
|
(5) The parking brake
warning lamp does not perform a self-check when the ignition system is
activated or does not function as originally designed if equipped.
|
K. Emergency Brake
Systems. Emergency brake systems are designed to stop a vehicle in motion. The
emergency brake may operate using the parking brake system, the service brake
system, or a separate brake system. To inspect, fully apply the operating control,
or deplete the pressure from a spring brake system to actuate the emergency
brake system, and observe if the emergency brake is mechanically engaging.
Fully release the operating control or restore pressure to a spring brake
system to release the emergency brake system and observe if the emergency brake
is fully releasing. The emergency brake shall be capable of stopping the
vehicle while in motion. This function may be inspected while the emergency
brake is engaged and attempting to move the vehicle. If the vehicle cannot be
moved, then no further inspection is required. A trailer of 3,001 pounds (1,361
kg) GVWR or more and any other trailer equipped with brakes shall be equipped
with an emergency brake system to stop the vehicle in the event of a disconnect
from the towing vehicle.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The emergency
brake does not fully engage when applied;
|
|
(2) The emergency
brake does not fully disengage when released;
|
|
(3) The emergency
brake is not capable of stopping the vehicle;
|
|
(4) During
disassembly, any emergency brake component is damaged, missing, or
excessively worn;
|
|
(5) Emergency brake
friction components are contaminated with grease, or coated with other
friction-reducing substances;
|
|
(6) Trailer with
brakes is not equipped with a functioning emergency brake; or
|
|
(7) Trailer emergency
brake does not stay applied for at least 15 minutes after activation.
|
L. Anti-Lock Brake
Systems. Anti-lock brake systems
automatically control the degree of rotational wheel slip during braking by
sensing the wheel rotational speed and modulates the pressure to the service
brake to prevent wheel lock-up during braking. A vehicle manufactured with an
anti-lock brake system in conjunction with electronic stability control under
the provisions of 49 CFR §571.126 or a vehicle equipped with anti-lock brake
system under the provisions of 49 CFR §393.55. Antilock brake systems for
commercial vehicles shall be maintained with the system in operational
condition, as designed by the manufacturer. Inspect for the presence and the
operation of anti-lock brake system warning light during system self-diagnostic
check. Inspect for activation of anti-lock brake system warning light during
operation of the vehicle that would indicate a fault or failure in the system.
Inspect anti-lock brake systems for missing, loose, damaged, worn, or
improperly mounted components, or the system is disconnected, disabled, or
removed.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The anti-lock
brake system warning light fails to light or function as designed during
self-diagnostic check;
|
|
(2) The anti-lock
brake system warning light remains lit indicating a system fault or
failure;
|
|
(3) The anti-lock
brake system warning light activates during operation of vehicle;
|
|
(4) The anti-lock
system has missing, loose, damaged, worn, or improperly mounted components;
or
|
|
(5) The anti-lock
brake system is disconnected, disabled, or removed.
|
M. Trailer Brake System
Requirements. Trailers up to 3,000 pounds (1,360 kg) GVWR are not required to
be equipped with brakes. Trailers 3,001 pounds (1,361 kg) GVWR to 10,000 pounds
(4,536 kg) GVWR shall be equipped with brakes on all wheel positions of at
least one axle. Trailers 10,001 pounds (4,536 kg) GVWR and over shall be
equipped with brakes on all wheel positions of all axles. A trailer that is
equipped with brakes shall be inspected to include the entire brake system,
which shall meet the standards of this regulation. A trailer 3,001 pounds
(1,361 kg) GVWR and over, and any trailer equipped with brakes shall be
equipped with an emergency brake system to stop the vehicle in the event of a
disconnect from the towing vehicle.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) A trailer 3,001
pounds (1,361 kg) GVWR to 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg) is not equipped with
brakes on all wheel positions of at least one axle;
|
|
(2) A trailer 10,001
pounds (4,536 kg) GVWR and over is not equipped with brakes on all wheel
positions of all axles; or
|
|
(3) A trailer brake
system does not meet the standard of this regulation.
|
.07 Wheels, Tire
Pressure Monitoring, and Tires.
A. Wheels. Inspect for
minimum wheel rating as specified by the vehicle manufacturer. This minimum
rating shall include tire type, design, rim diameter, rim width, and load
rating. Inspect the wheels, nuts, studs or wheel bolts, and tire inflation
valve, for missing, damaged, mismatched, or improperly installed or tightened
conditions. Wheel nuts or wheel bolts shall engage the threads of the
corresponding component to a depth that is at least equal to the diameter of
the wheel nut or bolt. For example, a ½ inch nut shall engage the corresponding
stud for at least ½ inch of depth. All wheels and associated components shall
be approved for on-road usage. Wheels shall be stamped or marked with Specialty
Equipment Market Association (SEMA), Japan Light Alloy Wheel (JWL), or DOT to
indicate the manufacturer’s compliance with federal standards for on-road usage
approval. Wheel adapters stamped or
marked in the same manner as approved wheels are permitted, but homemade
adapters are not approved. Wheel spacers are not approved for use. Any wheel or
component marked for “racing”, off-highway use only”, or other restricted use
shall be prohibited. Wheels and rims equipped with lock ring type retainers
shall also be inspected for missing, damaged, mismatched, or improperly
installed or tightened conditions. Multi-piece wheel or rim locking ring gap
shall meet the manufacturer’s specifications, or if the specification is not
available, the end gap shall not be less than 1/8 inch or 3mm.

|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The wheels are
damaged, mismatched, or not size or width recommended by the manufacturer;
|
|
(2) The wheels are
improperly installed or not correctly tightened;
|
|
(3) The wheel nuts,
studs, or wheel bolts are missing, damaged, mismatched, not of the proper
type, or improperly installed or tightened as required by this regulation;
|
|
(4) The wheel or tire
inflation valve is damaged, or has any other condition that would allow tire
air pressure to escape, or would prevent air pressure from being adjusted in
the tire assembly;
|
|
(5) The wheel or
wheel adapter, is not stamped or marked to indicate an approved component
design;
|
|
(6) A wheel or rim
lock ring component is missing, damaged, mismatched, or improperly installed;
or
|
|
(7) Multi-piece wheel
or rim locking ring gap shall meet the manufacturer’s specifications, or if
the specification is not available, the end gap shall not be less than 1/8
inch or 3mm.
|
B. Tire Pressure
Monitoring. The requirements for tire pressure monitoring are set forth in 49
CFR §571.138. Vehicles manufactured with tire pressure monitoring systems shall
be maintained with the system in operational condition, as designed by the manufacturer.
Inspect for the presence and the operation of tire pressure monitoring system
warning light during system self-diagnostic check. Inspect for activation of
tire pressure monitoring system warning light during operation of vehicle that
would indicate a fault or failure in the system. Inspect tire pressure
monitoring system for missing, loose, damaged, worn, or improperly mounted
components, or the system is disconnected, disabled, or removed.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The tire pressure
monitoring system warning light fails to function as designed during
self-diagnostic check;
|
|
(2) The tire pressure
monitoring system warning light is illuminated, indicating a system fault or
failure;
|
|
(3) The tire pressure
monitoring system warning light activates during operation of vehicle;
|
|
(4) The tire pressure
monitoring system has missing, loose, damaged, worn, or improperly mounted
components; or
|
|
(5) The tire pressure
monitoring system is disconnected, disabled, or removed.
|
C. Tire Size,
Construction, and Condition.
(1) Inspect for minimum
tire size and type as specified by the vehicle manufacturer. This minimum size
shall include required rim diameter, tread width, overall tire diameter, load
range rating, and construction type as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
Differences in brand or tread design or tread pattern by axle is not cause for
rejection. Tire size changes that do not require reduction of the wheel
diameter, tread width, overall tire diameter, load rating, or construction
type, and are compliant otherwise may be permitted. Visually inspect for
mismatching of tire construction types. Vehicle shall be equipped with tires
with the same type of construction at each wheel position. Vehicles equipped
with dual wheels may be equipped with tires of different construction on
separate axles. Tire circumference size shall be within 85 percent of all other
tires unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer of the vehicle. Dual wheel
tire assemblies shall not exceed ½ inch difference in diameter of the paired tires.
Dual wheel vehicles may be equipped with tires of a different construction on
separate axles.
(2) Inspect for tire
wear, tread cuts, cracks, bumps, bulges, fabric breaks, exposed or damaged body
cords. Inspect for improperly regrooved or recut tires. Visually inspect for
restricted usage marking on tire. Inspect the tire for proper size and load range
and compare to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Visually inspect, and
measure, if necessary, the tread of all tires in at least three locations
spaced equally around the circumference of the tire to locate the least amount
of tread. A tire tread wear indicator that contacts the road in any major
groove indicates low tread level without the necessity of performing a tire
tread measurement.
(3) Inspect for UV or
ozone degradation damage (weather cracking or checking) on tires. Cracks or
checking on tire sidewalls may be normal with age or may be caused by the
environment, improper tire maintenance, driver operating habits, cleaning or
tire treatment chemicals, or other adverse actions.
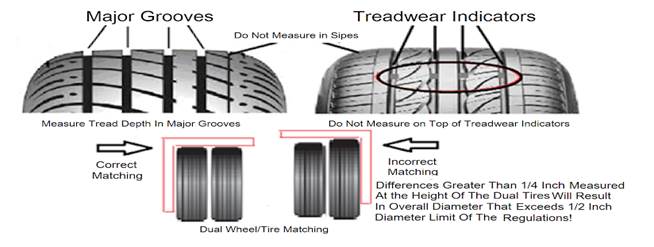
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) A tire is worn as
prescribed in this regulation:
|
|
(i) Less than 2/32 of
an inch is measured in any major groove, or a treadwear indicator in any
major groove contacts the road;
|
|
(ii) A motorcycle
tire is worn so that less than 2/32 inch tread is measured at the thinnest
point in any groove, or a treadwear indicator in any major groove contacts
the road; or
|
|
(iii) A steering tire
on a commercial vehicle over 10,000 pounds GVWR is worn so that less than
4/32 inch of tread is measured in a major groove;
|
|
(b) A tire is worn to
expose cords or belts, or has cuts, cracks, or damage in excess of one inch
in any direction, or that exposes the tire cords in the tread or sidewall;
|
|
(c) A tire has
visible unrepaired punctures, bumps, or bulges indicating partial failure or
separation of the tire structure. Tire is not mounted on the proper type or
width wheel as specified by the tire or vehicle manufacturer;
|
|
(d) Weather cracking
or checking is more than 1/16 inch or 2 mm in depth;
|
|
(e) A tire
circumference is not within 85 percent of the diameter or circumference of
all other tires unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer of the
vehicle;
|
|
(f) Dual wheel tires
are not within ½ inch diameter of each of the paired tires;
|
|
(g) The tires are not
the same type of construction, or as specified by the vehicle manufacturer;
|
|
(h) The tires are not
the same type of construction on the axle of a commercial vehicle;
|
|
(i) The tires do not
meet the load range rating for the actual vehicle weight (GVWR) or axle
weight (GAWR) as applicable;
|
|
(j) Equipped with a
tire that has rim diameter mounting size smaller than the manufacturer's
specified minimum, or equipped with a tread width, overall tire diameter, or
load range rating below the manufacturer's specified minimum;
|
|
(k) A regroovable
tire has been regrooved or recut below allowed groove depth, or cannot be
readily identified as regroovable;
|
|
(l) A tire is marked
“For farm use only”; “Off-highway use only”; “For racing use only”, “For
trailer use only” or any other restricted usage marking;
|
|
(m) A tire is
equipped with the incorrect type inner tube or inner tube protrudes from rim;
|
|
(n) A tube type tire
is equipped with the incorrect wheel liner, or the wheel liner protrudes from
the rim to contact other equipment;
|
|
(o) A metal studded
snow tire in Allegany, Carroll, Frederick, Garrett, and Washington counties
during period when prohibited (April 1 through October 31) reject in other
areas at any time; or
|
|
(p) A regrooved,
recapped, or retreaded tire is on the steering axle of a bus.
|
.08 Fuel Systems.
A. Motor Vehicle
Powertrain Fuel Systems. The fuel system includes any equipment or component
that provides for refueling of the vehicle, storing the fuel, conveying the
fuel to the engine, or controlling the flow of fuel into the engine. This
equipment includes the fuel filler components, the fuel tank and mounting
hardware, the fuel pump, and all necessary piping to carry the fuel from the
tank to the engine, including all components of the injection system or
carburetor. All components of the accelerator or any hand throttle or choke
shall be inspected for condition and function. Any fuel leakage indication
shall require visual inspection with the vehicle engine running to identify the
source of the fuel system leak.
B. Auxiliary Equipment
Fuel Systems. Auxiliary equipment systems include, but are not limited to
refrigeration units, auxiliary power supply units, pumps, generators, welders,
and any other fuel-powered auxiliary equipment permanently attached to a vehicle.
Visually examine the entire fuel system for the condition of the components,
and the use of approved components. Recreational vehicle equipment for heating
or cooking shall also be inspected for occupant safety. Auxiliary equipment is
not required equipment; however, fuel leakage is not acceptable for
environmental and safety issues, and therefore is cause for rejection.
C. Visually examine the
entire fuel system for leakage, presence of all required components, the use of
approved components, damage, corrosion to the extent that pitting is visible on
metal components, and proper mounting or securement of all fuel system
components. Inspect for proper operation of the accelerator, and any hand choke
or throttle, if equipped.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) There is fuel
leaking at any point in the fuel system;
|
|
(2) Any component of
the fuel system is missing or has been replaced with any component, not of
OEM design, or that is not at least equivalent to the OEM design;
|
|
(3) Any component of
the fuel system is damaged, deteriorated, collapsed, or corroded to the
extent that pitting or flaking is visible;
|
|
(4) Any component of
the fuel system is not properly mounted or secured as designed by the
manufacturer;
|
|
(5) The fuel tank cap
is missing, or capless system sealing is defective;
|
|
(6) The accelerator,
accelerator pedal, or other fuel control device does not function properly,
is damaged, or is replaced with any component that is not of OEM design, or
that is not at least equivalent to the OEM design; or
|
|
(7) The hand choke or
throttle does not function properly, is damaged, or is replaced with any
component that is not at least equivalent to the OEM design.
|
.09 Exhaust Systems.
A. Motor Vehicle
Powertrain Exhaust Systems. The exhaust system includes any equipment or
component that conveys vehicle exhaust gases from the engine of the vehicle
away from any operator or passenger of a vehicle. Exhaust system equipment
shall meet or exceed the OEM exhaust component equipment standards. Off-road,
racing, or other non-road vehicle approved exhaust equipment shall not be
allowed. The exhaust system must be securely fastened to the vehicle. Exhaust
system clamps, hangers, supports, seals and gaskets, and any other required
exhaust accessory shall be inspected for presence, function, condition, and
proper installation. A flexible exhaust pipe that does not leak is permitted.
Exhaust component placement regulated by emissions regulations require certain
equipment to remain in the original position and configuration. Alterations to
exhaust systems that affect the function or placement of emission control
equipment shall be prohibited. Heat shielding shall remain in place or be
replaced or repaired using shielding that meets or exceeds the OEM design.
Exhaust resonators are installed to supplement muffler effectiveness in the
reduction of exhaust sound levels to meet regulations and shall not be
eliminated. Certain vehicles are designed and not
manufactured with mufflers and meet exhaust sound levels without mufflers, and
are not required to be retrofitted with mufflers.
(1) A replacement
tailpipe that modifies the original discharge area of the exhaust, shall extend
to at least directly in front of the rearmost tire, and discharge beyond the
passenger compartment. Exhaust stacks on trucks and exhaust side pipes that are
equipped with heat shielding are acceptable so long as no part of this
regulation is violated.
(2) Motorcycle exhaust
shall discharge exhaust as originally designed, or if not as originally
designed, beyond the rearmost seating position of the vehicle, away from the
rider or passenger, and be equipped with heat shielding to prevent injury to
rider or passenger. Baffles inserted into exhaust piping are not suitable
replacements for mufflers.
(3) Exhaust System
Inspection. Visually inspect the entire exhaust system for approved equipment,
secure and proper mounting, deterioration, damage, and general condition.
Corroded areas shall be given particular attention. Manufacturer drainage holes
are not cause for rejection. Proper, non-leaking welded, or brazed repairs are
permitted. Any audible or visual indication of exhaust leakage or ineffective
equipment shall require inspection with the vehicle engine running as
applicable, to identify the source of the exhaust system leak.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The muffler is
missing, not approved, or not effective;
|
|
(b) The exhaust is
equipped with an exhaust cutout or similar device;
|
|
(c) Heat shielding,
as originally installed by the vehicle manufacturer or required by this
regulation, is missing, damaged, or not securely attached;
|
|
(d) Any exhaust
component that is not original or at least equivalent to the original has
damage or rust that allows exhaust gases to leak, does not properly discharge
exhaust gases, or is not securely attached to the vehicle;
|
|
(e) The tailpipe does
not discharge as originally designed or does not extend to at least directly
in front of the rearmost tire, and discharge beyond the passenger
compartment;
|
|
(f) There are loose
or leaking seams or joints in any exhaust system component or coupling, or
any fastener or clamp is missing or damaged;
|
|
(g) Temporary repairs
have been made to any exhaust system component, or the system is not properly
mounted to prevent excessive exhaust system movement;
|
|
(h) Any part of the
exhaust system passes through the passenger compartment, or there are any
leaks in the heat exchange system that warms the interior of the vehicle if
equipped;
|
|
(i) The tailpipe end
is pinched or obstructed, or any part of the exhaust system is located or
exposed in a manner that a person may be burned or injured;
|
|
(j) A vehicle is
equipped with exhaust stacks or exhaust side pipes without effective mufflers
and heat shielding;
|
|
(k) A motorcycle
exhaust has been modified from OEM design; and
|
|
(i) Does not
discharge exhaust beyond the rearmost seating position of the vehicle, away
from the rider or passenger;
|
|
(ii) Is not equipped
with a muffler, if originally equipped;
|
|
(iii) Is equipped
with baffles in exhaust piping other than as originally equipped; or
|
|
(iv) The exhaust
system component is missing, not approved, or not effective;
|
|
(l) The function or
the installed location of exhaust equipment has been altered to affect the
function or placement of emission control equipment.
|
B. Commercial Vehicle
Exhaust System. Commercial vehicle exhaust shall not be located where its
location would likely result in burning, charring, or damaging the electrical
wiring, the fuel supply, or any combustible part of the motor vehicle. No
exhaust system shall discharge to the atmosphere at a location immediately
below the fuel tank or the fuel tank filler pipe. No part of the exhaust system
shall be temporarily repaired with wrap or patches.
(1) The exhaust of a
truck or truck tractor shall discharge to the atmosphere at a location to the
rear of the cab, if the exhaust projects above the cab, at a location near the
rear of the cab. No part of the exhaust system shall leak or discharge at a point
forward of or directly below the driver/sleeper compartment. The exhaust outlet
may discharge above the cab/sleeper roofline.
(2) The exhaust of a
bus powered by a gasoline engine shall discharge to the atmosphere at or within
6 inches forward of the rearmost part of the bus.
(3) The exhaust system
of a bus using fuels other than gasoline shall discharge to the atmosphere
either:
(a) At or within 15
inches forward of the rearmost part of the vehicle; or
(b) To the rear of all
doors or windows designed to be open, except windows designed to be opened
solely as emergency exits.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(i) The muffler or
resonator is missing, not approved, or not effective;
|
|
(ii) The exhaust is
equipped with an exhaust cutout or similar device;
|
|
(iii) Heat shielding,
as originally installed by the vehicle manufacturer or required by this
regulation, is missing, damaged, or not securely attached;
|
|
(iv) Any exhaust
component is not original or at least equivalent to the original, has damage
or rust that allows exhaust gases to leak, or is not securely attached to the
vehicle;
|
|
(v) Truck or truck
tractor exhaust does not discharge to the rear of the cab, or discharges
forward or directly below the driver/sleeper compartment;
|
|
(vi) A gasoline
powered bus does not discharge within at least 6 inches of the rearmost part
of the vehicle;
|
|
(vii) A bus using
fuels other than gasoline does not discharge within at least 15 inches of the
rearmost part of the vehicle, or discharges beneath a door or window designed
to be open, except for windows solely designed as emergency exits;
|
|
(viii) There are
loose or leaking seams or joints in any exhaust system component or coupling,
or any fastener or clamp is missing or damaged;
|
|
(ix) Temporary
repairs have been made to any exhaust system component, or the system is not
properly mounted to prevent excessive exhaust system movement;
|
|
(x) Any part of the
exhaust system passes through the passenger compartment, or there are any
leaks in the heat exchange system that warms the interior of the vehicle if
equipped;
|
|
(xi) The tailpipe end
is pinched or obstructed, or any part of the exhaust system is located or
exposed in a manner that a person may be burned or injured;
|
|
(xii) A vehicle is
equipped with exhaust stacks or exhaust side pipes without effective mufflers
and heat shielding;
|
|
(xiii) The exhaust
system discharges to the atmosphere at a location immediately below the fuel
tank or the fuel tank filler pipe; or
|
|
(xiv) The function or
the installed location of exhaust equipment has been altered to affect the
function or placement of emission control equipment.
|
C. Auxiliary Equipment
Exhaust Systems. Auxiliary equipment
systems include, but are not limited to stoves, heaters, refrigeration units,
auxiliary power supply units, pumps, generators, welders, and other fuel powered
auxiliary equipment permanently attached to a vehicle. Visually examine the
exhaust system for the condition of the components, the use of approved
components, damage, corrosion to the extent that exhaust leaking is present,
and proper and secure mounting. Recreational vehicle equipment for heating or
cooking shall be equipped with proper venting to the exterior of the vehicle to
prevent asphyxiation of occupants. Auxiliary equipment is not required
equipment; therefore, exhaust system deficiencies are not cause for rejection.
Any deficiency shall be noted during the inspection and the owner or agent for
the vehicle will be advised not to operate the equipment until proper repairs
have been made.
|
Record Equipment Deficiency and Advise
the Owner or Agent if:
|
|
(1) The muffler or
resonator is missing, not approved, or not effective;
|
|
(2) The exhaust is
equipped with an exhaust cutout or similar device;
|
|
(3) Heat shielding,
as originally installed by the equipment manufacturer or required by this
regulation, is missing, damaged, or not securely attached;
|
|
(4) Any exhaust
component not original or at least equivalent to the original has damage or
rust that allows exhaust gases to leak, does not properly discharge exhaust
gases, or is not securely attached to the equipment;
|
|
(5) There are loose
or leaking seams or joints in any exhaust system component, any fastener or
clamp is missing or damaged;
|
|
(6) Temporary repairs
have been made to any exhaust system component, or the system is not properly
mounted to prevent excessive exhaust system movement;
|
|
(7) Any part of the
exhaust system leaks, or is not equipped with proper heat shielding;
|
|
(8) The tailpipe end
is pinched or obstructed, or any part of the exhaust system is located or
exposed in a manner that a person may be burned or injured;
|
|
(9) The function or
the installed location of exhaust equipment has been altered to affect the
function or placement of emission control equipment; or
|
|
(10) A stove, heater,
or refrigeration unit on a recreational vehicle does not properly exhaust or
vent to the exterior of the vehicle.
|
D. School Vehicle
Exhaust Systems. The inspection of school vehicle exhaust systems requires that
the additional protection and placement criteria required due to their unique
use be inspected. This includes component design, placement, and heat shielding
required in the school vehicle construction standards. An OEM flexible pipe or
its equivalent up to 24 inches in length is allowed at the front of the exhaust
system at or near the turbocharger. The exhaust system may not pass within 12
inches of a gasoline fuel tank or its connections without proper heat
shielding. The exhaust system of a Type I School Vehicle may not pass within 12
inches of a flexible brake or diesel fuel line without proper shielding. The
tailpipe of a Type II School Vehicle may exit behind the rear wheel or to the
left or right of the rear emergency door and shall not exit under a fuel
filler. Exhaust systems shall not be located under the emergency exit.
|
Reject
Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The exhaust pipe
is not of an OEM nonflexible 16-gauge material except as authorized by this
regulation;
|
|
(2) The muffler is
missing, not approved, or not effective;
|
|
(3) The exhaust is
equipped with a cutout or similar device;
|
|
(4) Heat shielding is
not OEM or equivalent, is missing, damaged, or not securely attached;
|
|
(5) An exhaust
component is not OEM or equivalent, or is not securely attached to the
vehicle;
|
|
(6) The exhaust
system discharges exhaust gases under an emergency exit;
|
|
(7) The tailpipe of a
Type II School Vehicle exits under a fuel filler;
|
|
(8) There are loose
or leaking exhaust seams or joints, or any fastener or clamp is missing or
damaged;
|
|
(9) Temporary repairs
have been made to any exhaust system component;
|
|
(10) Any part of the
exhaust system passes through the passenger compartment;
|
|
(11) The exhaust is
pinched or obstructed, or any part of the system is located or exposed in a
manner that a person may be injured; or
|
|
(12) The function or
the installed location of exhaust equipment has been altered to affect the
function or placement of emission control equipment.
|
.10 Emissions Control
Systems.
A. Emissions Equipment
Inspection. Emissions equipment conforming to United States EPA regulations for
the control of vehicle emissions originally installed by a vehicle or engine
manufacturer as applicable by year, model, engine, or application, as required
by 40 CFR §86 and in COMAR 11.14, shall be in its original location and
configuration. Each vehicle or engine shall be inspected for the emission
equipment identified by the emissions label in the engine compartment or on the
engine, or by published data from the manufacturer which indicates the
emissions equipment originally installed. Emission equipment replacement shall
be performed using only OEM equipment during the time and mileage limitations
regulated by 40 CFR §86 and in COMAR 11.14 and within the manufacturer’s
warranty guidelines. Emission equipment replacement beyond these specified time
and mileage limitations may be performed using OEM or equivalent equipment.
Fumes, smoke, or particulate matter emitted by a vehicle engine may indicate emission
equipment failure or powertrain problems that may cause emission control system
failure. Illumination of the Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) may be emission
failure related. Vehicles equipped with 2-cycle engines emit greater amounts of
smoke from the exhaust system due to the gas/oil ratio mixture. Smoke emitted
by 2-cycle engines for more than 10 seconds is excessive and does not meet the
requirements of this regulation.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Not equipped with
the required emission control equipment in its original location and
installed in the original configuration;
|
|
(2) Any emission
component is replaced with an aftermarket component during the time and
mileage requirements described in this regulation;
|
|
(3) Any emission
equipment component is replaced with an unapproved component;
|
|
(4) Fumes, smoke, or
particulate matter is emitted by the engine that obscures persons or objects
from a clear rear view; or
|
|
(5) A 2-cycle engine
or a 2-stroke equipped vehicle emits smoke that obscures persons or objects
from a clear rear view for more than 10 seconds.
|
B. OBD II Inspection.
The On-Board Diagnostic System (OBD II) compliant vehicle MIL shall be observed
for function and illumination during inspection, and the owner/agent for the
vehicle advised of potential emission equipment malfunction.
|
Record MIL Status and Advise the Owner
or Agent if:
|
|
(1) The MIL does not
illuminate during “self-check” inspection; or
|
|
(2) The MIL is
illuminated with the engine running.
|
.11 Powertrain and
Powertrain Components.
A. The powertrain
includes the engine, transmission, drive axles, and connecting equipment
components. Any mount or attachment devices that retain or help to retain the
engine, transmission, or drive axle components in their proper place on the
vehicle are also components of the powertrain. Drive shafts, universal joints,
constant velocity shafts and joints, carrier bearings and supports, and slip
joints for connecting drive shafts to drivetrain components are also components
of the powertrain. Inspect the powertrain and related components for equipment
not designed and approved for on-road use, or that is missing, loose, or
damaged.
B. Seals and gaskets on
powertrain components are designed to prevent the loss of coolant fluids,
lubrication fluids or greases, and contamination of powertrain fluids or
greases from external sources. The loss of fluids or greases from any
drivetrain component may cause a vehicle fire, powertrain damage, or
contamination of other components or systems that would adversely affect the
safe operation of the vehicle.
C. Inspect the fluid
levels in powertrain equipment and related components. Advise vehicle
owner/agent of any indication of leakage.
D. Powertrain
Condition. Inspect engine, transmission, drive axle, or other powertrain
component mounts for proper attachment, damage, dislocation, or for equipment
that is not designed and approved for on-road use. Accessory drive belts and
tensioners shall be inspected for excessive wear or damage, and proper tension.
E. School Vehicle
Drivetrain. Each segment of the drive shaft shall be equipped with a suitable
guard to prevent accident or injury in the event of fracture or disconnection.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The engine,
transmission, drive axle, or other powertrain component mount or attachment
is loose, damaged, dislocated, or is not designed and approved for on-road
use;
|
|
(2) The drive shaft,
universal joint, constant velocity shaft, constant velocity joint, carrier
bearing or support, slip joint, drive chain or drive belt is loose, damaged,
dislocated, or is not designed and approved for on-road use;
|
|
(3) The accessory
drive belts are excessively worn, damaged to affect operation, or loose;
|
|
(4) The tensioner
pulley, idler pulley, or other accessory drive belt pulley is excessively
worn, damaged to affect operation, or loose;
|
|
(5) The engine,
transmission, drive axle, or related component has any class of leakage
present, and the fluid operating level is below the manufacturer’s
recommended minimum level;
|
|
(6) The engine,
transmission, drive axle, or powertrain component has a Class-3 leakage of
coolant, lubrication, grease, or other operating fluid so that fluid or
grease is contaminating other components, presents a fire hazard, or is
leaking onto the road surfaces;
|
|
(7) The engine,
transmission, drive axle, or powertrain component is malfunctioning to the
extent that the vehicle cannot be driven;
|
|
(8) Continuous fumes
or smoke that obscures persons or objects from a clear rear view are being
emitted by the powertrain of the vehicle; or
|
|
(9) A school vehicle
drive shaft is not equipped with a suitable guard on every segment of the
drive shaft as required by this regulation.
|
.12 Body Components.
A. Hood, Hinges, and
Latches. Inspect for the presence and operation of hinges, latches, safety
latches, and hood latch release mechanisms. Stud and safety pin-type latches
are acceptable provided force is necessary to overcome the retention feature of
the pin to remove it from the stud. The hood shall cover the engine
compartment. If equipped with a hood air scoop or hood bubble, the maximum
height shall not extend higher than 1/3 of the vertical height of the
windshield. On cab-over-engine vehicles inspect the cab floor, hinges, and
latches as hood components, as they provide the engine coverage in place of a
hood.

|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The hood/engine
cover does not fully close and latch;
|
|
(2) The hood/engine
cover hinge, latch or hood safety latch is missing, loose, or otherwise not
functioning as designed;
|
|
(3) The hood/engine
cover remote release is missing, or damaged to the extent that it does not
function as designed;
|
|
(4) The hood/engine
cover does not cover the engine compartment; or
|
|
(5) The hood air
scoop or bubble is higher than 1/3 the vertical height of the windshield.
|
B. Fenders and Flaps.
(1) Fender inspection
shall include condition, mounting, and coverage of wheels and tires. Vehicles
shall be equipped with fenders that provide at least the same wheel and tire
coverage as originally designed by the manufacturer. Modifications of fenders
to accommodate tire, wheel, or suspension changes are permitted provided that
modifications provide coverage of wheels and tires equal to or exceeding that
provided by the vehicle manufacturer and do not violate any part of this
regulation otherwise. The top of all fenders shall extend outward from the body
to cover the top of wheels and tires. A rear fender is required on a
motorcycle, but a front fender is not required unless the motorcycle was
originally manufactured with a front fender.
(2) Many vehicles
provide coverage of wheels and tires with fender coverage being augmented by
the bumper covers, OEM fender extensions or flaps, or a combination of
components. Rear fenders are defined as the rear quarter panel of a vehicle
from the rearmost door opening rearward and from the window or trunk, or both,
opening downward to the extreme bottom edge, and shall include OEM components
that augment wheel and tire coverage.
(3) Protectors or flaps
required for rear coverage of wheels and tires shall have a ground clearance of
not more than 1/3 of the horizontal distance from the bottom edge of the
protector or flap to the centerline of the axle, provided, however, that no protector
or flap need be closer to the ground than 6 inches under any condition of
loading.
(4) Fender and Flap
Inspection. Inspect fenders for condition, presence, attachment, and damage. A
mere hole in a fender is not cause for rejection, however, any hole in a fender
that will allow exhaust fumes to enter the occupant compartment or is such that
jagged or sharp edges present a hazard to a pedestrian or passenger is cause
for rejection. Inspect for coverage of wheels and tires by fenders and related
components as required. The fenders and any augmented coverage shall be
constructed of substantial materials and shall be securely attached to the
vehicle. All edges shall be rolled or capped to eliminate sharp or jagged
edges. Fenders may not contact the tires during different vehicle attitudes. If
the bed of a light truck or van body has been changed, and wheel and tire
coverage is not provided by a fender or body, the vehicle shall be equipped
with flaps behind the rear tires. Uneven fitment or body lines may be
indications of improper attachment or hidden body damage present.
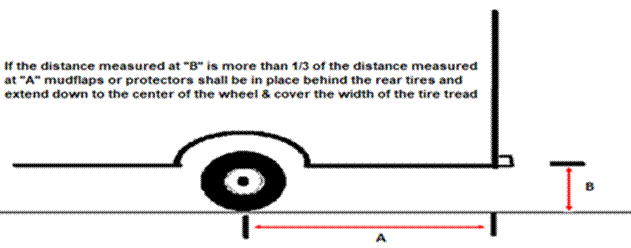
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The fender is not
OEM or equivalent to OEM, is missing, not securely attached, or is missing
components;
|
|
(b) The fender has
tears, sharp or jagged edges, or any hole or opening which would allow
exhaust fumes to enter the occupant compartment, or is jagged or has sharp
edges that present a hazard to persons;
|
|
(c) The fender
coverage does not equal or exceed the specifications provided by the vehicle
manufacturer;
|
|
(d) The fender
contacts tire during different vehicle attitudes; or
|
|
(e) The protector or
flap does not cover the width of the wheel and tire or extend to at least the
horizontal centerline of the wheel.
|
C. Doors, Hinges,
Handles, Latches, and Locks.
(1) Door Equipment
Inspection. Inspect the presence and operation of doors, hinges, latches,
safety latches, door latch release mechanisms, and door locks. Doors designed
for occupants to enter and exit a vehicle shall be equipped with safety
latches, interior door latch release mechanisms, and if equipped with door
locks, functioning interior lock mechanisms. Inspect all doors, hinges,
handles, latches, and interior locks for broken or missing, parts, equipment,
or components not certified for use with on-road vehicles, proper operation,
and improper adjustment. Electric push button or ring and cable means of
opening the door are acceptable provided they are readily accessible to operate
the door from both the interior and exterior of the vehicle. Electric door
locks that do not work, may be approved if the interior manual locks function
to lock and unlock passenger doors.
(2) Vehicles equipped
with both manual and electrical lock mechanisms may be certified as compliant
with this regulation if the interior manual lock functions without impediment
by the electrical mechanism. An electric lock mechanism is not required to function
if the manual lock is functional.
(3) Other doors for
storage or transportation of cargo, goods, or equipment shall be inspected to
ensure that the doors are securely attached to the vehicle and shut and latch
securely.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The passenger
door or door part is missing, has been modified from the original design, or
has been modified with components not certified for use with on-road
vehicles;
|
|
(b) The passenger
door is damaged, loosely attached, or latched and adversely affects the
operation of the door;
|
|
(c) The passenger
door handle or latch does not provide a means of readily opening the door
from both the interior and exterior of the vehicle;
|
|
(d) The passenger
door, hinge, handle, latch, or lock mechanism is not original equipment or
equivalent;
|
|
(e) The passenger
door interior lock does not lock and unlock;
|
|
(f) The passenger
door secondary or safety catch does not function properly;
|
|
(g) The passenger
door electric lock mechanism impedes the manual operation of a lock; or
|
|
(h) A cargo area door
or door part is missing, worn, or damaged so that the door is not securely
attached or will not securely close.
|
.13 Bumpers and Rear
Metal Frame.
A. Front bumper, rear
bumper, and rear metal frame shall be inspected for presence, broken or missing
components, abnormal protrusions or sharp edges, or other conditions that could
be hazardous to persons. Bumpers may be external and visible or hidden by
bumper covers. The bumpers shall be securely mounted to the vehicle and be
capable of absorbing a degree of impact equal to, or greater than the OEM
design. If equipped with any bumper that is not OEM, it shall be of equivalent
or greater strength than the OEM bumper. Inspect bumper height by measuring
from the level surface on which the vehicle stands to the bottom edge of the
main horizontal bar of the bumper, exclusive of any horizontal or vertical
extension bars or bumper guards. On vehicles equipped with soft bumper
covering, the measurement will be made on the reinforcing horizontal bar.
B. Passenger Vehicle.
Bumper shall be the original equipment or equivalent. Bumper covers are not
impact protection but may provide coverage of sharp edges or other hazardous
conditions and may also provide fender coverage for tires and therefore shall be
inspected as required by the regulations contained in this chapter, as
applicable.
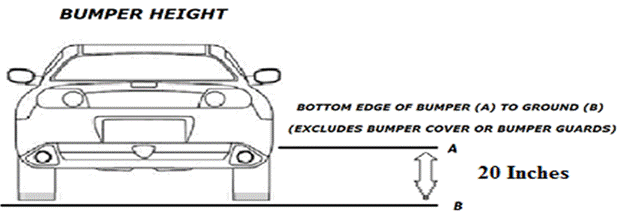
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The bumper is
missing, loose, has abnormal protrusions or sharp edges, or other conditions
that could be hazardous to persons;
|
|
(2) The bumper cover,
if equipped, is missing, loose, has abnormal protrusions or sharp edges, or
other conditions that could be hazardous to persons;
|
|
(3) The bumper is not
OEM or equivalent to OEM, or is not capable of absorbing a degree of impact
equal to, or greater than the OEM design;
|
|
(4) The bumper on a
passenger vehicle is higher than 20 inches from the road surface to the lower
edge of the major portion of the bumper; or
|
|
(5) The bumper
extends beyond the widest part of the vehicle.
|
C. Trailer or
Semitrailer 3,000 pounds (1,360 kg) GVWR or greater. Vehicle shall be equipped with a permanent
metal frame or bumper attached to the underside of the rear of the trailer. The
metal frame or bumper may not be wider than the body of the vehicle and shall
extend outward to the left and right sides of the vehicle as required in this
regulation. Low chassis vehicles, special purpose vehicles, or wheels back
vehicles constructed and maintained so that the body, chassis, or other parts
of the vehicle provide the rear end protection shall be considered to be in
compliance with this regulation. Pole trailers and pulpwood trailers are not
required to meet this regulation.
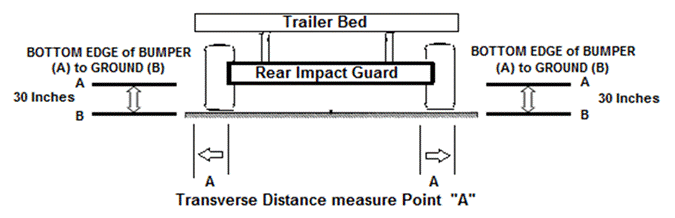
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The bumper, major
body assembly, or rear metal frame of a trailer 3,000 pounds (1,361 kg) GVWR
or more, exceeds the height for design model year as follows:
|
|
(a) A trailer
constructed after December 31, 1952 – exceeds 30 inches to the lower edge of
the frame or bumper; or
|
|
(b) A trailer
constructed on or after January 26, 1998 – exceeds 22 inches to the lower
edge of the frame or bumper.
|
|
(2) The bumper, major
body assembly, or rear metal frame of a trailer 3,000 pounds (1,361 kg) GVWR
or more, does not extend transversely towards the left and the right
outermost sides of the vehicle as follows:
|
|
(a) A trailer
constructed after December 31, 1952 – within 18 inches of the left and the
right sides of the vehicle; or
|
|
(b) A trailer
constructed on or after January 26, 1998 – within 4 inches of the left and
the right sides of the vehicle.
|
|
(3) The bumper, major
body assembly, or rear metal frame is missing, loose, has abnormal
protrusions or sharp edges, or other conditions that could be hazardous to
persons;
|
|
(4) The bumper, major
body assembly, or rear metal frame is not capable of absorbing a reasonable
degree of impact; or
|
|
(5) The bumper, major
body assembly, or rear metal frame extends beyond the widest part of the
vehicle.
|
D. Truck Chassis
Vehicle, Bus, and Multipurpose Vehicle 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg) GVWR and under.
The bumper shall be the original equipment or equivalent. A vehicle
manufactured with a reinforced body assembly to provide rear impact protection
shall be considered to be in compliance with this regulation, otherwise, the
vehicle shall be equipped with a rear bumper. Bumper covers are not impact
protection but may provide coverage of sharp edges or other hazardous
conditions, may also provide fender coverage for tires, and therefore shall be
inspected as required by the regulations contained in this chapter.
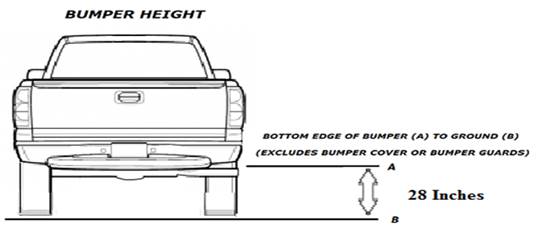
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The bumper, body
or if the body provides impact protection, is missing, loose, has abnormal
protrusions or sharp edges, or other conditions that could be hazardous to
persons;
|
|
(2) The bumper cover,
if equipped, is missing, loose, has abnormal protrusions or sharp edges, or
other conditions that could be hazardous to persons;
|
|
(3) The bumper, body
or if the body provides impact protection, is not capable of absorbing a
reasonable degree of impact;
|
|
(4) The bumper, body
or if the body provides impact protection, is higher than 28 inches from the
road surface to the lower edge of the major portion of the impact protection
or bumper; or
|
|
(5) The bumper, body
or if the body provides impact protection, extends beyond the widest part of
the vehicle.
|
E. Truck Chassis
Vehicle, Bus, and Multipurpose Vehicle 10,001 – 18,000 pounds GVWR. Exceptions:
truck tractors and vehicles engaged in drive-away or tow-away operations are
not subject to this regulation due to the specific design and purpose of the
vehicle which prevents compliance. A vehicle manufactured with a reinforced
body assembly to provide rear impact protection shall be considered to be in
compliance with this regulation, otherwise, the vehicle shall be equipped with
a rear bumper or rear metal frame. The rear bumper, major body assembly, or
rear metal frame may not be any wider than the width of the truck and may not
be more than 30 inches above the ground. The maximum transverse distance from
the widest part of the vehicle at the rear to the bumper or metal frame may not
exceed 18 inches. The provisions of this section do not apply to vehicles where
the installation of the required bumper or metal frame would prevent operation
of the vehicle for its designated purpose.
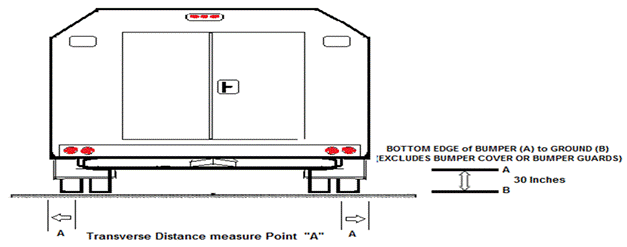
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The bumper, major
body assembly, or rear metal frame is missing, loose, has abnormal
protrusions or sharp edges, or other conditions that could be hazardous to
persons;
|
|
(2) The bumper, major
body assembly, or rear metal frame is not capable of absorbing a reasonable
degree of impact;
|
|
(3) The bumper, major
body assembly, or rear metal frame extends beyond the widest part of the
vehicle; or
|
|
(4) The bumper, major
body assembly, or rear metal frame does not extend to within 18 inches of the
left and right sides of the vehicle.
|
F. School Vehicle
Bumpers and Rear Metal Frame. Bumpers
are regulated on Type I and Type II school vehicles for material size, height,
width, and color. Rear bumpers shall extend beyond the rearmost part of the
body surface at least 1 inch, measured at the floor line.
(1) Type I School
Vehicle. The front bumper shall be of heavy-duty steel channel or equivalent,
at least 3/16 inch thickness and not less than a 9 inch face, painted black,
and shall extend around the outer edges of the fender. Bumper and bumper
supports shall be of sufficient strength to permit towing or pushing by another
vehicle without damage. The rear bumper shall be of 3/16 inch pressed steel
channel or equivalent and shall have not less than a 9 inch face. It shall wrap
around the back corners of the bus and shall extend forward at least 12 inches
measured from the rearmost point of the body at the floor line. The maximum
height of the rear bumper shall be no more than 30 inches when measured from
the bottom edge to the level surface upon which the unloaded vehicle stands.
(2) Type II School Vehicle. The front bumper shall
extend to protect the outer edges of the fenders. The front bumper shall
measure between 14 and 18 inches when measured from the bottom edge to the
level surface on which the unloaded vehicle stands. The rear bumper shall be of
3/16 inch-thick steel, or equivalent material, and have at least a 7 inch face.
The rear bumper shall be attached directly to the chassis frame at a height
between 14 and 18 inches from the bottom edge to the level surface upon which
the unloaded vehicle stands.
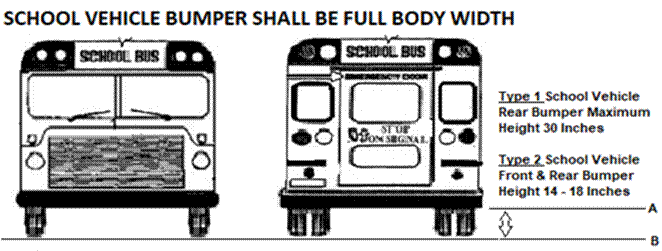
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The bumper is not
constructed of an approved material, or is not mounted to the vehicle as
required;
|
|
(b) The bumper is any
color other than black;
|
|
(c) The bumper is not
constructed and maintained using the required dimensions by type of vehicle,
or has sharp edges that could injure persons;
|
|
(d) The bumper is
missing, damaged, or otherwise not structurally able to absorb an impact, or
is not able to be towed or pushed by another vehicle;
|
|
(e) A Type I School
Vehicle rear bumper measured height exceeds 30 inches from the level surface
upon which the unloaded vehicle stands, or the bumper does not extend at
least 12 inches forward from the rearmost point of the body at the floor
line;
|
|
(f) A Type II School
Vehicle front or rear bumper measured height is not between 14 and 18 inches
when measured from the bottom of the bumper to the level surface upon which
the unloaded vehicle stands; or
|
|
(g) The rear bumper
of a school vehicle does not extend beyond the rearmost part of the body at
least 1 inch, measured at the floor line.
|
.14 Floor, Trunk,
Bulkhead, and Interior Engine Covers.
A. Enclosed motor
vehicle floor, trunk, and bulkhead shall be inspected for holes or corroded or
weakened conditions. Loose floor covering may present a hazard to occupants of
the vehicle and may expose electrical wiring to damage. Engine covers within the
occupant compartment of the vehicle shall be sealed against the entry of
exhaust gases or other fumes and firmly fastened down.
B. Open cockpit
autocycles are not required to meet the requirements to be sealed against the
entry of exhaust gases or other fumes.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The floor
(underside of vehicle and bulkhead), is cracked, has holes, or is corroded
through or weakened to cause a hazard to an occupant, affect the secure
mounting of seats, or permit exhaust gases or engine fumes to enter the
occupant compartment;
|
|
(2) The
trunk/underside of vehicle or cargo area is corroded out, contains holes or
openings, or permits exhaust gases or engine fumes to enter the occupant
compartment;
|
|
(3) The floor
covering is missing, cracked, curled, or worn, not properly sealed or
attached, presents a tripping hazard or exposes wiring to damage; or
|
|
(4) The interior
engine cover in the occupant compartment of the vehicle is not sealed against
the entry of exhaust gases or fumes or is not firmly fastened down.
|
C. School Vehicle
Interior Floor. Covering shall be the
required thickness of fire-resistant, nonskid rubber, permanently bonded to the
floor. There shall be a heavy-duty, white-nosed rubber wear plate where the floor
covering meets the steps.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The school
vehicle floor covering is not comprised of the proper material;
|
|
(2) The school
vehicle floor covering is missing, damaged, or not permanently bonded to the
floor;
|
|
(3) The school
vehicle floor joints or seams are not bonded, welded, or not covered by
approved strips or moldings; or
|
|
(4) The school
vehicle floor to step area is not equipped with heavy-duty
white-nosed wear plates as required.
|
D. Cargo Area Floor,
Sides, and Bulkhead. Cargo areas shall
be constructed of substantial materials and able to support the specified or
rated payload of the vehicle for cargo and prevent cargo from falling or spilling
from the vehicles. The floor of a vehicle designed to carry cargo that is
separate from a passenger compartment shall be inspected for holes, corroded,
or weakened conditions to ensure that cargo transported on or within the
vehicle does not fall or spill through the surface. Bulkheads and sides
designed to contain cargo or protect vehicle occupants shall be inspected for
hazardous or unsafe conditions. The supporting equipment to include the cross
members and bracing shall also be inspected.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The floor
(underside of vehicle) of cargo area contains holes or openings that could
allow cargo to fall or spill through, or is damaged or weakened to the extent
that the load-carrying capacity is adversely affected;
|
|
(2) The cross member
or bracing is missing, cracked, corroded, or has other unsafe or hazardous
condition;
|
|
(3) The bulkhead
separating the occupant compartment of the vehicle from the cargo area is not
sealed against the entry of exhaust gases or fumes, or is damaged or weakened
so as to allow cargo to fall or spill from the vehicle;
|
|
(4) The bulkhead is
damaged, weakened, or has holes that would allow cargo to fall or spill from
the vehicle, or allow cargo to impact a motor vehicle towing the trailer; or
|
|
(5) The sidewall,
sideboard, or other body equipment that is designed to contain cargo is
damaged, weakened, or has holes that would allow cargo to fall or spill from
the vehicle.
|
.15 Rearview Mirrors.
A. All motor vehicles
shall be equipped, as applicable, with rearview mirrors. Enclosed vehicles
shall be equipped with an inside rearview mirror and a driver's side rearview
mirror providing a view of the highway for a distance of at least 200 feet to the
rear. If the interior rearview is obstructed by design, a vehicle shall be
equipped with an outside passenger side rearview mirror. From the driver's position, visually inspect
all rearview mirrors for a clear and reasonably unobstructed view to the rear.
Look for the correct location, stable mounting, cracks, ease of adjustment, and
ability to hold an adjustment. Intersecting cracks or other damage or condition
that result in multiple images being reflected shall not be permitted.
B. Motorcycle Mirrors.
Inspect for proper size, secure mounting, visibility, and condition of mirror
and its mounting hardware. The mirror shall be securely mounted and
sufficiently stable to provide a readily distinguishable image to the rider
under normal conditions. The mirror shall be regular in shape (circular, oval,
rectangular, or square) and may not contain sharp edges, projections, or
irregular indents capable of producing injury. Motorcycles shall be equipped
with two rearview mirrors, one on each side of the vehicle with a reflective
area of at least 12.5 square inches of reflective surface or, if convex, at
least 10 square inches of reflective surface.
Agency Note:
Mirrors on 1977 and earlier motorcycles were only required to have at least 7
square inches of reflective surface.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) A motorcycle is
not equipped with both a left-side and a right-side rearview mirror meeting
size requirements of this regulation;
|
|
(2) A mirror is
cracked or discolored, causing a distorted view;
|
|
(3) A mirror is
improperly installed or loosely mounted;
|
|
(4) A minimum
200-foot visibility cannot be achieved; or
|
|
(5) A mirror has
intersecting cracks or other damage or condition that distort or result in
multiple images being reflected.
|
C. Exterior Mirrors.
All motor vehicles shall be equipped with an outside rearview mirror on the
driver's side providing a view of the highway for a distance of at least 200
feet to the rear. From the driver's position, visually inspect all exterior
mirrors for a clear and reasonably unobstructed view to the rear. Look for
correct location, stable mounting, ease of adjustment, and ability to hold an
adjustment. Cracks or other damage or condition that result in multiple images
being reflected shall not be permitted. Vehicles equipped with AS-3 glazing
material, add-on tinting material, or approved stickers shall be equipped with
outside mirrors on both the left and the right side.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The exterior
rearview mirror is missing (when required);
|
|
(2) The exterior
rearview mirror mounting is loose so that rear vision does not provide
visibility at least 200 feet to the rear, or is otherwise impaired;
|
|
(3) The exterior
rearview mirror cannot be adjusted or will not hold an adjustment;
|
|
(4) The exterior
rearview mirror does not provide an unobstructed view to the rear;
|
|
(5) The exterior
rearview mirror is obscured by windshield pillar;
|
|
(6) The exterior
rearview mirror is pitted, or discolored to the extent that rear vision is
obscured; or
|
|
(7) The exterior
rearview mirror has intersecting cracks, other damage, or conditions that
distort or result in multiple images being reflected.
|
D. Interior Mirrors.
Vehicles shall be equipped with an inside rearview mirror as designed. A
vehicle designed or constructed where the view through an inside rearview
mirror is obstructed shall be equipped with outside rearview mirrors on both
sides. The inside rearview mirror shall be adjustable and provide a clear,
stable reflected view 200 feet to the rear. From the driver's position,
visually inspect the interior mirror for proper mounting, location, sharp
edges, ease of adjustment, and ability to hold an adjustment. Cracks or other
damage, or condition that distort or result in multiple images being reflected
shall not be permitted.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The interior
rearview mirror is missing (when required);
|
|
(2) The interior
mirror cannot be adjusted, or will not hold an adjustment;
|
|
(3) The interior
mirror is pitted, or discolored to the extent that rear vision is obscured;
|
|
(4) The interior
mirror has sharp edges that could be hazardous to occupants of the vehicle;
|
|
(5) The interior
mirror does not provide an unobstructed view at least 200 feet to the rear;
|
|
(6) The interior
mirror view is obstructed by vehicle design, and vehicle is not equipped with
outside rearview mirrors on both the left and right exterior sides of the
vehicle; or
|
|
(7) The interior
rearview mirror has intersecting cracks, other damage, or conditions that
distort or result in multiple images being reflected.
|
E. School Vehicle
Mirrors.
(1) Type I School
Vehicle interior rearview mirror size shall be at least 6 by 30 inches with
rounded corners and protected edges. If the mirror is not metal backed and
framed, the mirror shall be of laminated safety glass; and
(2) Type II School
Vehicle interior rearview mirror shall be at least 5 by 15 inches with rounded
corners and protected edges. If the mirror is not metal backed and framed, the
mirror shall be of laminated safety glass.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The interior
rearview mirror is missing or not of the proper size by type of vehicle;
|
|
(b) The interior
mirror cannot be adjusted or will not hold an adjustment;
|
|
(c) The interior
mirror is pitted or discolored to the extent that rear vision is obscured;
|
|
(d) The interior
mirror has sharp edges that could be hazardous to occupants of the vehicle;
|
|
(e) The interior
mirror does not provide an unobstructed view at least 200 feet to the rear;
or
|
|
(f) The interior
mirror has intersecting cracks or other damage, or condition that distort the
view or result in multiple images being reflected.
|
(3) School vehicle
exterior mirrors shall include two adjustable exterior clear view mirrors with
black housings, one installed on each side of the vehicle. Fender mounted
mirrors may be mounted using a tripod or solid piece mirror brackets. A convex
mirror shall be mounted on each front fender. A single mirror of a type
approved by the administration in conjunction with the State Department of
Education may be used in place of the convex mirrors in this regulation.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The exterior
rearview mirror is missing or not of an approved type;
|
|
(b) The exterior
rearview mirror is loose, so the rear vision is impaired;
|
|
(c) The exterior
rearview mirror cannot be adjusted or will not hold an adjustment;
|
|
(d) The exterior
rearview mirror does not provide visibility at least 200 feet to the rear, or
is otherwise impaired;
|
|
(e) The exterior
rearview mirror is obscured by windshield pillar;
|
|
(f) The exterior
rearview mirror is pitted or discolored to the extent that rear vision is
obscured;
|
|
(g) The exterior
rearview mirror has intersecting cracks or other damage, or conditions that
distort vision, or result in multiple images being reflected; or
|
|
(h) The convex mirror
on a front fender does not provide a close infield of vision to eliminate
blind spots.
|
.16 Equipment for
Operator and Passengers.
A. Front Driver’s Seat
and Passenger Seats. The front driver's seat adjusting mechanisms shall operate
as designed to provide adjustment for the driver. The front driver’s seat and
all other seats provided for passengers while the vehicle is being operated
shall be securely and properly anchored to the vehicle and shall not have
damage or other conditions that may be hazardous to occupants of the vehicle.
(1) Inspect for the
presence of the front driver's seat and its condition. Inspect seat adjustment
for proper function. Inspect all seat anchor bolts. Inspect all seating for
protruding springs or other objects that could catch clothing or cause injury.
|
Reject Vehicle
If:
|
|
(a) The front driver's seat is missing or unsafe;
|
|
(b) The front driver’s seat position adjusting mechanisms
do not adjust to all positions, slips out of position, or does not provide
for adjustment;
|
|
(c) Any seat is not securely and properly fastened to the
floor;
|
|
(d) The driver or other occupant seat has protruding
springs or other objects that could catch clothing or cause injury;
|
|
(e) The headrest is damaged, or is missing from a seat that
was originally equipped with a headrest;
|
|
(f) A motorcycle passenger handhold device is missing or
unsafe; or
|
|
(g) The motorcycle foot pegs are missing or unsafe.
|
(2) School Vehicle
Upholstery and Covers. Seat, crash barrier, padding, and other covered or
upholstered interior equipment procured for use in this State as of January 1,
2014, are required to be constructed with materials that enable them to meet
all the criteria of the school vehicle upholstery fire block test established
by the National School Transportation specifications and procedures adopted at
the most recent national congress on school transportation.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The upholstery or
cover for a seat, crash barrier, inner liner, paneling, or other covered
interior equipment is missing, damaged, or not securely attached; or
|
|
(b) The upholstery,
cover, or padding is not constructed with fire block material as required.
|
B. Defroster. Inspect the defroster system to ensure that
the defroster discharges air onto the windshield, and the windows to the left
and right of the driver, if so designed.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Discharged air
from the defroster is not warm when the engine is at operating temperature;
or
|
|
(2) Air does not
discharge from the defroster vents, or it is not directed onto the
windshield, and windows to the left and right of the driver, if so designed.
|
C. Driver Sun Visor.
Visually inspect visor for presence, function, and stable adjustment.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The visor is
missing on driver's side;
|
|
(2) The visor does
not restrict light as designed; or
|
|
(3) The visor cannot
be maintained in a set position.
|
D. School Vehicle
Visor. Type I School Vehicle visor shall be at least 6 inches wide and 30
inches long. Type II School Vehicle visor shall be at least 5 inches wide and
30 inches long.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
School vehicle visor does not meet the
minimum OEM size requirement for the type of vehicle.
|
E. School Vehicle
Heater. The heating system shall be capable of maintaining at least a 50°F
interior temperature.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
Vehicle heater cannot
maintain a temperature of at least 50°F.
|
F. Motorcycle Rider and
Occupant Safety Equipment. This includes seating, passenger handhold devices,
and footrest assemblies. A motorcycle seat that provides for a passenger seat
position that cannot be utilized by a passenger due to other installed equipment
is not required to be equipped with passenger handhold devices or passenger
footrest assemblies. If the passenger seat is made accessible, then all
passenger safety devices shall be in place. Motorcycles built before 1975 were
not required to be equipped with retractable footrest assemblies.
(1) Rider and passenger
seats shall be properly attached. Seat locking device shall function where
applicable;
(2) If a passenger is
to be transported, a properly attached handhold device shall be provided on the
motorcycle and shall be of sufficient strength and size to provide adequate
support to any passenger. A strap or bar device is acceptable; and
(3) For each designated
seating position, or if a passenger is to be transported, the motorcycle shall
be equipped with a footrest assembly on each side of the motorcycle. The
passenger footrest shall not extend more than 1 inch beyond the widest part of
the motorcycle and shall be retractable.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The seat is
improperly attached to the motorcycle, or seat locking device does not
function where applicable;
|
|
(b) The seat has
protruding springs or other objects that could catch clothing or cause
injury;
|
|
(c) The passenger
seat is not equipped with a handhold device, or the handhold is damaged,
loose, or otherwise defective;
|
|
(d) A required
footrest is missing, damaged, or loose;
|
|
(e) A passenger is
capable of being transported and passenger footrests are not present;
|
|
(f) The passenger footrests extend more than 1 inch beyond the widest part
of the motorcycle excluding handlebars; or
|
|
(g) The passenger
footrest does not retract.
|
.17 Seat Belts, and
Supplemental Restraint Systems.
A. Seat Belts. A motor
vehicle transporting passengers shall be equipped with seat belts for each
occupant position of the vehicle, as required by 49 CFR §571.208 and 49 CFR
§571.209. A vehicle registered as a taxicab or as a school bus shall be
equipped with a driver’s seat belt but is not required to be equipped with
passenger seat belts under this regulation.
Agency Note:
Vehicles manufactured or assembled before June 2, 1969, were not required to be
equipped with rear seat belts, and vehicles manufactured or assembled before
June 2, 1964, were not required to be equipped with front seat belts, but if
equipped with seat belts, they shall comply with the standards of this
regulation.
B. Inspect seat belts
for presence, mounting, function, and damage that obstructs the correct
operation of the belt or significantly weakens the webbing. Fraying on edges
that does not result in fabric separation of the webbing is not a cause for
rejection. Damaged webbing shall be replaced, repairs to webbing shall not be
permitted.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) A seat belt is
not OEM or equivalent;
|
|
(2) A seat belt is
missing or does not function properly. (Each passenger seating position shall
be equipped with seat belts);
|
|
(3) A seat belt is
not properly secured;
|
|
(4) A seat belt is
damaged to affect safe operation;
|
|
(5) A seat belt
webbing is frayed resulting in fabric separation of the webbing, has
incomplete or loose stitching;
|
|
(6) A seat belt
webbing has been repaired;
|
|
(7) A seat belt
buckle does not operate properly;
|
|
(8) A seat belt
mounting surface is badly deformed, damaged, corroded, or inadequate; or
|
|
(9) A seat belt retracting/inertia mechanism
does not operate properly.
|
C. Passenger Airbag
Restraint Systems. FMVSS 49 CFR §571.208 requires certain vehicles to be
equipped with front driver and passenger airbags. All 1998 model year or newer
passenger vehicles are required to be equipped with front driver and passenger
airbags. All 1999 model year or newer trucks, buses, or multipurpose passenger
vehicles with a GVWR of 8,500 pounds (3,855 kg) or less are required to be
equipped with front driver and passenger airbags.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) An airbag is
deployed on any vehicle;
|
|
(2) An airbag is not
present if originally required to be equipped;
|
|
(3) The airbag
warning indicator does not self-check if originally required to be equipped;
or
|
|
(4) The airbag
warning indicator is illuminated during operation if originally required to
be equipped.
|
.18 Automatic
Transmission Gear Indicator and Neutral Safety Switch for Starter.
A. The transmission
gear indicator and a neutral safety switch are required for a vehicle with an
automatic transmission. Inspect the gear selector for proper indication of the
engaged gear/transmission position with engine running. Test the park, neutral,
forward, and reverse positions for accuracy.
B. Inspect neutral
safety switches for proper function and condition for automatic transmissions.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The gear
selection indicator is missing or does not accurately indicate the correct
position or direction of travel; or
|
|
(2) The neutral
safety switch allows the engine to start in any gear or will not start in
park or neutral with automatic transmission.
|
.19 Manual Transmission
Neutral Safety and Clutch Safety Starter Switches.
Manual transmission
clutch or neutral safety switch shall be inspected for proper function and
condition, if so equipped.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The manual
transmission clutch safety switch allows the starter to operate without
depressing clutch pedal, as applicable to a vehicle so equipped when
originally manufactured; or
|
|
(2) The neutral
safety switch allows the engine to start in any gear, as applicable to a
vehicle so equipped when originally manufactured.
|
.20 Speedometer and
Odometer.
Motor vehicle
speedometer and odometer shall be present and operate with a degree of
accuracy. The dial and calibration shall be legible and calibrated in miles or
kilometers. Speedometer shall register speed, and odometer shall register and
retain the total distance traveled but are not subject to certification for
accuracy.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The speedometer,
odometer, or both, are disconnected, inoperable, or operate without a degree
of accuracy;
|
|
(2) The dial and
calibrations are not legible;
|
|
(3) The speedometer
does not register speed in miles per hour, kilometers, or both; or
|
|
(4) The odometer does
not register distance traveled.
|
.21 Windshield Wipers
and Washers.
A. Windshield wipers
shall operate as originally designed to clear the windshield for a safe view by
the driver of the vehicle from the driver’s position. Inspect for function,
proper size of wiper blades, hardened rubber elements of wiper blades, and damaged
or loose wiper blades or wiper arms. Inspect for proper contact of the wiper
blades to the windshield by raising the wiper arm and observing that the arm
returns and contacts the windshield firmly. Inspect for proper operation of the
windshield wiper control switch on all speeds. Windshield shall be free of
insects, oil film, or other foreign matter, and should be continuously wet when
tested. School vehicle wiper blades shall be at least 14 inches long.
Intermittent wipers that do not function may be certified if high and low wiper
speeds are functioning properly.
B. Vehicles
manufactured with windshield washers, and vehicles that are equipped with
windshield washers shall have operational systems capable of containing washer
fluid and distributing washer fluid onto the windshield from the driver’s
position to aid in clearing and cleaning the windshield.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The windshield
wipers do not function, or cannot be controlled or operated from the driver's
position;
|
|
(2)A wiper blade is
missing, is not the proper size or the rubber element is hardened or damaged;
|
|
(3) A windshield
wiper arm is missing, loose, or damaged;
|
|
(4) A windshield
wiper arm does not have sufficient tension to hold the wiper blade against
the windshield;
|
|
(5) The wiper control
switch does not function as originally designed;
|
|
(6) The windshield
wipers do not clear the windshield properly, (Full clearing of the wiper
sweep area);
|
|
(7) The windshield
wiper arms do not return to park position when the windshield wipers are
turned off;
|
|
(8) The windshield
washers do not function properly, or are not directed onto the windshield
wiper sweep area;
|
|
(9) A windshield
washer system leak impedes proper operation;
|
|
(10) The windshield
washer reservoir has damage or other conditions that cause loss of washer
fluid; or
|
|
(11) A school vehicle
wiper blade is less than 14 inches.
|
.22 Glazing.
A. In this regulation,
the following terms have the meanings indicated.
(1) “Acute area” means the windshield area 8
inches wide by 5 inches high, located directly in front of the driver, centered
vertically on the steering wheel, and horizontally in the center of the
critical area.
(2) “Cloudiness” means
any degree of visible discoloration or separation, except tinting that does not
affect clear vision.
(3) “Critical area”
means the normal windshield wiper sweep, excluding the acute area, and any area
obscured by the hood, fenders, or rearview mirror.
(4) “Damage” means
cracks, nicks, pits, chips, star breaks, half-moons or bullseye fractures,
discoloration, sharp edges, wiper blade scratches, or other obstructions to
driver’s view, or other broken or exposed sharp edges.
(5) “Discoloration”
means a condition that impairs the transparency of the glazing.
(6) “Medical exemption”
means a written certification from a physician licensed to practice medicine in
the State of Maryland. This must remain in the vehicle for presentation to law
enforcement personnel, upon request.
(7) “Non-critical area”
means all windshield area outside the critical area.
(8) “Normal windshield
wiper sweep” means the area of the windshield cleaned by the windshield wiper,
excluding the return position on both passenger's and driver's sides.
(9) “Post Manufacture
Window Tint Medical Exemption Form” means a form completed by the Division
after examination of a vehicle owner’s medical exemption from a physician
licensed to practice medicine in the State of Maryland. The form authorizes a
licensed inspection mechanic to exempt the vehicle's windows, equipped with
post manufacture window tint, from meeting the light transmittance requirement
during a vehicle inspection or during certification of a SERO.
B.
Markings for Glazing. Safety glazing material is marked with the letters “AS”
followed by a number from 1 through 16B, which indicates where the glazing may
be used on the vehicle. Safety glazing material also has the symbol DOT and a
manufacturer’s code mark that the NHTSA, assigns to the manufacturer. Windows
located to the rear of the driver position of passenger vehicles, trucks,
tractors, buses, vans, and multipurpose passenger vehicles may be equipped with
AS-3. A vehicle shall be equipped with properly marked and utilized glazing.
Glazing shall be clear of foreign matter and load obstructions when presented
for inspection.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
Glazing material is
not marked to indicate type or improper glazing is used in any vehicle
window.
|
C. Side and Rear
Windows.
(1) Driver's side
window operation. Inspect operation of window on driver's side. Window shall
open and close, except driver’s side windows equipped with AS-10 glazing.
(2) Passenger side windows and rear windows.
Inspect for presence of passenger windows or rear windows as applicable.
(3) School vehicle side
and rear windows. Window and door glazing material to the left and right sides
of the driver shall be AS-2 laminated safety sheet, and the passenger
compartment windows shall be AS-2 or AS-3 material. Passenger compartment
windows shall open from the top at least 9 inches by 22 inches to provide an
emergency exit.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) A driver's side
window does not open and close to permit hand signals;
|
|
(b) A window crank
handle is loose, damaged, or contains sharp edges hazardous to occupants;
|
|
(c) A passenger window is missing or
not of an approved glazing material;
|
|
(d) A rear window is
missing or not of an approved glazing material;
|
|
(e) A school vehicle
window is not of an approved material, or is missing;
|
|
(f) A school vehicle
passenger window does not open from the top at least 9 inches by 22 inches;
or
|
|
(g) A school vehicle
window has missing or damaged banding resulting in exposed edges.
|
D. Glazing Damage.
(1) Windows. Inspect
for damage as defined in §A(4) of this regulation, or unapproved modification.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Any window is
modified, or has exposed sharp edges;
|
|
(b) There is damage,
foreign matter obstruction, or conditions that interfere with the driver's
view to the left and right outside of the vehicle through vehicle side window
glazing;
|
|
(c) There is damage,
foreign matter obstruction, or conditions that interfere with the driver's
clear view 200 feet to the rear of the vehicle through vehicle rear window
glazing; or
|
|
(d) There is
permanent equipment installed or other condition which obstruct the driver's
view to the rear, and the vehicle is not equipped with an outside rearview
mirror on each side.
|
(2) Windshield. Inspect
windshield for any damage as defined in §A(4) of this regulation, unapproved
modifications, discoloration, wiper blade scratches, or other obstructions to
driver view. Motorcycles are not required to be equipped with windshields or
windscreens. If a motorcycle is equipped with a windshield or windscreen, it
shall be of an approved type with the appropriate markings indicating type and
approved usage. A motorcycle windshield shall be inspected for foreign matter
obstructions, damage, and proper installation. A motorcycle windscreen is not
subject to inspection for light transmittance, view, or color.
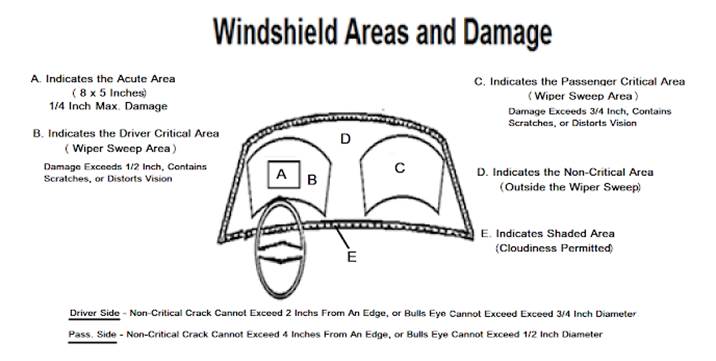
(a) Windshield Driver's
Side Inspection.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(i) Cloudiness
exceeds 1 inch from the top or side or 1 inch into the critical area from the
bottom. If the windshield is divided, the cloudiness may not exceed ½ inch
from the center divider;
|
|
(ii) Acute area
contains any damage in excess of ¼ inch in diameter or length or any
combination of damage which cumulatively exceeds ¼ inch in diameter or length
or any condition which significantly interferes with the driver's vision;
|
|
(iii) Critical area
contains wiper blade scratches which are severe enough to distort vision, or
any damage in excess of ½ inch in diameter or length, or any combination of
individual damage, which cumulatively exceeds ½ inch in diameter or length or
any condition which significantly interferes with the driver's vision except
in the permitted cloudy area;
|
|
(iv) Non-critical
area contains any individual or combination of intersecting damage extending
inward more than 2 inches separately or cumulatively from the outer frame on
flat or curved windshields or over 4 inches on wraparound windshields. Damage
in excess of ¾ inch in diameter or length, or any combination of damages
which cumulatively exceed ¾ inch in diameter or length or any permanent
condition which significantly interferes with the driver's vision except in
the permitted cloudy area may not be present; or
|
|
(v) Any part of the
windshield is missing, has an unapproved modification, or has damage or other
condition that is prohibited in this regulation.
|
(b) Windshield
Passenger Side Inspection.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(i) Cloudiness
exceeds 2 inches from the top or side or extends more than 2 inches into the
critical area from the bottom. If the windshield is divided, the cloudiness
may not exceed ½ inch from the center divider;
|
|
(ii) Critical area
contains wiper blade scratches that are severe enough to distort vision, or
any damage in excess of ¾ of an inch in diameter or length, or any
combination of individual damage, which cumulatively exceeds ¾ of an inch in
diameter or length or other condition which significantly interferes with the
driver's vision except in the permitted cloudy area; or
|
|
(iii) Non-critical
area contains any individual or combination of intersecting damage extending
inward more than 4 inches separately or cumulatively from the outer frame on
flat or curved windshields, or over 6 inches on wraparound windshields.
Damage in excess of 1½ inch in diameter or length, combination of damages
which cumulatively exceed 1½ inch in diameter or length, or permanent
condition that significantly interferes with the driver's vision except in
the permitted cloudy area shall not be present.
|
(c) Motorcycle
Windshield or Windscreen. A windshield is defined as being in the operator’s
line of vision and therefore is required to have at least 70 percent light
transmittance in the viewable area. Windshield areas in front of vehicle
equipment, which are not in the operator’s line of vision, may have tinting or
stickers applied. A windscreen is defined as not in the operator’s line of
vision and therefore is not required to have at least 70 percent light
transmittance, but shall be of an approved material with the appropriate AS
marking.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(i) The windshield or
windscreen is not of an approved type, or is improperly installed;
|
|
(ii) The windshield
or windscreen is damaged;
|
|
(iii) The windshield
viewable area is obstructed, or equipped with tinting material of any kind;
or
|
|
(iv) The windscreen
or fairing extends into the operator’s line of vision.
|
E. Signs and Materials
on Windshield or Windows. Glazing shall not be equipped with unauthorized
material or have conditions that obscure the driver's vision.
(1) Except as provided
in §F(2) of this regulation, a vehicle may not be equipped with any sign,
poster, card, sticker, or other nontransparent material on the windshield, side
wings, or side or rear windows of the vehicle;
(2) This does not apply
to:
(a) Materials placed on
the windshield sun band above the AS-1 line, or 5 inches from the top edge of
the windshield, whichever is less, if the material does not interfere with the
driver’s clear view;
(b)
Materials placed on the windshield or rear window, within a 7 inch square area in the lower corner, or on the side
windows of the vehicle to the rear of the driver, if the materials are placed as not to interfere with the driver’s clear view;
(c) Direction,
destination, or termini signs on any passenger common carrier motor vehicle;
(d) An electronic toll
collection device placed in the windshield of a vehicle in accordance with
guidelines established by the Maryland Transportation Authority;
(e) Security stickers
authorized by a federal or state government agency that measure not more than 2
inches high and not more than 4 inches long, and are placed as required by the
issuing agency; or
(f) Materials placed on
AS-3 glazing to the rear of the driver on trucks, vans, and multipurpose
vehicles.
(3) All vehicles
equipped with permitted signs, posters, cards, stickers, or other
nontransparent materials on windows to the rear of the driver shall be equipped
with an outside rearview mirror on each side.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Glazed surfaces
contain any sign, poster, card, decal, sticker, or other nontransparent
material in violation of this regulation;
|
|
(b) The driver’s
vision through glazing is obscured by any material or condition;
|
|
(c) Equipped with
authorized toll collection device or security sticker in violation of
placement or size as required in this regulation; or
|
|
(d) Equipped with
permitted signs, posters, cards, stickers, or other nontransparent materials
on windows to the rear of the driver and not equipped with an outside
rearview mirror on each side.
|
F. Post Manufacture
Window Tint Material, Color, and Light Transmittance. All glazing shall be
inspected for the application of post manufacture window tint (add-on tint).
Post manufacture window tint is prohibited that has a mirrored or one-way
vision, or a sparkling effect, is red, yellow, or amber in color, or changes to
a red, yellow, or amber color.
(1) A commercial
vehicle or a for-hire limousine (Class Q) may not be equipped with any color of
post manufacture window tint on a side window to the immediate right and left
of the driver, however, clear tint material may be applied to the glazing.
(2) A school vehicle
may not be equipped with post manufacture window tint on any glazing material.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Glazing is
equipped with post manufacture window tint that causes a mirrored or one-way
vision effect, or a sparkling effect, or is equipped with tint that changes
to a prohibited effect;
|
|
(b) Glazing is
equipped with red, yellow, or amber colored tint or tint that changes to a
prohibited color;
|
|
(c) A commercial
vehicle is equipped with a colored post manufacture window tint on a
windshield or side windows to the immediate right and left of the driver;
|
|
(d) A for-hire
limousine (Class Q) is equipped with a colored post manufacture window tint
on a windshield or side windows to the immediate right and left of the
driver; or
|
|
(e) A school vehicle
is equipped with post manufacture window tint on any glazing material.
|
(3) Post Manufacture
Window Tint Light Transmittance. Glazing materials, regulated for the
transmittance of light, shall have at least 35 percent light transmittance. Post manufacture window tint may not be
applied to the windshield below the AS-1 line or below 5 inches from the top of
the windshield, whichever is less. A vehicle equipped with post manufacture
window tint or authorized AS-3 glazing shall be equipped with an outside
rearview mirror on each side. A commercial vehicle or a for-hire limousine (Class
Q) may not be equipped with post manufacture window tint which reduces the
transmittance of light through the glazing to less than 70 percent. Windows to
the rear of the driver may be tinted to any degree of darkness.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Post manufacture
window tint is applied to the windshield below the AS-1 line or below 5
inches from the top of the windshield, whichever is less;
|
|
(b) The light
transmittance through a side or rear window of a passenger car, convertible,
or station wagon, is less than 35 percent;
|
|
(c) The light
transmittance through a side window to the immediate right or left of the
driver on a non-commercial truck, tractor, bus, van, or multipurpose
passenger vehicle is less than 35 percent;
|
|
(d) The vehicle is
equipped with permitted post manufacture window tint on any side or rear
window and is not equipped with an outside rearview mirror on each side of
the vehicle;
|
|
(e) A truck, tractor,
bus, van, or multipurpose passenger vehicle equipped with post manufacture
window tint to the rear of the driver is not equipped with outside rearview
mirrors on each side of the vehicle; or
|
|
(f) A commercial
vehicle or a for-hire limousine (Class Q) has post manufacture window tint
applied to the side windows to the immediate right and left of the driver
which is not clear or reduces the transmittance of light through the glazing
to less than 70 percent.
|
(4) Window Tint
Application with Center High Mount Stop Lamp. Vehicles equipped with a center
high mounted stop lamp mounted inside the vehicle may not be equipped with post
manufacture window tint in the area of the rear window that would obscure the
stop lamp.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
Post manufacture
window tint is applied to the area of the rear window that would obscure the
stop lamp.
|
G. Medical Exemption
for Post Manufacture Window Tint Light Transmittance. Transportation Article, §22-406, Annotated
Code of Maryland, provides an exemption for a person who must be protected from
the sun for medical reasons from having a light transmittance of at least 35
percent on regulated windows equipped with post manufacture window tint. The
law requires the owner to have in the vehicle, at the time the vehicle is
stopped by a police officer, a written certification that details the owner’s
medical need for tinted windows, from a physician licensed to practice medicine
in the State of Maryland. A vehicle owner whose vehicle is undergoing
inspection or has been issued a safety equipment repair order for defect #61
“TINT” and indicates to the authorized inspection station their possession of a
medical exemption, shall be referred to the ASED of the State Police for
examination of the vehicle owner’s medical documentation and the vehicle’s post
manufacture window tint. If the owner meets the requirements specified in
Transportation Article, §22-406, Annotated Code of Maryland, for the medical
exemption and the vehicle is compliant with all post manufacture window tinting
regulations in this chapter, excluding the light transmittance requirement of
regulated windows equipped with post manufacture window tint, the Division,
when applicable, shall be authorized to:
(1) Issue a post
manufacture window tint medical exemption form to be provided to the authorized
inspection station performing an inspection of the vehicle which shall permit
the registered inspection mechanic to exempt the vehicle's windows equipped with
post manufacture window tint from meeting the light transmittance requirement;
or
(2) Certify the safety
equipment repair order for defect #61 “TINT”.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
The vehicle is
equipped with post manufacture window tint with less than 35 percent light
transmittance on glazing regulated for the transmittance of light, and the
owner/agent for the vehicle does not present a Post Manufacture Window Tint
Medical Exemption issued by ASED to the inspection mechanic at time of
inspection.
|
.23 Lighting.
A. Definitions. In this
regulation, the following terms have the meanings indicated.
(1) “Auxiliary lamp”
means a lamp that supplements the main headlamps of a vehicle.
(2) “Back-up lamp”
means a lamp used to provide illumination behind the vehicle and to provide an
indicator when the vehicle is in reverse gear.
(3) “Center high mount
stop lamp” means a red high mounted stop lamp as required by 49 CFR §571.108,
and as identified by the year of manufacturer, shall be equipped and function
as originally designed, including any means provided to minimize reflections
from the light of the lamp upon the rear window glazing that might be visible
to the driver when viewed directly, or indirectly, in the rearview mirror.
(4) “Composite headlamp
assembly” means a lamp assembly consisting of a plastic housing and reflector
bonded to a plastic or glass lens and fitted with a bulb equipped with a seal
used to provide illumination ahead of the vehicle.
(5) “Cornering lamp”
means a steadily burning lamp used when the turn signal system is operating to
supplement the headlamps by providing additional road illumination in the
direction of the turn.
(6) “Daytime running
lamp” means any pair of lamps on the front of a passenger car, multipurpose
passenger vehicle, truck, or bus, other than parking lamps, driving lamps, or
fog lamps, which may be wired to be automatically activated in a steady burning
state, and are automatically deactivated when the headlamp control is in any
“on” position, and as otherwise determined by the manufacturer of the vehicle:
(7) “Driving lamp”
means an auxiliary lamp that may be used to supplement the upper beam of the
headlamps.
(8) “Emergency warning
lamp” means a lamp that provides a flashing light to identify an authorized
vehicle on an emergency mission. The emergency signal may be an oscillating
lamp, a rotating beacon, or pairs of alternating or simultaneously flashing lamps.
(9) “Fog lamp” means a
lamp that may be used with the lower beam headlights to provide illumination
under condition of rain, snow, dust, or fog.
(10) “Hazard warning
lamps” means turn signal lamps that flash simultaneously to warn of the
presence of a hazard.
(11) “Headlamp” means
an adjustable lamp that projects white light to the front of a vehicle to
illuminate the roadway and shoulder to permit the operation of a vehicle during
periods of low visibility such as darkness, fog, rain, or other conditions. Headlamps
may be sealed beam units or composite units with replaceable bulbs providing a
low beam distribution of light, an upper beam distribution of light, or a
combination of both lower and upper beams.
(12) “Headlamp low
beam” means a distribution of white light directed to avoid glare in the eyes
of oncoming drivers while providing illumination ahead of the vehicle.
(13) “Headlamp high
beam” means a distribution of white light intended primarily for distant
illumination and for use on the open highway when not meeting other vehicles.
(14) “Indicator lamp”
means a lamp visible to the operator of a vehicle that indicates appropriate
electrical circuits are in operation.
(15) “Lane changer”
means a device, usually incorporated in the turn signal switch, which will
actuate the turn signal lamps when held by the driver. It is intended for
momentary use for signaling a lane change. When released by the operator, it
will return to neutral and deactivate the signal lamp.
(16) “License-plate
lamp” means a lamp used to illuminate the license plate on the rear of a
vehicle.
(17) “Off-road lamp”
means a lamp designed and manufactured solely for off-road use that does not
meet DOT or SAE requirements for beam color, pattern, or luminosity.
(18) “Operating units
or switches” means devices by which the functioning of lamps are controlled.
(19) “Parking lamp”
means lamps used to designate the front of a parked vehicle.
(20) “Rear fog lamp”
means a single, or pair of high-intensity red rear position lamps to be turned
on by the driver in conditions of poor visibility to make the vehicle more
visible from the rear.
(21) “Reflective
device” means a device used on vehicles to indicate to an approaching driver by
reflected light from the headlamps of approaching vehicles.
(22) “SAE Lighting
Identification Code” means a series of standardized North American lighting and
signaling function markings for lighting devices that a manufacturer or a
supplier may use to mark his product to indicate the SAE lighting standard or
standards to which the device is designed to conform. The code is not intended
to limit the manufacturer or supplier in applying other markings to the
devices.
(23) “Sealed beam unit”
means an integral and hermetically sealed optical assembly with the name
“Sealed Beam” molded in the lens.
(24) “Sealed headlamp
assembly” means a major lighting device used to provide general illumination
ahead of the vehicle. It consists of the following:
(a) Housing containing
a reflector designed for specific bulb types, and a sealed lens;
(b) One or more beam
units (bulbs) with seals;
(c) Means for mounting
securely to the vehicle; and
(d) Means to permit
required aim adjustment.
(25) “Side marker lamp”
means a lamp on the left and right sides, visible to the side, and intended to
indicate vehicle length. They are located near the front and rear on each side,
and for vehicles 30 feet or more in length, they are located at the midpoint
(intermediate side marker).
(26) “Stop lamp” means
a lamp giving a steady warning light to the rear of the vehicle, to indicate
the intention of the operator of the vehicle to reduce speed or stop.
(27) “Tail lamp” means
a lamp used to designate the rear of a vehicle.
(28) “Turn signal lamp”
means a lamp that provides a flashing warning light to indicate the intended
direction of the turn.
(29) “VOL” means a
headlamp that is designed to be visually optically aligned left. VOL systems
have a vertical aiming plane 0.6° below the vertical reference point on the
alignment screen or image. VOL headlamps are aimed using the vertical aiming
plane 0.6° below the left side top of the sharp cutoff of the beam as the
reference to the measured height of the headlamp at the center of the lamp
beam.
(30) “VOR” means a
headlamp that is designed to be visually optically aligned right. VOR headlamps
are aimed using the right portion of the beam as the reference. VOR headlamps
are aimed using the top right portion of the beam as the reference to the measured
height of the headlamp at the center of the beam.
B. North American SAE Lighting and Signaling
Function Markings.
|
Lighting and Signaling Device
|
SAE Code
|
|
Retro-reflector
|
A
|
|
Wide-angle retro-reflectors (reflex reflectors)
|
A2
|
|
Motorcycle auxiliary “passing” lamp
|
C
|
|
Motorcycle turn
signal lamp
|
D
|
|
Side turn signal
lamps – vehicles at least 12 m (39.3701 ft.)
in length
|
E
|
|
Side turn signal
lamps – vehicles less than 12 m (39.3701 ft.) in length
|
E2
|
|
Front Fog lamps
|
F
|
|
Rear Fog lamps
|
F2
|
|
Front fog lamp (to
updated and increased performance requirements)
|
F3
|
|
Cargo lamp
|
G
|
|
Sealed beam
headlamps (marking applies to housing or unit)
|
H
|
|
Gas-discharge (HID
“Xenon”) headlamp
|
HG
|
|
Sealed beam
headlamp housing
|
HH
|
|
LED
(Light-emitting diode) headlamp
|
HL
|
|
Halogen
replaceable-bulb headlamp
|
HR
|
|
Turn signal lamp –
front
|
I
|
|
Turn signal lamp –
front, spaced from 75mm to 99mm from low beam headlamp
|
I3
|
|
Turn signal lamp –
front, spaced from 60mm to 74mm from low beam headlamp
|
I4
|
|
Turn signal lamp –
front, spaced less than 60mm from low beam headlamp
|
I5
|
|
Turn signal lamp –
front (also front for vehicles at least 80 inches wide)
|
I6
|
|
Lighting and
Signaling Device
|
SAE Code
|
|
Turn signal lamp –
front, vehicle 80 inches wide, spaced less than 100mm from the headlamp
|
I7
|
|
Front cornering
lamp
|
K
|
|
Rear cornering
lamp
|
K2
|
|
License plate
lamps
|
L
|
|
Motorcycle
headlamp
|
M
|
|
Moped headlamp
|
N
|
|
Spot lamp
|
O
|
|
Parking lamp –
front
|
P
|
|
Clearance or side
marker or identification lamp
|
P2
|
|
Clearance or side
marker or identification lamp, vehicles at least 80 inches wide
|
P3
|
|
Combination
clearance and side marker lamps
|
PC
|
|
Combination
clearance and/or side marker lamp for vehicles at least 80 inches wide
|
PC2
|
|
Back-up lamps
|
R
|
|
Stop lamp
|
S
|
|
Stop lamp,
vehicles at least 80 inches wide
|
S2
|
|
Tail lamp
|
T
|
|
Tail lamp (Tail
lamps for use on vehicles 2032mm or more in overall width)
|
T2
|
|
Supplemental high
mounted stop and turn signal lamp
|
U
|
|
Supplemental high
mounted stop and turn signal, vehicle at least (78.74 inches) wide
|
U2
|
|
Central
high-mounted brake lamp (CHMSL), for passenger cars
|
U3
|
|
Warning lamps for
emergency, maintenance, and service vehicles
|
W or W1
|
|
Warning lamps for
school buses
|
W2
|
|
360 – degree
emergency warning lamps
|
W3
|
|
Emergency warning
device
|
W4
|
|
Electric emergency
lanterns
|
X
|
|
Driving lamp
|
Y
|
|
Daytime Running lamp
|
Y2
|
|
Auxiliary low beam
lamp
|
Z
|
C. General Lamps and Reflectors. Vehicles shall be equipped
with lamps and reflectors as originally required by 49 CFR §571.108. This
includes all exterior lighting, interior dash lamps, interior indicator lamps,
and driver warning lamps. Actuate all general lamps on the vehicle and inspect
the condition, mounting, and function of any authorized or allowed lamp.
Reflectors may be incorporated into lamp assemblies or be separate equipment.
Inspect the reflectors for condition and mounting. All lamps and reflectors
shall be approved and marked with the proper code letter. The table in §B of
this regulation lists many of the common North American lighting codes for
reference but is not all-inclusive regarding lighting codes. Lamps to the front
of a vehicle shall either emit white or amber color. A lamp that is not
functioning properly or is improperly marked for use shall be rejected. Light
Emitting Diode (LED) lamps emit light from multiple LEDs in the lamp. At least
50 percent of the LEDs shall illuminate when the lamp is activated. Off-road
lamps shall not illuminate when required or approved lighting is operated.
(1) Lamps to the front of a vehicle shall be white or amber.
Tail lamps and reflectors at the rear of a vehicle shall be red. Stop lamps and
turn signals to the rear of a vehicle shall be red or amber. Center high mount
stop lamp shall be red only. Back-up and license plate lighting shall be white
only. Side marker lamps and reflectors shall be red to the rear of the vehicle,
and amber at all positions forward of the rear of the vehicle. Variations of
colors used in OEM lighting such as daytime running lamps may appear to be red
or blue to the front of some vehicles which are shaded to a range of color
chromaticity that does not meet the federal definition for red or blue light
which is incorporated from 49 CFR §571.108, and have therefore been certified by
the manufacturer as approved on-road lighting are acceptable.
(2) Aftermarket replacement lighting shall emit or display
the same color as the OEM lamp. Authorized optional or auxiliary lighting is
not required to be present, but shall meet the same requirements as required
lighting, including proper color as required by design or placement on the
vehicle, or shall be removed from the vehicle.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) Not equipped with a required lamp, or a
required or authorized lamp is obscured by any non-transparent material or
object, not mounted to operate as designed:
|
|
(i) Is damaged;
|
|
(ii) Is not
functioning properly;
|
|
(iii) Shows a
different color than as originally equipped;
|
|
(iv) Is equipped with
any exterior aftermarket lamp that shows a color contrary to Maryland law; or
|
|
(v) Additional
lighting has been added which interferes with any required lamp, reflector,
or other regulated equipment;
|
|
(b) Equipped with an
unauthorized lamp that does not comply with this regulation;
|
|
(c) A required or
approved optional lamp shows color contrary to Maryland law, excluding OEM
lighting with approved variations or shading of colors:
|
|
(i) License plate
lighting and back-up lighting is any color other than white;
|
|
(ii) Reflector on the
rear or the rear side of a vehicle is not red;
|
|
(iii) Reflector
mounted forward of the rear of the vehicle is not amber;
|
|
(iv) Side marker lamp
is not red to the rear and rear sides of the vehicle;
|
|
(v) Side marker lamp
mounted forward of the rear of the vehicle is not amber;
|
|
(vi) Clearance and
identification lamp is not red to the rear and rear sides of the vehicle, or
not amber mounted forward of the rear of the vehicle;
|
|
(vii) Front park lamp
is not amber or white;
|
|
(viii) Headlamp does
not emit white light only;
|
|
(ix) Fog lamp is not
amber or white; or
|
|
(x) Driving lamp is
not white;
|
|
(d) A turn signal is
designed to self-cancel and does not self-cancel, is missing, is not properly
mounted, is damaged to affect function, is not visible, or does not match the
color of the other lamp to the front or the rear as applicable, or otherwise does
not function as designed;
|
|
Agency Note: Motorcycles built before January 1, 1973,
were not required to be equipped with turn signal lamps.
|
|
(e) A hazard signal
lamp is missing, not properly mounted, damaged, or otherwise does not
function as designed;
|
|
(f)
A stop lamp is missing, not properly mounted, is damaged, does not match the
color of the other stop lamps, or otherwise does not function as designed,
including the center high mount stop lamp;
(i) High center mounted stop lamps on passenger vehicles
manufactured on or after September 1, 1985, but before September 1, 1986, may
flash when the hazard warning system is activated;
(ii) High mounted center stop lamps on multipurpose
passenger vehicles, trucks, and buses, whose overall width is less than 80
inches, whose GVWR is 10,000 pounds or less, which were manufactured on or
after September 1, 1993, shall be equipped with a high-mounted stop lamp.
|
|
Agency Note:
Vehicles built before September 1, 1985, were not required to be equipped
with center high mount stop lamps.
|
|
(g) A reflector is missing, is the incorrect color, is not
properly mounted, is damaged, or otherwise does not function as designed;
|
|
(h) A side marker is missing, not properly mounted,
damaged, or otherwise does not function as designed;
|
|
Agency Note:
Motorcycles are not required to be manufactured with side marker lamps.
|
|
(i) A tail lamp is not red or is missing, not properly
mounted, damaged, or otherwise does not function as designed;
|
|
(j) A park lamp is missing, not properly mounted, damaged,
or otherwise does not function as designed;
|
|
(k) A license plate light is missing, is not the correct
color, is improperly mounted, damaged, or otherwise does not function as
designed;
|
|
(l) Clearance or identification lamps are not properly
mounted, are damaged, are not the correct color, or otherwise do not function
as designed;
|
|
(m) Backup lamp is
missing if the vehicle was originally equipped with a backup lamp, is not the
correct color, does not come on when vehicle is in reverse gear or comes on
in any other gear position, or not properly mounted, damaged, or otherwise
does not function as designed;
|
|
(n) A lamp is not
located or mounted to operate in accordance with its intended function, as
indicated by the SAE/DOT markings on the lamp;
|
|
(o) Daytime running
lamp is missing, non-functioning, damaged, or otherwise rendered inoperative;
|
|
(p) More than 50
percent of the LEDs in any general lamp are not illuminated when the lamp is
activated; or
|
|
(q) An off-road lamp
illuminates when any required or approved on-road lamp is activated.
|
D. Headlamps. Headlamps
shall project white light only and shall not have any damage to the lamp
assembly or lens that adversely affects the operation of the lamp. Sealed beam
lamps may not contain cracks or holes. Composite lamp units shall be maintained
in a sealed condition or may be re-sealed with products designed to permanently
repair automotive lamps. LED headlamps shall illuminate fully and shall not
have any non-functioning LEDs when activated. Lamp descriptions and lens code
markings are listed in §§A and B of this regulation. Headlights shall not be
obscured or covered by any non-transparent material or object or equipped with
a colored lens cover. Clear DOT approved impact covers may be acceptable,
provided they do not affect the operation of the headlamp. Headlights shall be
mounted at a height no lower than 22 inches, or higher than 54 inches from the
center of the lamp to the surface the vehicle is operated upon. Lamp assemblies
designed for use with replaceable bulbs (composite headlights), shall be
equipped with the proper type of bulb, as indicated by the SAE/DOT markings on
the lamp.
(1) Headlamp
Inspection. Headlamps shall be inspected to ensure that the lamps illuminate
from left to right sides with approximately the same intensity of light.
Noticeable differences in illumination may indicate improper or defective
lamps. Auto-adjusting headlamps do not need to be aimed. These headlamps are
equipped with a malfunction indicator light, which will illuminate if they fail
the self-test. In the event of a headlamp malfunction, the owner/agent shall be
referred to a dealer or qualified repair shop for repairs. Headlamps federally designated and marked as
VOL, or VOR, are prohibited from having horizontal adjustment capability. Other
earlier headlamps were designed with both horizontal and vertical aim
requirements and capabilities. Manually adjusted headlamps found out of
alignment shall be properly aligned using the inspection mechanic’s experience,
training, and knowledge to properly align the headlamps. Those headlamps with
both low and high beam lamps located in the same assembly shall be aimed on low
beam unless specified otherwise by the manufacturer, or the Division.
(2) Headlamp Aiming.
Headlamps shall be aimed at the same height left and right. The height of the
center of the headlamp beam intensity zone shall be referenced to establish the
aiming height of the vehicle. Headlamp aiming may be performed using aiming
equipment meeting SAE standards or may be performed at not less than 10 feet
from a vertical flat surface. VOL and VOR headlamp patterns shall be observed
and adjusted, if necessary, to within 2 inches up or down of the height
measured as described in this regulation, while ensuring the heights of the
lights are the same side to side. Headlamps with horizontal and vertical aim
capability shall also be aimed vertically within 2 inches of the center of the
headlamp left to right. (See Diagram)
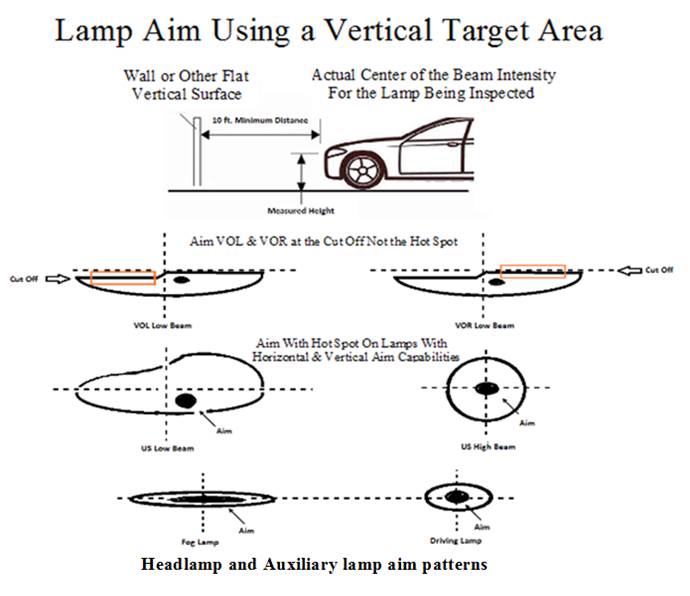
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) The headlamp has
an excessively clouded lens which adversely affects the operation of the
lamp;
|
|
(b) The headlamp is
obscured or covered by a non-transparent material or object, is equipped with
an unapproved lens cover, or has a hole in the lens;
|
|
(c) The headlamp is
mounted lower than 22 inches, or higher than 54 inches when measured from the
center of the lamp to the level surface the vehicle is operated upon;
|
|
(d) The headlamp is
improperly mounted, or is equipped with the incorrect bulb type in a
composite headlight assembly;
|
|
(e) The headlamp does
not illuminate or is noticeably dim;
|
|
(f) The aim point of
a headlamp beam, as applicable to headlamp design, is more than 2 inches left
or right of the vertical centerline of the lamp, or is more than 2 inches
above or below the horizontal centerline of the lamp;
|
|
(g) The
auto-adjusting headlamp malfunction indicator light is illuminated indicating
a system fault;
|
|
(h) A sealed beam
headlamp has a crack or defect compromising the lamp;
|
|
(i) A composite
headlamp assembly has an unrepaired, or improperly repaired hole, which could
allow contamination of the interior of the lamp surfaces;
|
|
(j) A LED headlamp
does not illuminate fully or has non-functioning LEDs when activated; or
|
|
(k) A composite lamp
is equipped with a bulb or other illuminating device not specified for use
with the lamp.
|
E. Fog and Driving
Lamps.
(1) Front-mounted fog
and driving lamps are designed to illuminate the driver’s view to the front of
the vehicle and emit beam patterns that meet FMVSS for on-road operation. If a
vehicle is equipped with either front fog lamps or driving lamps they shall
activate with the appropriate headlamp beam, and be properly aimed using the
same procedure for aiming headlamps. The mounting
heights of driving lamps do not apply to emergency vehicles. A motor vehicle
equipped with required headlamps and also equipped with any auxiliary lamp, or
any other lamp on its front, shall not be capable of illuminating more than
four of these lamps at any one time when on a highway. A utility spot lamp
mounted on the side or roof of a vehicle and controlled by a vehicle occupant
is not considered a driving lamp, therefore is not subject to inspection. Work
lighting for commercial vehicles shall not operate on the same circuit as regulated
lighting. Fog and driving lamps are optional but shall illuminate with the
proper color if operational.
(2) Front Fog Lamps.
Front fog lamps supplement low beam headlamps and shall not illuminate with
high beam headlamps. Fog lamps shall be mounted on the front of the vehicle at
a height, not more than 30 inches or less than 12 inches above the level surface
on which a vehicle stands when measured from the center of the lamp. Only two
front-mounted fog lamps are allowed by law. Fog lamps may be white or amber but
shall match color side to side.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) A front fog lamp
is mounted higher than 30 inches above, or lower than 12 inches above the
surface on which a vehicle stands;
|
|
(b) Equipped with
more than two front-mounted fog lamps;
|
|
(c) The front fog
lamp is not white or amber, or is mismatched in color side to side;
|
|
(d) The front fog
lamp can be operated while the high beam headlamps are illuminated;
|
|
(e) The front fog
lamp does not display the proper asymmetrical beam pattern or the center of
the intensity zone of a fog lamp beam is more than 2 inches left or right of
the vertical centerline of the lamp or is more than 2 inches above or below
the horizontal centerline of the lamp; or
|
|
(f) The front fog
lamp is equipped with the incorrect bulb type in a composite assembly.
|
(3) Rear Fog Lamps.
Rear fog lamps are permitted to be mounted on the rear of a vehicle either
singularly or in pairs and supplement tail lamps and serve as high-intensity
rear position lamps to be turned on by the driver in conditions of poor
visibility to make the vehicle more visible from the rear.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) A rear fog lamp
is not mounted as required by this regulation;
|
|
(b) A rear fog lamp
is any color other than red; or
|
|
(c) More than two
rear fog lamps are installed on a vehicle.
|
(4) Driving Lamps.
Driving lamps supplement high beam headlamps and shall not illuminate with low
beam headlamps. Driving lamps shall be mounted on the front of the vehicle at a
height, not more than 42 inches or less than 16 inches above the level surface
on which the vehicle stands when measured from the center of the lamp. Only two
driving lamps are allowed by law. Driving lamps shall be white.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(a) A driving lamp is
mounted higher than 42 inches above, or lower than 16 inches above the
surface on which a vehicle stands;
|
|
(b) Equipped with
more than two driving lamps;
|
|
(c) A driving lamp is
not white;
|
|
(d) A driving lamp
can be operated while the low beam headlamps are illuminated;
|
|
(e) A driving lamp
does not display the proper symmetrical beam pattern or the center of the
intensity zone of a driving lamp beam is more than 2 inches left or right of
the vertical centerline of the lamp or is more than 2 inches above or below
the horizontal centerline of the lamp; or
|
|
(f) A driving lamp is
equipped with the incorrect bulb type in a composite assembly.
|
F. Driver Information
Lamps. Dash lamps, driver warning lights, and driver indicator lamps for
regulated safety equipment shall be inspected for presence and function. Dash
lamps shall illuminate the speedometer and odometer, fuel gauge, oil gauge,
alternator gauge, temperature gauge, and any other gauge that provides vehicle
operating information to the driver. Driver indicator lamps for turn signal and
hazard lamps, high beam headlamps, or the indicator lamp or any authorized lamp
shall illuminate when the specific lamp is actuated.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Dash lamps do not
illuminate fuel, oil, alternator, and temperature gauges, speedometer,
odometer, or any other gauge that provides vehicle operating information to
the driver; or
|
|
(2) Indicator lamps
do not properly illuminate to indicate the operation of the turn and hazard
signal lamps, the high beam headlamps, the fog/driving lamps, or the
indicator lamp for any other authorized lamp does not illuminate to indicate
the operation of the associated lamp.
|
G. Emergency Lamps.
Certain lamp colors and uses are restricted by Maryland law. Blue emergency
lamps are only authorized for use on law enforcement vehicles, which may also
be equipped with red, white, and amber lights.
Red, white, and amber emergency lamps are authorized for use on fire
department vehicles, rescue vehicles, ambulances, and State vehicles used for
hazardous material spills. Amber service emergency lamps may be used by
maintenance vehicles, tow trucks, escorts, experimental test vehicles, and
slow-moving farm and rural letter carrier vehicles. Rural letter carrier
vehicles may use two bi-directional lights on each side of the vehicle on the
roof. Green emergency lamps may be used by taxi cabs as hold up alert lights.
Work lamps are permitted to be installed on service and emergency vehicles. A
vehicle privately owned by an officer of a volunteer fire company may be
equipped with red and green, or red and white lights or signal devices as
authorized in Transportation Article, §22-218, Annotated Code of Maryland.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Equipped with an
unauthorized emergency lamp that does not comply with this regulation;
|
|
(2) An authorized
emergency lamp is obscured by any non-transparent material or object, is
damaged or not mounted to operate as designed, is not mounted securely or is
not functioning when required; or
|
|
(3) Authorized
emergency lamp shows color contrary to Maryland law and this regulation.
|
H. School Vehicle
Warning Lamps. A school vehicle shall be equipped with four red flashing
warning lights and four amber flashing warning lights, installed so that each
amber flashing warning light shall be located near each red flashing warning
light, at the same level, but closer to the vertical centerline of the vehicle.
The red flashing lights shall be equipped with an override switch which shall
function with the master switch on or off. Shields shall be installed on
warning lights, except those equipped by the manufacturer with halogen lights,
or LEDs. Shields may be of a single type to cover both color lights and shall
be painted black, with a minimum depth of 4 inches. The system shall be wired
so that the amber flashing warning lights are activated only by hand operation,
and if activated, are automatically deactivated when the entrance door is
opened. There shall be red and amber warning light switches and pilot lights
mounted to the right and within reach of the seated driver in a panel or specific
area in the dash, and may not be incorporated with other switches. The
appropriate pilot lights shall either go out or flash at an obvious altered
rate to indicate malfunction. A school vehicle may be equipped with an approved
flashing white strobe light no further than 1/3 of the body length forward from
the rear edge of the roof. A manual switch and pilot light shall be installed
in the driver’s compartment if equipped with a flashing white strobe light.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Not equipped with
required alternating flashing warning lights;
|
|
(2) The amber
flashing light and pilot light do not illuminate when the momentary switch is
depressed with the master switch on and the door closed;
|
|
(3) The amber
flashing light or pilot light stays illuminated when the door is opened;
|
|
(4) The red flashing
light and pilot light do not illuminate, or the stop arm and crossing arm, if
equipped, does not automatically extend;
|
|
(5) The red flashing
light and pilot light stay illuminated, or the stop arm and crossing arm, if
equipped, does not immediately retract when the door is closed;
|
|
(6) The red flashing
light and pilot light do not illuminate, or the stop arm and crossing arm, if
equipped, does not automatically extend when the door is opened without
depressing the momentary switch;
|
|
(7) Depressing the
momentary switch with the master switch off activates the amber flashing
lights;
|
|
(8) Opening the door
activates the red flashing light or stop arm with the master switch off;
|
|
(9) An override
switch is not provided, or does not function to activate the red warning
lights and pilot light without opening the service door;
|
|
(10) The vehicle is
equipped with a flashing white strobe light which does not comply with this
regulation;
|
|
(11) The vehicle is
not equipped with the required functioning manual switch or pilot light if
equipped with a flashing white strobe light; or
|
|
(12) Less than 33
percent of the LEDs in any warning lamp are not illuminated when the lamp is
activated.
|
.24 Electrical Systems.
A. Inspect alternator
or generator mounting, and the drive belt condition. Inspect electrical wiring
and components for proper connections, insulation of wiring, and secure
mounting to protect equipment from damage. Control switches for regulated
equipment shall be inspected for proper function and condition. Regulated
equipment that can be operated manually in the event of an electrical control
system failure shall be certified as compliant. The battery, or batteries,
shall be inspected for condition, secure mounting, and proper cable
connections. The horn shall be inspected for proper function, condition, secure
mounting, and horn button location. Inspect the electrical system for improper
wire type or other electrical components that are not designed for use with
automotive on-road vehicles. Industrial or residential type electrical
components shall not be permitted.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Alternator, or
generator, is loose, damaged, not charging properly, or is incorrect for the
vehicle;
|
|
(2) The drive belt
for alternator or generator is missing, loose, damaged, or is incorrect for
the vehicle;
|
|
(3) The ignition
switch does not function to allow the engine to start, run, and apply power
to electric systems as designed, or does not function to allow the engine to
be turned off and remove power from electric systems as designed;
|
|
(4) The horn is
loose, fails to function, or produces loud or harsh sound;
|
|
(5) The horn button
is missing, or is not within arm's reach of driver;
|
|
(6) The wiring
insulation is missing, cracked, or broken;
|
|
(7) The wiring shows
evidence of burning or short-circuiting;
|
|
(8) The electrical
connections are loose or show signs of excessive corrosion;
|
|
(9) The electrical
systems that control regulated equipment fail to function, and equipment
cannot be manually controlled;
|
|
(10) The electrical
wiring or other components are not designed for automotive use;
|
|
(11) The battery case
is cracked or broken;
|
|
(12) The battery
connections are loose or show signs of excessive corrosion;
|
|
(13) The battery is
not held down securely;
|
|
(14) The battery is
not covered by the vehicle body or is not equipped with a cover when the
vehicle body does not provide coverage;
|
|
(15) The battery
vents are not open if equipped, or battery is low on fluid, if applicable; or
|
|
(16) The battery is
not capable of holding a charge.
|
B. School Vehicle
Electrical Systems. Type I and Type II school vehicles shall comply with the
electrical standards in §A of this regulation. Due to the unique function of
school vehicles, the Administration has other specific additional requirements
for battery ratings. Type I School Vehicle shall be equipped with a graduated
voltmeter.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The Type I school
vehicle battery is not rated for at least 1,000 cold cranking amperes
measured at 0°F; or
|
|
(2) The Type II
school vehicle battery is not rated for at least 650 cold cranking amperes
measured at 0°F.
|
.25 Load Covers.
A. This regulation
applies for issuance of a safety equipment repair order to a:
(1) Vehicle registered
or capable of being registered under Transportation Article, §13-917, Annotated
Code of Maryland, on which the manufacturer's original design specifications
for bed enclosures have been altered to increase the vehicle's load;
(2) Part of a load
touching a bed enclosure which is within 6 inches of the top of the enclosure
that it touches; or
(3) Part of the load
which is higher than any of the enclosures.
B. This regulation does
not apply for issuance of a safety equipment repair order to a:
(1) Class K (farm area)
vehicle as defined in Transportation Article, §13-935, Annotated Code of
Maryland; or
(2) Class E (truck)
vehicle registered or capable of being registered under Transportation Article,
§13-917, Annotated Code of Maryland if the vehicle manufacturer's original
design specifications for bed enclosures have not been altered to increase the vehicle's
load-carrying capacity.
(3) A construction
vehicle working within the confines of a public works construction work project
site as outlined in the construction project's plans and specifications,
provided the distance traveled does not exceed 1 mile or the distance specified
in an extension granted by the Maryland Department of Transportation;
(4) A construction
vehicle or mining equipment crossing a highway between construction or mining
sites; or
(5) Vehicle, within the
Port of Baltimore for a distance not to exceed 1 mile, carrying a load of loose
material between a stockpile or storage facility and a vessel docked at the
Port.
C. After January 1,
1992, any vehicle on which the manufacturer's original design specification for
bed enclosures has been altered to increase the vehicle's load capacity shall
have the load covered with a firmly attached canvas or similar type covering
regardless of how the vehicle is loaded.
D. Vehicles undergoing
safety inspection that are equipped with load covers shall be inspected for
proper installation and operation of the load cover, and all associated
components of the load cover system. Inspect cover, if equipped, for holes,
rips, tears, or broken mesh that would permit any part of the load to blow,
fall, or spill from the bed, and for proper attachment to the vehicle.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The cover does
not fully cover the top of the vehicle bed if equipped;
|
|
(2) The cover
contains holes, rips, tears, or broken mesh which would permit any part of
the load to blow, fall, or spill from the bed; or
|
|
(3) The cover is not
securely attached to the bed, or securement hardware is missing, broken, or
damaged.
|
.26 School Vehicle
Color and Identification (Lettering).
A. School vehicle color
and identification is regulated in COMAR 11.19.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The main vehicle
body color is not National School Bus Yellow;
|
|
(2) The hood is not
National School Bus Yellow (non-reflective paint may be used on the hood);
|
|
(3) The vehicle’s
grill is not chrome or manufacturer's grey;
|
|
(4) The vehicle’s
main roof is not National School Bus Yellow or white (excludes the front and
rear roof caps which shall be National School Bus Yellow only);
|
|
(5) Exterior body
trim or bumper is not black;
|
|
(6) The rub rails,
seat lines, or snow rails are not painted gloss black;
|
|
(7) The painted wheel
rims are not gray, silver, or black; or
|
|
(8) The Type I School
Vehicle is equipped with accessories that cover the axle nuts, wheels, or lug
nuts.
|
B. Lettering. Lettering
and emergency door arrow shall be painted black or applied using vinyl die-cut
self-adhering material, (yellow numbers on front bumper are acceptable).
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The lettering is
not painted black or applied using vinyl die-cut self-adhering black letters
and numbers;
|
|
(2) The lettering is
not block type or located as shown in the diagrams in this regulation;
|
|
(3) The school
vehicle does not have the words “School Bus” in letters, 8 inches high by 1
inch on both the front and rear of the vehicle body;
|
|
(4) The lettering is
not placed as high as possible without impairment of its visibility;
|
|
(5) The lettering is
mounted on a reflective area that exceeds 12 inches high by 49 inches wide,
however, area may be reduced in size to conform to the contours of the
vehicle body;
|
|
(6) The emergency
exit door or push-out window is not labeled at the top of, or directly above
with the words “Emergency Exit Door” or “Emergency Exit” using 2 inches high
lettering, both inside and outside of the vehicle;
|
|
(7) A Type I School
Vehicle rear emergency door is not equipped with a 6 inches high by ¾ inch
wide black arrow applied both inside and outside the vehicle that indicates
the direction to release the exit;
|
|
(8) The school
vehicle identification number is not located and visible on all four sides
using letters 6 inches high by ¾ inch wide;
|
|
(9) The rear number
is not located above the rear bumper and below the window line. (Excludes
temporary numbers placed in the second window on the lower glass on each
side);
|
|
(10) The applicable
local school system name is not located on both sides of the vehicle or is
not properly centered, using letters 6 inches high by ¾ inch wide; or
|
|
(11) The applicable
contractor’s or private owner’s or operator’s names is not located to the
rear of the entrance door and on the left side of the vehicle in the same
approximate location using lettering 2 ½ – 3 inches high by ¼ – ½ inches wide
in a 16 by 30 inches area.
|
C. Additional
Lettering.
(1) Only signs and
lettering approved by State law or regulation, and any numbers necessary for
identification shall appear on school vehicles. Bumper stickers are not
permitted. The fleet number may be on the front bumper, yellow numbers on the
front bumper are acceptable. The following lettering may be used if required or
desired:
(a) ICC number, if
applicable, to the rear of the entrance door in lettering 2 ½ – 3 inches high by ¼ – ½ inch wide;
(b) Address and
telephone number of the owner to the rear of the entrance door in lettering 2 ½
– 3 inches high by ¼ – ½ inch wide;
(c) “Stop on Signal”
when required, 4 inches high lettering below the rear window.
(d) "Drug-Free
School Zone" lettering; and
(e) If desired,
"Drug-Free School Zone" may be on the exterior of the vehicle.
(2) The lettering, if
used shall be:
(a) Located under the
first window on the service door side or at another location near the service
door as approved for each individual school vehicle;
(b) Using letters 2
inches high by ⅜ inch wide; or
(c) A decal may be used
provided the background is National School Bus Yellow and the decal is not
larger than 8 by 18 inches.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
The school vehicle is
equipped with lettering or numbers in violation of this regulation.
|
D. Yellow Reflective
Tape.
(1) Reflective tape at
least 1 inch wide and not wider than 6 ½ inches may be used to form a:
(a) Single horizontal
line on each side of the school vehicle immediately below the upper rub rail or
at the floor line; or
(b) Rectangular figure
on the rear of the school vehicle body;
(i) The vertical lines
of the rectangle shall be as close to the sides of the school vehicle as
possible without extending over the sides of the vehicle; and
(ii) The horizontal
lines of the rectangle shall consist of one straight line above and near the
rear bumper and one straight line at or near the roofline.
(2) The reflective tape
specified may be applied in a discontinuous fashion so as to not cover any
existing or required lettering.
E. Roof Identification
Number. ID numbers may be used on the roof. If so equipped, they shall be:
(1) Located in the most
forward section of the roof as possible;
(2) Lettered from the
left side to the right side of the school vehicle; and
(3) Letters shall be 18
inches high by 10 inches wide, with a 2 ¾ inch stroke.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
The school vehicle is
not equipped with required reflective tape, or tape is not compliant with
this regulation.
|

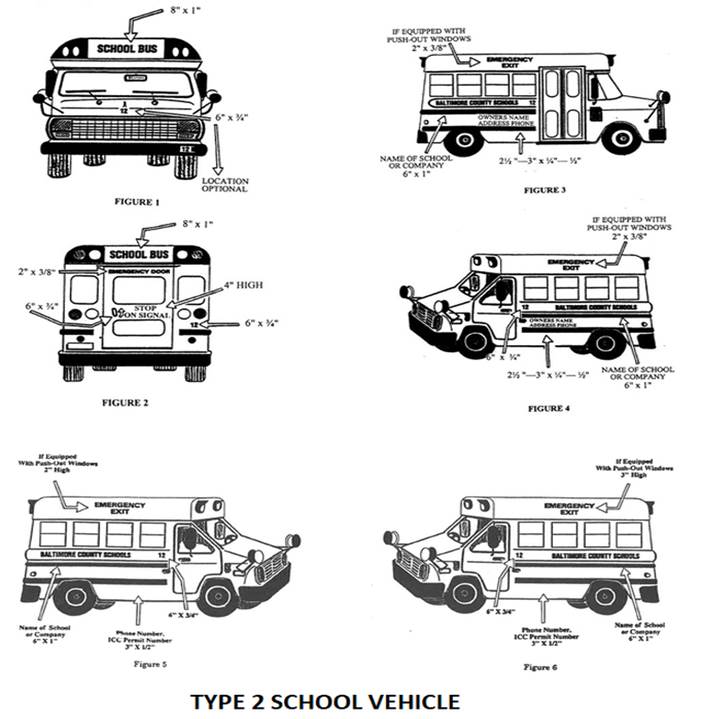
.27 School Vehicle
Emergency Equipment.
A. Fire Extinguisher. A
school vehicle shall be equipped with at least one 5-pound capacity,
pressurized, dry chemical fire extinguisher complete with hose. The
extinguisher shall:
(1) Be mounted in a
bracket located below the window line in the driver’s compartment and shall be
readily accessible;
(2) Be equipped with a
pressure gauge that shall be easily read without removal of the fire
extinguisher from its mounted position;
(3) Be of a type with a
total rating of 2A 10 BC or greater; and
(4) Have an operating
mechanism sealed with a type of seal that does not interfere with the use of
the fire extinguisher.
B. First Aid Kit. A
school vehicle shall carry a weatherproof first aid kit, removable and readily
identifiable, mounted in an accessible, non-enclosed location in the driver’s
compartment. The kit shall contain at a minimum, the contents suggested by the
national standards for school transportation specifications and procedures.
C. Reflectors and
Flares.
(1) A school vehicle
shall be equipped with three red triangular emergency reflectors in a suitable
holder located in the driver’s area; or
(2) A school vehicle
shall be equipped with three 30-minute stand-up flares stored in a red canister
in the driver’s area.
D. Body Fluid Clean-Up
Kit. A school vehicle shall have a removable and moisture-proof fluid clean-up
kit. The kit shall be properly mounted in the driver’s compartment and
identified as a body fluid clean-up kit.
E. Storage. The
emergency equipment may be stored in a non-locking compartment that is
permanently labeled “Safety Equipment Inside”.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) Not equipped with
a fire extinguisher of the required type, rating, and capacity;
|
|
(2) The fire
extinguisher is not mounted as required;
|
|
(3) Not equipped with
a first aid kit, or kit does not contain the proper contents;
|
|
(4) The first aid kit
is not identified and mounted as required;
|
|
(5) Not equipped with
three red triangular reflectors;
|
|
(6) The reflectors
are not stored as required;
|
|
(7) Not equipped with
three 30-minute flares, or flares are not stand-up or lean-to flares;
|
|
(8) Flares are not
stored as required;
|
|
(9) Not equipped with
a body fluid clean-up kit as required; or
|
|
(10) The body fluid
clean-up kit is not identified or mounted as required.
|
.28 School Vehicle
Approved Optional Systems.
A. Video Cameras. Video
cameras may be installed in a school vehicle if:
(1) The camera system
has been approved by the administration;
(2) The system is
installed in an area of the school vehicle with no sharp edges or an area not
likely to cause student injury; and
(3) The system is
outside the federal head impact zone.
B. A safety detection
system approved by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) may be installed
to warn drivers of moving objects, such as children, within areas around a
school vehicle considered to be most dangerous.
|
Reject Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) The video camera
system is not an approved type;
|
|
(2) The video camera
system is installed in a prohibited manner;
|
|
(3) The safety
detection system is not an approved type;
|
|
(4) The safety
detection system does not operate automatically, and when the stop arm is
extended;
|
|
(5) The safety
detection system is not equipped with audible and visual alarms with volume
adjustment to compensate for background noise;
|
|
(6) The safety
detection system is not located in the driver’s compartment, visible from the
driver’s seat; or
|
|
(7) The safety
detection system is not equipped with a delay feature to operate the
detection system unit for a brief period of time after the school vehicle
resumes motion.
|
.29 Type I School
Vehicles for Transporting Special Needs Children.
A. School vehicles
constructed for transporting special needs children shall comply with vehicle
equipment standards, but because of the use of specialized equipment installed,
may have certain modifications that result in alterations in vehicle equipment
configurations.
B. Special Service
Doors (Wheelchair Door). If equipped, the special service door shall be
manually operated, padded over the door header, and equipped with a functioning
audible signal in the driver’s compartment to warn if the door is not securely
closed. Double doors shall overlap where they meet, and all doors shall be
equipped with weather seals. A light shall be inside the vehicle to illuminate
the area of the special service door, operated from the door area. Aisles
leading to the doors shall be maintained with a minimum of 30 inches width to
permit passage of wheelchairs. Door panels shall extend below the floor line
when ramps are used and cover the ramp container opening.
C. Ramp. A ramp shall
be of sufficient strength to support at least 600 pounds and at least 88 inches
long and of the same width as the door opening at the floor level, and be
equipped to secure to the vehicle. A ramp shall be equipped with a protective flange
on each side to keep wheels on the ramp, and the floor of the ramp shall be of
nonskid material.
D. Power Lift (Elevator
and Fold-Up Platform). A power lift shall have at least a 660 pound working
capacity with power up capability. A lift platform shall be at least 26 inches
wide and 40 inches long with a ramp with nonskid surface material and safety
stops at both ends. The power lift shall be controlled from a panel within the
vehicle adjacent to the lift, operational by an attendant standing on the lift.
The lift shall not operate unless the door is opened. A manual backup system
shall be provided in the event of power failure of the lift.
E. Wheelchairs.
Forward-facing wheelchairs shall be secured by a four-point fastening system.
F. Grab Handles. May be used on each side of the
front service doors.
G. Book Racks. May be
installed on residential special education vehicles above the side windows from
the front cross seat to the rear transverse seat, except across or above an
emergency door. Bookrack shall be padded and cover the edges and lower surfaces
of the rack.
|
Reject
Vehicle If:
|
|
(1) A school vehicle service door is not in compliance with
this regulation;
|
|
(2) The aisles leading to the door are not at least 30 inches
wide;
|
|
(3) The header over door area is not padded, or padding is
damaged;
|
|
(4) A special door is not equipped with a functioning audible
signal in the driver’s compartment to warn if the door is not securely
closed;
|
|
(5) A school vehicle ramp is not in compliance with this
regulation;
|
|
(6) A school vehicle power lift is not in compliance with this
regulation;
|
|
(7) The wheelchair fastening system is not a four-point system
or is damaged;
|
|
(8) The bookrack is installed across or above an emergency
door; or
|
|
(9) The bookrack is not padded to prevent impact injuries as
required.
|
CHRISTINE NIZER
Administrator